1.2 Science and Technology to Create a New Society
1.2.1 Science and Technology to Respond to Demographic Change
Summary
As a nation facing an aging society with fewer children it is necessary to bear and raise healthy children, maintain health throughout life and stretch the potential abilities of each individual to the fullest. To achieve this there is a need to clarify the mechanisms of biological phenomena and various diseases, and to develop the means to prevent, diagnose and treat diseases. In addition more effective welfare tools should be developed to assist the elderly in being independent and participating in society, as well as to reduce the burden on care-givers, and working styles providing a better balance with private life should be achieved by making it possible to simultaneously work and raise children as well as allowing active elderly people to contribute to society through further promotion of telecommuting and lifelong learning utilizing IT (information technology). Such efforts will be effective not only for distributing the burden imposed by an aging society with fewer children, but also for changing the trend of fewer children by altering the balance between family and the workplace.
Furthermore, the social infrastructure in an aging society with fewer children should encourage participation in society by those raising children and the elderly, and must also be of high-quality and able to be used effectively for many years so as to be appropriate for the mature economy. Therefore, it is necessary to develop materials that are highly durable and easily recycled, efficient and strong construction methods, and maintenance and management methods to ensure safety over the long term.
On one hand, the expansion in human activity that has accompanied the progress of science and technology has placed a burden on the global environment, and increased the fragility in terms of safety. The public desires a safe and secure society, and this is particularly important for the weaker members of society, such as children and the elderly. From a long-term perspective, harmony between the environment and human activity, and assured resources, like energy, are crucial for a safe and secure daily life. Therefore, it is necessary to be aware of the potential risks in advance, and to establish the appropriate preventive and response measures, and to promptly implement effective measures if a situation occurs. In addition to developing the technology for making measurements and predictions at a variety of levels, detection, damage prevention and mitigation, and for emergency response, there must also be progress on the development of energy conservation technology and alternate energy sources to support sustainable development. Furthermore, there is a social demand for the development of systems to grasp the production history information of products, and to support reliable information sharing and the establishment of communication.
To meet the demands of society it is necessary to continue with a wide range of research and development, from basic research to applications, while keeping in mind these demands; and then to proceed with social change through innovation based on the results.
1.2.1.1 Science and Technology for Lifelong Health
According to surveys by the Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, in 2005 there were more than 25,000 people aged 100 years or more. In the first national census conducted in 1920, there were only 113 people aged 100 or more, so there has been a more than 200 times increase in the last 85 years. The average lifespan of 42.1 years for males and 43.2 years for females in 1921-1925 has been nearly doubled to 78.6 years for males and 85.6 years for females in 2004, reaching the top level in the world.
This enormous increase in the average lifespan is largely due to the contributions from improved medical standards, nutrition and sanitation that have sprung from advances in science and technology. (Figure 1-2-1) In general, today's children can grow up without fear of infectious diseases like tuberculosis or other ailments that threatened the lives of children and youths in the past. The elderly too are able to maintain better health in comparison to people of the same age in the past.
However, for Japan, now facing an aging society with fewer children, in order to maintain and improve the vitality of society and the quality of the daily lives of individuals in the future, there are three big issues regarding the health of the citizens.
The first is to make it possible for people who desire children to bear them safely and in good health. The second is to assist in raising healthy children. The third is to make it possible for the elderly to continue to enjoy good health throughout a long life, and to maintain vigor.
The role of science and technology in addressing these issues is summarized below.
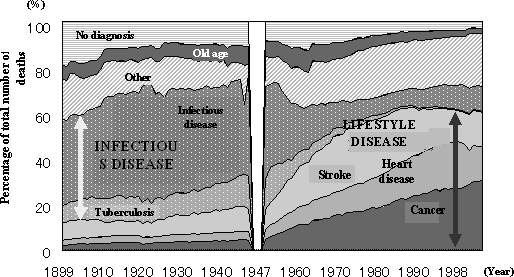
Figure 1-2-1 Epidemiological trends regarding cause of death in Japan.
Source:
Created by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports,
Science and Technology based on the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare "2004
White Paper on Health, Labour and Welfare" with some revisions.
(1) Building a society favorable to be- aring and raising children
According to the "2002 Japanese National Fertility Survey" reported by National Institute of Population and Social Security Research, married couples felt that the ideal number of children was an average of 2.56, but the actual number of children planned was an average of 2.13. For couples who plan to have fewer children than they feel would be ideal, when the wives were asked the reason, many indicated the burdensome costs of raising and educating children. Among the couples surveyed, 12.7% had no children, and about half of the couples without children were concerned about infertility. Furthermore, more than half of those who were concerned about infertility responded that they had undergone tests and/or treatment for infertility.
In a 2004 White Paper on Birthrate-Declining Society, the changes in the birth rates were analyzed, and it was confirmed that there has been an increase in the number of people who have never married, who marry later, and bear children later, and that the trend of fewer children was produced by couples married since about 1990. It is pointed out that some of the factors are delays in the preparation of the environment to support working while raising children, more people pursuing higher education, changes in the sense of values regarding marriage and child birth, increases in the feeling of burden from raising children, and an increase in economic uncertainty. This indicates that the major influences on the birth trends are the timing of marriage and the decision whether to have children. There are limits to what can be accomplished with science and technology in this regard, but IT could probably make some contribution, such as through telecommuting, and remote learning during maternity and child care leave or before re-entry to the work force, helping society to prepare the environment to support people desiring to simultaneous work and rear children. This is discussed separately later.
According to research by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, in FY2002 it was estimated that about 467,000 people had gone through fertility treatment for infertility. The in vitro insemination and embryo transplant technology that is part of the available fertility treatments were first performed in the United Kingdom in 1978; and in Japan in 1983 the first baby resulting from in vitro insemination was born. Since then, the technology has spread rapidly, with the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology (JSOG) reporting in 2003 that about 68,000 people underwent in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer at 648 facilities registered with the JSOG, resulting in the births of about 17,000 children. Fertility treatments assist couples afflicted by infertility, but the technology is left up to the individual medical facilities. In addition to improving technology, such as increasing the implantation rate, there are other issues to be resolved, including provision of information clarifying the limitations and scientific basis of in vitro insemination and its therapeutic application, safely providing new infertility treatments, not only from the medical aspects, but also including psychological support, as well as dealing with the life ethics and health problems for women resulting from a multiple pregnancy.
