1. What is ESD (Education for Sustainable Development)?
ESD is an abbreviation for Education for Sustainable Development.
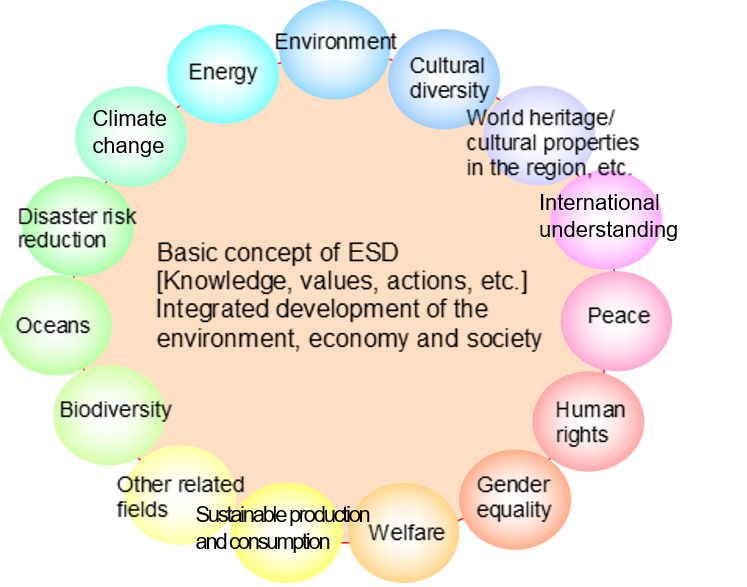
Today, the world is facing a variety of problems caused by human development activities such as climate change, biodiversity losses, resource depletion and the expansion of poverty. ESD comprises learning and educational activities that aim to develop alternative values and transformative actions that lead to problem-solving and to realize a sustainable society by taking the initiative to accept these problems of modern society as our own and tackling the problems in our immediate environment (think globally, act locally) in order to ensure that human beings are able to secure an abundant life for future generations.
In short, ESD is education that fosters the builders of a sustainable society.
2. Relationship between ESD and the SDGs
ESD is a concept which was first proposed by Japan at the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable Development, and UNESCO, the lead UN agency for ESD, has since been taking the lead in global efforts based on the global framework, the “UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (DESD)” (2005-2014) adopted at the 57th Session of the General Assembly of the United Nations in 2002 and the “Global Action Programme on Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) (GAP)” (2015-2019) adopted at the 37th UNESCO General Conference in 2013.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were adopted as goals for the entire international community, including developed countries, at the United Nations Sustainable Development Summit 2015. SDGs consist of comprehensive 17 goals and 169 targets with a deadline of 2030 to achieve them with the aim of ensuring a society where “Leave No One Behind”. ESD is positioned as Target 4.7, “By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development” of Goal 4, “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”.
On the other hand, ESD is not only positioned as one of the targets, but was also affirmed at the 74th Session of the UN General Assembly in 2019 as a key enabler of all 17 goals of SDGs. ESD, which develops the builders of a sustainable society, is expected to contribute to the realization of quality education, which is essential to achieve the SDGs.
This concept is also clearly stated in the new international framework for ESD adopted at the 40th UNESCO General Conference in 2019, “Education for Sustainable Development: Towards achieving the SDGs (ESD for 2030)” (2020-2030).

ESD is an integral element of SDG 4 on Education and a key enabler of all the other SDGs
3. Education for Sustainable Development: Towards achieving the SDGs (ESD for 2030)
A global framework for implementation of ESD for the period of 2020 to 2030, “Education for Sustainable Development: Towards achieving the SDGs (ESD for 2030)”, which is the successor to the United Nations Decade of ESD (DESD) (2005-2014) and the Global Action Programme on ESD (GAP) (2015-2019), was adopted at the 40th session of the UNESCO General Conference in November 2019, and acknowledged by the 74th session of the UN General Assembly in December 2019. ESD for 2030 aims to build a more just and sustainable world by strengthening ESD implementation and contributing to the realization of all 17 of the SDGs.
Following the adoption of ESD for 2030, UNESCO published a roadmap indicating specific actions to be taken under this framework. The roadmap includes five priority action areas (1. Advancing policy, 2. Transforming learning environments, 3. Building capacities of educators, 4. Empowering and mobilizing youth, 5. Accelerating local level actions) and six key areas of implementation (1. Implementing ESD for 2030 at country level (development of country initiatives), 2. Harnessing partnership and collaboration, 3. Communicating for action, 4. Tracking issues and trends (evidence-based progress review), 5. Mobilizing resources, 6. Monitoring progress). The main advances from the GAP that were called for were an emphasis on education’s role for the 17 SDGs, a focus on the big transformation towards sustainable development and an emphasis on UNESCO member states’ leadership.
A Roadmap on “ESD for 2030” (* Link to UNESCO website)
4. Positioning of ESD in school education –The National Curriculum Standards and ESD
The report of the Central Council for Education announced in December 2016, Improvement of the National Curriculum Standards for kindergartens, elementary schools, lower secondary schools, upper secondary schools and schools for special needs education, and necessary measures mention, Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) is the foundational principle of the next revision of the National Curriculum Standards. Based on the report, fostering the builders of a sustainable society is referred to in the National Curriculum Standards for kindergartens, elementary schools, lower secondary schools, upper secondary schools and schools for special needs education that have sequentially started to implement since 2018 academic year.
5. Aims of the ESD
(1) Teachers and students elicit issues related to building a sustainable society, centering on the “six perspectives” that constitute the building a sustainable society.
Concepts of sustainable society-building
1 Diversity (variety exists)
2 Interdependence (relating to each other)
3 Limitation (limits exist)
4 Fairness (valuing everybody)
5 Cooperation (cooperating with others)
6 Responsibility (taking responsibility)
(2) Teachers and students acquire the “seven competencies and attitudes” necessary to solve problems in order to build a sustainable society
Competencies and attitudes to be emphasized in ESD
1. Ability to think critically
2. Ability to plan with anticipation of a future scenario
3. Ability to think in multidimensional and integrative ways
4. Ability to communicate
5. Ability to cooperate with others
6. Attitude to respect relations and connections
7. Attitude to participate proactively
*Source: National Institute for Educational Policy Research “Study on Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) in Schools [Final Report]”
6. ESD practices
- How to learn
It is important to improve learning and pedagogies continuously, from the perspectives of “proactive learning, interactive learning, and in-depth learning”. This means not only focusing on the exploratory learning process, such as appropriately positioning problem-solving learning, enriching opportunities for proactive, learner-centered learning and adding in experiences and activities, but properly examining which part of the learning process would be most effective and how they should be positioned. This means aiming to implement cooperative learning by incorporating group activities, and getting students to discuss and work together to carry out investigative and summarizing activities or give presentations.
- What students will become able to do
Rather than just seeking to acquiring knowledge and understanding, ESD aims to build on learning to develop ability to take action on a range of problems while taking these problems as their own issues. In addition, by becoming aware of the perspective of “building a sustainable society”, it becomes possible to bring out a transformation in the values of students.
- How to implement ESD
In order to promote ESD effectively, it is important that the implementation of ESD is positioned in the school management strategy, the internal school organization is streamlined and the school as a whole systematically handles ESD, ESD is appropriately positioned in the teaching plans, the perspective of collaboration with local community, universities and businesses is incorporated, and the communication and reflection on learning outcomes by students are appropriately carried out.
(Reference)
〇ESD QUEST
[PDF:7,789KB]
(Office of the Director-General for International Affairs)