(2)Raising healthy children
● Improving medical technology to help raise healthy children
The perinatal (Note 4), newborn infant and infant mortality rates in Japan are among the best in the world. With regard to deaths of pregnant women as well, the level is on par with other developed nations, though not as high as in some countries in Europe (Table 1-2-2).
Pediatrics covers the health, growth and development of infants, small children and youths. This is a field of medicine that was born more than a century ago in response to an increasing awareness that the health problems of children are different from those of adults, and that there are varied reactions by children to stress and illness, depending on their age. At the start of the 20th century (1904) the neonatal and infant mortality rates in this country were 73.9 and 151.9, respectively (per 1,000 live births). One hundred years later (2004), these rates are 1.5 and 2.8, respectively, a drastic improvement. (Figure 1-2-3) These improvements are the result of progress in the prevention and treatment of disease, as well as other areas of science and technology. Consequently, pediatric care can focus attention even on diseases that have relatively few patients. There is ongoing development of treatments and research to elucidate the mechanisms of intractable diseases like pediatric cancers, metabolic disorders like endocrinological disease, asthma, and allergic reactions like atopic dermatitis. In addition, in order to support health throughout a long life in an aging society with fewer children, follow-up study, such as surveys of the later rate of incidence of cancer for childhood cancer patients, will be important, so there is starting to be research on building a database of chronic pediatric disease patients. By building mechanisms to appropriately manage and utilize the information based on the consent of the participants, and recording as much information as possible in the databases, this is expected to contribute to the future development of pediatric medicine.
Note 4:
Perinatal mortality indicates the total of fetal deaths
after 22 weeks of pregnancy and early stage newborn infant deaths (deaths within
one week of birth) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare "Vital
Statistics." Internationally, the comparison is for fetal deaths in and
after the 28th week of pregnancy and early stage newborn infant deaths.
Table 1-2-2 International comparison of perinatal, infant and maternal mortality rates.
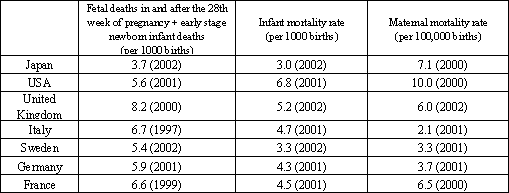
Source: Based on the United Nations "Demographic Yearbook" 2001 and 2002
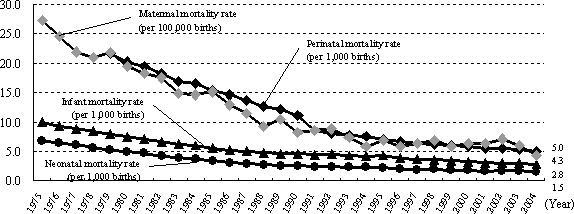
Figure 1-2-3 Trends in indicators of mother-child health
Notes 1:
The births for the maternal mortality rate are the number
of foetal death (after 12 or more weeks of pregnancy) added to the number
of live births.
Notes 2:
The births for the perinatal mortality rate are the number of foetal
death after 22 or more weeks of pregnancy added to the number of live births.
Source:
Created by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and
Technology using the Vital Statistics of the Ministry of Health, Labour and
Welfare
● Incorporation of Brain Science Research
In a resource-poor nation like ours the most important issue is making the fullest possible use of the talents of each individual. As we face an aging society with fewer children learning and education throughout a lifetime becomes even more important. In particular, the period of infancy and early childhood is an extremely important time in which the foundation of the neural circuit that forms the base of thoughts and feelings is developed. While the various artificial devices that have arisen from the development of science and technology, such as television and the internet are drastically changing the living environments and behavior patterns of people, there is a growing concern about the effect of these changes on the development of children.
On the other hand, due to the recent advances in brain science, it has become possible to seek biological processes in the mechanisms of human learning and education. Progress in brain function imaging technology, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has enabled empirical study of the function of the human brain. There is also progress on the identification of genes that contribute to intellectual activities in humans along with advances in molecular biology using model organisms, such as mice. These advancement of studies lead to the rise of research to elucidate genetic and environmental impact on human intellectual ability. From the biological point of view, "learning" is a process of the brain reacting to stimuli from the environment, and building or modifying it's own neural network for managing and processing information; while "education" can be called a process of controlling/supplementing the necessary stimuli to build/modify the neural network.
The human brain has evolved by adapting to a changing, uncertain environment. The brain is the source of desires and emotions (feelings), which interact with memory and learning in various ways. The above-mentioned learning can occur in a sudden flash of understanding. If research based on scientific, empirical evidence progresses with regard to the important working of the brain in establishing human social activity, including the development of creativity and insight, empathy and understanding of the emotions and context of the speech of other people, and the ability to express one's own thoughts and feelings with appropriate behavior, it should be possible to obtain important knowledge on raising people with sound bodies and minds. (Figure 1-2-4)
From this perspective, in 2000, Japan was the first in the world to establish an interdisciplinary field that combined brain science and education and subsequently initiated research in this area. The subject goes beyond the boundary between natural science and humanities/social science, integrating many different fields, including brain science, developmental psychology, ethology, linguistics and pedagogy. Research is proceeding using advanced brain function measurements and various information technologies. Through the collaborative efforts of scientists and teachers and other people directly involved in education, the accumulated on-site knowledge and know-how is being systematized based on the empirical evidence. To give one example, abnormalities in bodily rhythms, such as autnomic nerve/hormone secretion/body temperature regulation/sleep-waking functions, are one of the major factors in poor school attendance. It is gradually becoming clear from brain function imaging and physiological and molecular biology methods that if the situation continues, there is damage to higher-order functions, such as recognition abilities and judgment abilities. Based on this understanding, treatment methods are being developed, such as high-intensity light treatments, and progress is being made to clarify the lifestyle conditions that contribute to poor school attendance, and applications in actual society are being tried. In addition, basic research is being undertaken with the goal of clarifying the principles and mechanisms of brain development, with the focus on the growth and development of the human mind. For the first time in the world the mechanisms of the critical period (period in which functional changes of the brain can easily occur through experience and learning) have been clarified on a molecular level, and results are being obtained, such as success in achieving pharmaceutical manipulation. It is expected that connections with the acquisition of language and sociability will be clarified in the future. Japan has also sponsored a network conference attended by educators and brain science researchers from throughout the world, focusing on "Brain Development and Lifelong Learning" as part of an OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) project. The goal is to contribute to a dialog between brain science researchers and educators to identify issues in education and provide some brain science solutions, or provide new avenues of development for brain science. There is a demand for means to connect brain science and education, including the fostering of personnel with a deep understanding of both brain science and education.
Neuroethics have played an extremely important role in the advancement of the above-mentioned research and efforts to return the results to society. In addition to study on how to confirm the consent of the people participating in the research (informed consent), it is important to verify the knowledge obtained from a variety of perspectives, and to clarify what is clear and what is not known, and announce this to society. In the future, new problems may arise, such as how to handle the technology if it does become possible to externally read the thoughts of people, or if drugs are developed to improve performance, who would have permission to use them. For this, it is necessary to hold discussions with a wide range of interested people, and to proceed in ways that improve the quality and happiness of society and the daily lives of individuals.
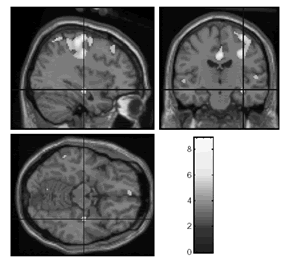
Figure 1-2-4 Activity in the hippocampus during intellectual learning
Photo courtesy of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
(3) Healthy aging for the elderly
According to the "Population Estimates" by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications Statistics Bureau, as of October 1, 2004 the percentage of the total population aged 65 years or more was 19.5%, and the percentage of those ages 75 years or more was 8.7%. The 2002 projections by the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research indicate that by 2030 these percentages will be 29.6% and 17.8%, respectively. In an aging society with fewer children, it is very important for the elderly to keep fit and to support themselves for the purpose of increasing the quality of life of the citizens and decreasing the burden on society (Figure 1-2-5). From this perspective it is necessary to continue with research and development on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases including cancer and other lifestyle-related diseases, fractures and dementia that require full-time nursing care. Below is a description of the trends in research and development related to major illnesses.
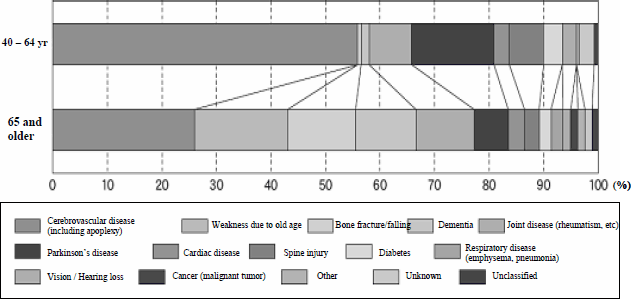
Figure 1-2-5 Reasons nursing care is required
Source:
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare "2004 White
Paper on Health, Labour and Welfare"
● Cancer
Since 1981 cancer has been the number 1 cause of death in Japan. As the aging of society progresses, the number of patients increases. In recent years more than 300,000 people die of cancer annually, accounting for more than 30% of all deaths. Controlling cancer is a common problem for all mankind, and various countries, including the USA, are placing a focus on cancer research. Researchers in Japan have long played an important role in cancer research, starting with the first successful carcinogenesis experiment in the world in the 1910s. The government has also provided focused support, including continuing research since fiscal year 1984 based on the "Comprehensive 10-year Strategy for Cancer Control" and the "New 10-year plan to overcome cancer."
Since the beginning of the 1980s genes related to the growth of human cancers have been discovered. These are widely present in nature, and it is known that originally they have important roles in normal cell growth and differentiation. It is also becoming clear that a single cancer cell is formed after a combination of successive mutations in various cancer genes and cancer-suppressing genes, and that it means there are abnormalities in the DNA replication function. This understanding is being applied to cancer prevention, diagnosis and treatment methods, and is producing significant results. For example, the location of a virus that causes a type of leukemia common in the Kyushu region and suppression of the main infection paths, resulted in a drastic decrease in infections.
Research on the diagnosis and treatment of cancer is proceeding rapidly, such as the development of cancer diagnosis at the molecular level, molecule targeted therapies (Note 5), and immunotherapy (Note 6). Japan is also at the forefront in the development of medical equipment, such as the development of helical CT (Note 7), which is effective for early detection, and particle ray treatment facilities to enable the treatment of formerly difficult-to-treat cancers.
In addition, cancer epidemiology and the development of a foundation
of cancer information have made it clear that changes in the cancer incidence
rates have accompanied changes in customs of daily activities, such as westernized
dietary patterns, revealing the importance of environmental factors in cancer
prevention.
Much has been clarified by research so far, but details of the
mechanisms that cause cancer to occur are still not clear, including how normally-functioning
cells become cancerous, grow, invade surrounding cells, metastasize, and avoid
attacks from the immune system. There are still cancers that are difficult to
treat, like pancreatic cancer, and it is necessary to further improve cancer
prevention, diagnosis and treatment methods.
In order to further improve the effectiveness of cancer countermeasures and increase the benefits to all citizens, "The Third Term Comprehensive 10-year Strategy for Cancer Control" was established as a strategy starting in FY 2004. Under this strategy, aiming at reducing the mortality rate due to cancer and maintaining the quality of life (QOL) of patients with cancer, in addition to technology development of molecular imaging research, there is also research being done to improve cancer prevention, early diagnosis and treatment methods, including promotion of translational research (Figure 1-2-6) applied to active prevention, diagnosis and treatment using the results of basic research obtained from research labs, as well as promotion of personalized medical care that is adapted to the characteristics of each individual (Figure 1-2-7).
Note 5:
Molecule targeted therapy: Conventional anti-cancer drugs
have been poor at differentiating between cancer cells and normal cells, creating
many adverse drug reactions. Molecule-targeted therapy is a new kind of treatment
that makes use of cancer research results to target the unique characteristics
of the cancer cells at the molecular level with drugs. It is becoming an effective
treatment method for leukemia, breast cancer and lung cancer.
Note 6:
Immunotherapy: A method of treating cancer by targeting the various
"tumor antigens" characteristic of cancer and directing the immune
functions using a variety of cells and molecules involved in immunity to have
the immune system attack the tumor, or suppress the tumor cells ability to avoid
the attack from the immune system.
Note 7:
Helical CT: A CT system is equipment to scan an object (patient's
body, etc.) with x-rays, process the data with computers and create detailed
cross-sectional images of structures inside the object. Helical CT is a form
of CT in which the x-rays are emitted in spiral and images are obtained while
the support table is moving. This makes it possible to obtain higher-resolution
images in less time than with ordinary CT, and is effective for early detection
of lung cancers, which can be difficult to find.
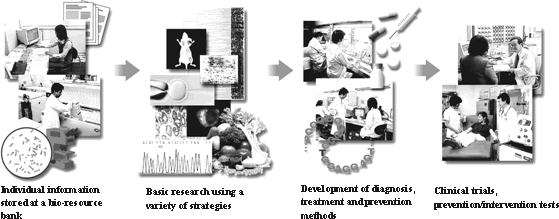
Figure 1-2-6 Translational research
Source:
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare/Ministry of Education,
Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
● Cardiovascular diseases
Heart disease and stroke (apoplexy) are cardiovascular diseases that, along with cancer, make up the three main lifestyle diseases.
According to the fiscal year 2004 vital statistics compiled by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, heart disease and stroke account for about 16% and 13%, respectively, of the deaths of Japanese people. The typical form of heart disease is a cardiac infarction, or heat attack. The vessels carrying blood to the heart muscle become blocked and a portion of the cardiac muscle tissue dies, resulting in a loss of heart function. A stroke (apoplexy) occurs when blood vessels in the brain become blocked or break. In many cases of stroke, even if the patient's life is saved, there is permanent damage that interferes with daily activities.
Arteriosclerosis is often associated with cardiovascular diseases. It was once thought that arteriosclerosis occurred as fatty deposits gradually accumulated on the inner walls of blood vessels. Recent research, however, indicates that the fatty deposits accumulate within the walls of the blood vessels, rupture and create lumps in the blood (thrombi) which cause spasms, such as heart attacks. It has become clear that inflammation during this process plays an important role. This knowledge is already being utilized for surgical tools. As research progresses in the future, it is expected that new diagnostic and treatment methods will be developed.
There is also research to comprehensively find the genetic factors associated with heart attacks. If the relevant genes can be identified, drugs can be developed to suppress their function, or an individual person's genes could be examined and advice on behavior and diet could be made, or medications administered to prevent the onset or recurrence of the disease.
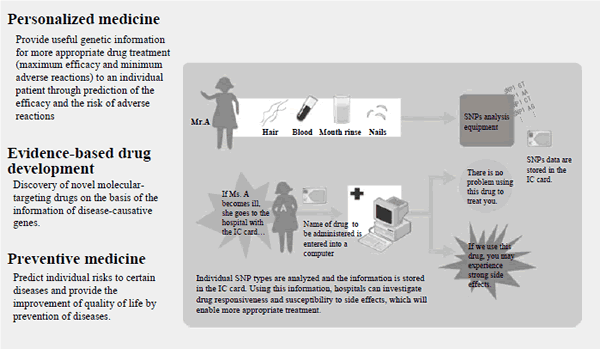
Figure 1-2-7 Hospitals of the future
Source:
RIKEN
● Diabetes
In Japan there are about 7 million people afflicted by diabetes, and that number is estimated to be twice as large if potential diabetes patients are included. There are several types of diabetes, including varieties that appear during childhood, but more than 95% of the cases are Type 2 diabetes, which appears in middle age or later. Diabetes is associated with complications such as numbness or gangrene of the hands and feet, diabetic nephropathy, and loss of vision, and an increased susceptibility to arteriosclerosis and autonomic nerve malfunction. The impact of diabetes on society is quite large, not only due to the deaths directly attributed to diabetes, but also including all the complications that occur and the costs of medical treatment while fighting the illness.
In diabetes glucose, which is the source of energy for cells inside the body, is not taken up by the cells, so high concentrations of glucose remain in the blood, having a damaging effect on the blood vessels throughout the body, which causes the various symptoms described above. The concentrations of glucose in the blood are regulated by insulin secreted from the pancreas. Diabetes is thought to occur because of reduced secretions of insulin from the pancreas and/or resistance to the action of insulin in peripheral tissues such as skeletal muscles, adipose tissues and the liver. Obesity is a factor that increases the risk of diabetes. Dietary measures and exercise are necessary for the treatment of diabetes. At the same time, medications have been developed and used to stimulate the secretion of insulin and improve the insulin's effectiveness. In patients for whom it is not possible to obtain a sufficiently high insulin secretion, insulin manufactured using gene recombination technology is administered. This is cheaper and has fewer side effects than the insulin derived from cows and pigs.
● Bone and Joint disease
Many people are bothered by bone and joint diseases. In Japan out of the top 10 diseases that are generally treated on an out-patient basis, three are bone and joint diseases (2001 Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, "Comprehensive Survey of Living Conditions of the People on Health and Welfare"). The diseases are expected to increase as society continues to age. Damage to locomotive organs due to bone and joint disease has an especially large impact on the quality of daily life; it also imposes a large economic burden on society, as evidenced by the estimated 26 trillion yen (1995) spent on countermeasures in the USA. Bone and Joint diseases are a worldwide problem, and the World Health Organization (WHO) has engaged in countermeasures by positioning the 10-year period starting in 2000 as "Bone Joint Decade."
Bones and joints repeatedly break and form in response to external factors throughout life. In recent years research has made it clear that bone and joint diseases are multi-factorial hereditary diseases that result from genetic factors (multiple susceptibility genes) and environmental factors (exercise, diet, load from body weight, etc.). There are more than 10 million osteoporosis patients in Japan. There are anti-osteoporosis drugs that work on the metabolic processes, but they do not fully satisfy the needs of most patients. Through animal experiments a substance that attacks cells that destroy bone has been discovered in Japan. There will be efforts to develop marketable medications with minimal side effects in the future.
For other bone and joint diseases, currently there are basically no effective treatment methods. There is currently work underway to clarify the genetic factors, such as for osteoarthritis that affect approximately 7 million people in Japan, the herniated disks that are the major cause of lumbago and sciatica, in order to achieve a breakthrough. Application to develop effective treatments through functional analysis for the genes that are identified is expected.
● Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is a representative disease that causes dementia. It is a disease in which the neurons of the brain slowly die over a long period of time and about one out of 5 people over the age of 85 is affected. There is concern about an increase in the number of patients as the aging of society progresses. In the past, the mechanisms of onset of the disease were not well understood and the treatment was to administer drugs to promote the transmission of information between neurons, rather than trying to prevent the death of neurons. In recent years there have been rapid advances in research on the mechanisms, including the production and breakdown of substances called tau proteins and β-amyloid, which is thought to contribute to neuron damage (Figure 1-2-8). Based on the research results, efforts are being made to develop prototype vaccines and drugs to suppress these substances.
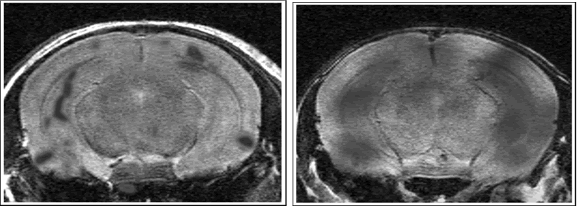
Figure 1-2-8 Bioimaging of a mouse with Alzheimer's disease
This is the first successful imaging of β-amyloid using MRI (red portion
in the photo) on a living animal. The photo on the left was taken at a younger
stage. In comparison, it is clear that the β-amyloid accumulation has advanced
in the photo on the right.
Photo courtesy of RIKEN
(4) Contributions to health from fundamental research of biological systems and nanotechnology
● Application of immunology to medical care
The immune system is a mechanism to monitor and defend the body. The immune system recognizes not only pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses that invade the body, but also foreign bodies, like cancers, that originate inside the body, and uses a variety of cells and molecules to destroy and eliminate them to maintain the body in a fixed condition. For the proper working of the immune system it is necessary to accurately select the target of the attack and perform the appropriate adjustment. The human immune system is a complex and ingenious mechanism comprising a diversity of cells and groups of molecules.
However, the performance of the immune system declines with increasing age after adolescence, increasing susceptibility to immune disorders and infectious diseases. As the aging of society progresses, there is a concern that there will be an increase in rheumatoid arthritis and auto-immune disorders (Note 8) Japan has been a world leader in immunology, starting with Shibasaburou Kitasato, generating major results, such as clarification of the information transmission system of the immune system, but the immune system is an extremely complex network, and there is still much that remains unknown.
Treatment drugs for auto-immune diseases are being developed, but the immune system is a complex mechanism, and a broad suppression of immunity causes other problems, including increased susceptibility to cancer and infectious disease. Obtaining a more detailed understanding of the mechanisms of the immune system should make it possible to develop treatment methods that are better targeted and have fewer side effects.
Note 8:
Auto-immune disorders: The original role of the immune
system is to recognize and eliminate foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses
and tumors. This is a general term for the diseases in which the immune system
over-reacts and attacks normal cells and tissues of its own body.
● Cutting-edge technology - Regenerative medicine
Developmental biology is the study of the processes of aging and regeneration to restore lost tissue, focusing on the process (development) of the repeated cellular division and differentiation from a fertilized egg to form an individual, multi-celled organism. Modern medicine, including advancements in regenerative medicine, is opening the possibilities for the treatment of lifestyle diseases and difficult ailments, like spinal cord injury and cardiac infarction, through the use of cell and tissue transplants.
In addition, development is also promoted on such technologies as strong, readily-accepted artificial bones and ligaments that gradually release substances to promote tissue regeneration through the application of nanotechnology, artificial organs including artificial livers and pancreases that are a fusion of cells and nano-biomaterials, and nano drug delivery systems to deliver medications or genetic material to targeted areas in the body in order to treat difficult diseases or to provide genetic treatment.
● Fundamental research
In October 2004, the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium, composed of research centers in six countries including Japan, announced results of verification and analysis of the precise sequencing of the human genome, including the approximately 22,000 genes that regulate the structure of the proteins that make up the human body. This number is significantly lower than expected. This has led to the extremely interesting new discovery that the RNA that can be read as the pattern for DNA has a wide variety of functions besides the previously-known role as the blueprint for creating proteins.
Progress continues on genome research, including study of the background behind the differences in abilities, such as between humans and chimpanzees and between exceptionally long-lived people and ordinary people; research on how living things develop from fertilized eggs, the kinds of RNA produced at each of the various stages as aging progresses, and how this RNA works; research on the tertiary structure of proteins that fill a variety of functions within the body, as well as making up the body; and research using computers, etc. to understand the actions and interactions of these various components as a complete biological system. There is also continuing development on the basic technology required for the research, including analytical technology.
This research provides the knowledge that forms the foundation for a variety of research, such as molecular biology, cellular biology, developmental biology and immunology that is being advanced at universities, as well as promotes the understanding of life phenomena. It is expected that this will help support the development of medications and an understanding of the causes of various diseases.
1.2.1.2 Science and Technology to Improve Social Welfare
In 2004 the Cabinet Office conducted a survey, "Opinion Survey on Normal Daily Activities of the Elderly," with men and women aged 60 and older as the subjects. In response to the question "Are there times you feel any disability in conducting ordinary daily activities?" 86% of all respondents indicated "generally fine," but this drops to 54% among those 85 years or more (Figure 1-2-9). To a separate question, about 70% of all subjects indicated "concern about ordinary daily activity in the future," with the number one reason for the concern being "health and sickness of myself and my spouse," and the number two reason "me or my spouse becoming bedridden or disabled and requiring nursing care."
In the "Public Opinion Poll on Nursing Care of the Elderly" conducted by the Cabinet Office in 2003 subjects were asked a question allowing multiple responses about problems in the case it becomes necessary for a family member to have nursing care. The number one response, selected by over 60% of subjects, was the heavy burden of care and physical burden, with the number two response being the stress and emotional burden.
Increasing the quality of life for the elderly and being able to remain largely independent and able to participate in society throughout life, and reducing the burden on care-givers are important issues for an aging society and are highly demanded by society. The cutting edge science and technology to supplement the functions lost due to age or injury, and to support care-givers and relieve them from the heavy work of nursing care is introduced (Figure 1-2-10).
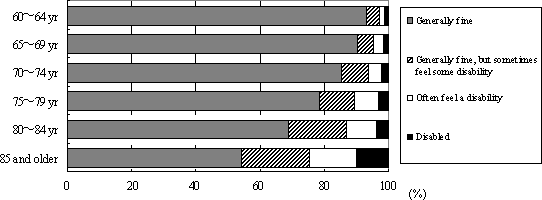
Figure 1-2-9 Are there times you feel any disability in conducting ordinary daily activities
Source:
Cabinet Office "Opinion Survey on Normal Daily Activities
of the Elderly" (2004)
● Cyborg technology
Research is progressing on cyborg technology, replacing some of the functions of the body by applying neuro-engineering, which is technology that makes use of brain information. Muscles are the devices that drive the hands and legs, and operate according to electric pulse signals that run through the nerves. If it were possible to read these signals, and feed them to an external drive device (a motor, etc. to produce motion instead of the muscles), it might be possible to cause an external device to move using biological signals. This concept is the origin of neuro-engineering.
Even if you lose an arm in an accident, if you think "move arm," the same signals are still transmitted from the brain to the nerves that originally were involved in moving your arm. By reading the electrical signals from those nerves and connecting them to the controller for a robotic arm designed to move in response to those signals, it is possible to create a robotic arm that can be moved like your own arm, simply by thinking, without any other special operations.
Furthermore, there is research being conducted on replicating the sense of touch, so that by attaching touch sensors to an artificial hand, the electrical signals from the sensors can be converted and transmitted through the nervous system. By gaining an understanding of the pattern of the signals that flow throughout the nervous system, it is becoming possible to take signals from external devices and send them as signals that the brain will interpret as signals from an actual sense organ. There is already development being done on artificial eyes and ears using this kind of technology, with more than 60,000 people throughout the world already using this kind of artificial ear.
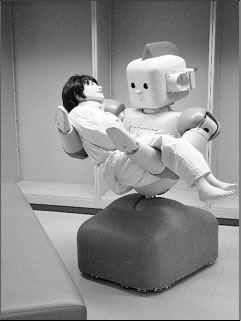
Autonomous daily-activity support robot that is equipped
with soft skin, sight, hearing, sense of smell and sense of touch, and can perform
tasks with a delicate touch.
Photo courtesy of RIKEN

A therapeutic robot designed to help reduce stress for elderly and
caregivers
Photo courtesy of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and
Technology
Figure 1-2-10 Various types of care-giving robots
1.2.1.3 Science and Technology to Enable Diversification of Work Styles
There are various analyses being performed on the impact of an aging society with fewer children on the daily lives of the people. It has been pointed out that there is a concern that the number of buyers of goods and services will be reduced and the domestic markets will shrink, and that a reduction in the number of workers will hinder the productive activity of business.
As a nation of advanced industrial technology, it is extremely important for Japan that individual citizens improve their abilities to support the society. The full utilization of abilities in society throughout life is also important from the perspective of self-realization and living a meaningful life. Furthermore, for a knowledge-based society talented people with superior skills are required, regardless of nationality, and Japan is no exception.
For the "Special Public Opinion Poll on Countermeasures to the Declining Birthrate" conducted by the Cabinet Office in September 2004 the most popular response to the question on specific hopes regarding the policies for measures to counter the declining birthrate (multiple responses allowed) was "promotion of support to balance work and family life and a reform in working styles," with more than 50% of the respondents choosing this answer. In a "Survey on the Employment Situation of the Elderly" conducted by the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare the same year, employed people between 55 and 69 years of age were asked their main reason for working. Among males between the ages of 55 and 59, 4% indicated reasons such as "to have a meaningful life or active citizenship," "for health reasons (good for health)," and "because I was asked, because I have extra time." Among males between the ages of 65 and 69, however, 34% chose these reasons. In the same survey the percentage of employed people who were part-time employees was reported to be 48% for males, and 61% for females between 65 and 69 years of age.
Thus in an aging society with a declining birthrate it is important to have greater flexibility from the perspective of how to spend time throughout life on work, study, leisure, care giving, etc. Furthermore, since the labor force will become a more precious resource, the abilities of individuals must be developed to the fullest, regardless of age, gender or nationality, and the mechanisms must be developed to make full use of these abilities in society. Up until now science and technology has contributed to replacing the use of physical labor with machines. In the future, science and technology will be able to contribute to enhancing social vitality and making work easier for individuals by way of controlling and compensating for the decrease in mental and physical abilities with increasing age and improving individuals' abilities through lifelong learning, and supporting both work and family activities with domestic work support systems and telecommunications systems, along with reforms of social systems.
● Aging and Physical and Mental Function
In order for elderly people with a wealth of life experience to remain active in society it is important to prevent lifestyle diseases and to slow the deterioration of body and nerve functions that accompanies advancing age. Thus, science and technology should be effectively used to maintain and improve mental vigor by delaying the decline in physical function that accompanies physiological aging as well as preventing depression and preserving intellectual ability.
Eternal youth and longevity has been a topic of interest to mankind since ancient times, and research on the mechanisms of aging has progressed since the later half of the 20th century in conjunction with the development of the basic technology for biological research. In the mid 1990s the gene that causes premature aging was identified. Over the past 10 years the genes that affect the lifespan of individual organisms have been discovered using model organisms like nematodes, fruit flies, yeast, and mice. Research on these genes and the associated molecular structures suggests possibilities for the relevance of energy metabolism and stress response pathways to the lifespan. With clarification of the network of the group of genes associated with longevity and aging it may be possible to delay the progress of aging and make it possible for people to age while maintaining good health. It is also possible that this kind of application of technology in society may give rise to a variety of ethical problems, so it is necessary to proceed with research while holding careful and thorough discussion.
For many years it was believed that the cells of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) had no ability to regenerate, and that the numbers declined after a person was born. However, the latest results in brain science reveal that there is a process, called "neurogenesis," in which new nerve cells are generated even in the brains of adults, and that new connections between neurons are made even later in life. In addition, it has become clear that human embryonic stem cells (Note 9) can be differentiated to form nerve cells, so it may be possible in the future for regenerative medicine to be applied for Parkinson's disease and spinal cord injuries, areas that had lacked fundamental countermeasures. However, in order for the stem cells in the brain to differentiate into nerve cells and fulfill their role, they need to move to the proper location and form a network with other suitable cells. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct further studies including the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms for this process.
In addition, depression in the elderly is a growing concern. Regarding this topic, it has become clear that stress inhibits neurogenesis and that atrophy of the hippocampus, which plays an important role in memory, is seen in patients with chronic depression. Animal experiments have shown that anti-depressants promote neurogenesis, indicating the possibility that they may be effective for promoting neurogenesis in cases of depression or Alzheimer's. It is known empirically that depression in humans can be improved through daily exercise, like running. It has also been discovered that adult mice produce a large number of new neurons in the hippocampus after they are moved from dull and uninteresting breeding cages into amusing playgrounds. With future scientific discoveries on how memory and judgment ability is improved through exercise, proper diet and adequate sleep, it will be possible to improve the quality of life through daily activities with more consideration of health based on this knowledge.
Note 9:
Embryonic stem cell (ES cells): The stem cell stock
made from the inner cell mass associated with part of the blastocyst at the
initial formation stage of animals. In theory, these have the potential to be
differentiated to form any type of tissue, and can be cultivated nearly without
limit, so ES cells are receiving a great deal of attention for applications
to regenerative medicine.
● Development of lifelong learning and vocational skills
In modern society, with the pace of knowledge change increasing, its foundation on information, and in which people are connected by communications technology, it is of increasing importance to continue learning and to maintain and improve vocational skills throughout life. There is thought to be a growing demand for distance education that provides education programs that meet the needs of many people and can be conducted at times and locations that are convenient for individuals. To meet this kind of demand measures are being implemented, such as the operation of an engineer's web learning system (http://weblearningplaza.jst.go.jp/) by the Japan Science and Technology Agency in order to support the reeducation and continuing skills development of engineers.
The development of learning and vocational skills using communications technology will support the return to the work force of those who took childcare leave, as well as the re-employment of people who have retired from another job. Furthermore, it is of great importance in an aging society with fewer children, because it is an effective method for older people to further improve their quality of life, pursue study after reaching retirement and work to obtain an academic degree.
● Telecommunications systems to support more flexibility in styles of working
According to the "2004 White Paper Information and Communications in Japan," about 15% of companies in Japan, and 69% of companies in the USA are using telework for employees to work at locations other than the office using telecommunications networks. The importance of telework will probably grow as a style of working in an aging society with a declining birthrate, because it allows people to work while also raising children, and reduces the physical burden of commuting to an office. The Second Basic Plan for Gender Equality (determined in a cabinet meeting in December 2005) presents a numerical goal to increase the percentage of telecommuting workers in the working population to 20% by 2010.
There is also development of video monitoring at nursery schools and day care, services to check on the whereabouts of children and the elderly outside the home using a home computer, systems to detect and report on intruders or disasters like fire to the place where one has gone, as well as systems that enable people to remotely check on the operation and status of home devices, such as air-conditioning systems, laundry and cooking equipment.
To achieve widespread use of telecommuting and intelligent home appliances, security countermeasures to protect company secrets and the personal information of individuals are important. Therefore, it is necessary to implement a variety of management and operation measures, including technology measures such as violation detection technology.
1.2.1.4 Science and Technology to Contribute to the Effective Utilization of Social Capital
Social capital stock, such as the roads, airports and sea ports under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transportation has been steadily accumulating. In the near future a large amount of this stock accumulated during the periods of high economic growth will begin to require updating or renewal, and it is expected that there will be a large increase in the demand for funding for maintenance, operation and renewal of this social capital stock in the future (Figure 1-2-11). In 2004 a public opinion poll on the development of social capital stock was conducted by the Cabinet Office. Subjects throughout the nation aged 20 and older were asked what kind of results should be emphasized in developing social facilities. The most popular response at 48% was "deal with aging society with a declining birthrate," and many voiced the opinion that there should be special consideration of use by the elderly and disabled.
In Japan, one of the reasons thought to be a factor in the low number of children, particularly in metropolitan areas, is the small size of the houses. In comparison to the west, where it is common to renovate and update houses and use them for several generations, the average service life for a residence in Japan is very short, lasting only about 30 years. This is considered to be one of the reasons for the poor quality living environment despite the cost. In an aging society with fewer children, it is, of course, necessary to develop facilities that are easy for the elderly and disabled to use, but it is also necessary to prepare social capital and housing that can be used comfortably for a long time and can withstand disasters in the harsh natural conditions of the nation, including earthquakes, typhoons, and the hot, humid climate. There should be an emphasis on maintenance management and effective use of resources, so that this housing and social capital can be used with care for a long time.
Therefore, in addition to steps and elevators, there should be progress on creating barrier-free public facilities and transportation, such as making it possible to access public transportation without buying tickets, using just a single smart card. It is also necessary to continue with the development of technology for the planning, construction and maintenance, and development of structural materials with a long lifespan and suitable for recycling, so that social capital can be utilized efficiently for a long time.
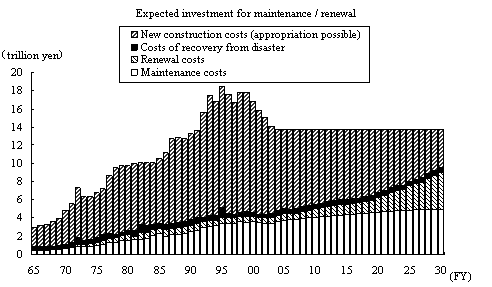
Figure 1-2-11 Estimates of demand for funding for maintenance and replacement investment
Note:
The expansion of total possible investment is shown for the case assuming
0% relative to the previous year in and after 2005.
The total amount for maintenance and renewal costs as a percentage of the
total possible investment increases from about 31% to 65%; while the amount
available for new construction as a percentage of the total possible investment
decreases from 65% to about 31%
Source:
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transportation
● New construction materials
In order to extend the service life of social capital, there is development underway on high-strength materials with a long useful life, having superior recycling characteristics and resistance to weather. (Figure 1-2-12) In addition, there is development underway on risk management methods and detection/measurement/assessment of damage and deterioration of materials and structures in order to effectively develop and maintain a variety of public buildings, as well as development of technology for planning, construction, repair, maintenance, corrosion prevention, etc. in order to reduce maintenance costs and improve the durability of concrete structures like roads and bridges.
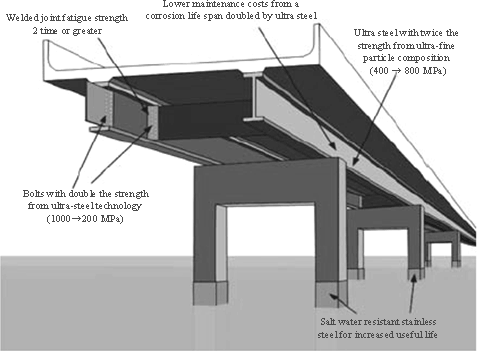
Figure 1-2-12 High-strength, long-life construction materials
Source:
National Institute for Materials Science
1.2.1.5 Science and Technology for Safe and Secure Society and Sustainable Society
Most of our daily activities in modern society depend on social systems that are supported by advanced science and technology, such as telecommunications, transportation for distribution of goods, and energy supply. These social systems are expected to contribute to a sense of security and ensure the stability of the activities of everyday life. The tragic railroad accident and the scandal over buildings based on fabricated structural calculation sheets in 2005 demonstrated how the safety in our daily lives depends on the social systems, and how confidence in the social systems is vital for feeling a sense of security. Safety and security in society is even more important for vulnerable members of community, such as children and the elderly, who are likely to be unable to flee from disaster or killers targeting young children.
In 2005 the USA was struck hard by hurricane Katrina, while Japan saw an increase in typhoons and record-breaking high temperatures; and unusual weather phenomena seem to occur more frequently in recent years. The direct and indirect effects of changes in climate, including desertification due to changes in rainfall patterns, decreases in food production, and increases in tropical infectious disease due to global warming, along with an increasing impact on the environment from human activity accompanying a growing world population and rising standards of living, may destabilize world society, including refugees and conflicts arising from threats to the stable supply of food and energy, and threaten the foundations of the existence of mankind. This places Japan, a nation long dependent on importing energy, food and other resources, in an especially vulnerable position regarding this kind of supply instability. Furthermore, as globalization progresses, there is even greater danger of unexpected movement of pathogens and international terrorism.
In the "Special Public Opinion Poll on Science and Technology" conducted by the Cabinet Office in May 2005, there was the most support for "preservation of the environment" and "achieving a safe society (prevention of disaster and crime, food safety, etc.)" as the important focal points for support for science and technology (Figure 1-2-13), and nearly 70% of citizens agreed that "a high level of science and technology is required to ensure safety" (Figure 1-2-14). It is clear that there are high expectations from the citizens regarding the contributions of science and technology on these problems.
There is a need to address the demand of the people to provide a safe and secure society, along with achieving both environmental conservation and sustainable development through the strategic advancement of science and technology research and development. It is also necessary to secure the foundations for safely conducting social and economic activities, building close reciprocal relationships with many nations by using this science and technology to help solve global problems.
To handle large-scale disaster and terrorism, it is necessary to improve security standards, by establishing the possible scenarios, and devising measures to first prevent damage, and then minimize the expected damage. On top of this, there must be measures implemented for initial response and disaster recovery to handle incidents if they do occur. It is also important to develop an environment where the risks can be objectively assessed and appropriately handled, and build relationships of confidence through the accurate provision of reliable information, while keeping in mind the necessary information control to ensure safety in order to build a safe society.
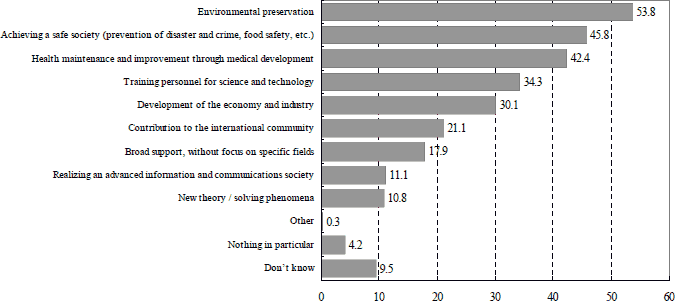
Figure 1-2-13Points that should be the focus of support for science and technology (multiple answers)
Source:
Cabinet Office "Special Public Opinion Poll on Science
and Technology" (June 2005)
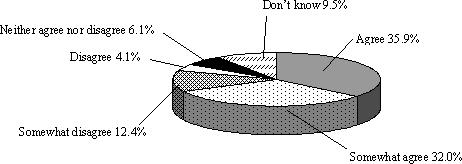
Figure 1-2-14 High levels of science and technology required to ensure safety for familiar activities and the overall security of the nation
Source:
Cabinet Office "Public Opinion Poll on Science &
Technology and Society" (February 2004)
● Global environmental change and largescale natural disasters
We are now facing global-scale environmental problems, such as global warming, desertification, deforestation, water source problems, acid rain, loss of bio-diversity, damage to the ozone layer, and marine pollution. These problems are affected by human behavior and activity, and there is a high risk that if these problems progress, there may be a point of not return, from which recovery is not possible.
Last year, there was a record-breaking water shortage in the Amazon river, a river that accounts for nearly 20% of the river water in the world. For the Fourth report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), forecasts were made using Japan's high-performance supercomputer "Earth Simulator" (Figure 1-2-15). The results of the forecast suggest that there is a possibility that rainfall in the Amazon river basin will decrease in the future, and that tropical rainforests will be lost. Abnormal weather indicating the effects of global warming has been seen in various countries in recent years. In Japan also, there have been frequent unusually-high temperatures and record rainfall (Figure 1-2-16). In 2003 there were 35,000 deaths, primarily among the elderly, during a heat wave in Europe. In 2005 1,300 people in the USA were victims of a series of enormous, record-breaking hurricanes.
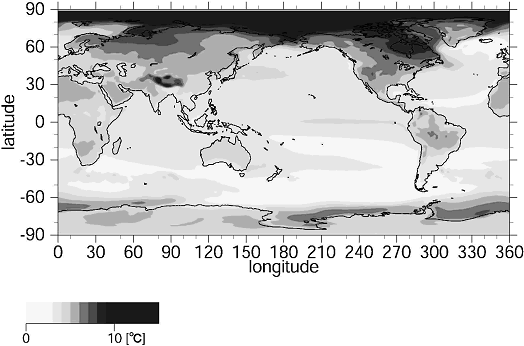
Figure 1-2-15 The projected Geographical distribution of annual mean surface air temperature increases
Shows the difference between the average air temperature between 1971 through 2000 and the predicted average air temperature between 2071-2100 in the future scenario created by the IPCC, assuming the world continues internationalization focused on economic gain
Source:
Joint research team of University of Tokyo Center for
Climate System Research (CCSR), National Institute for Environmental Studies
(NIES), and the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, Frontier
Research Center for Global Change (FRCGC)
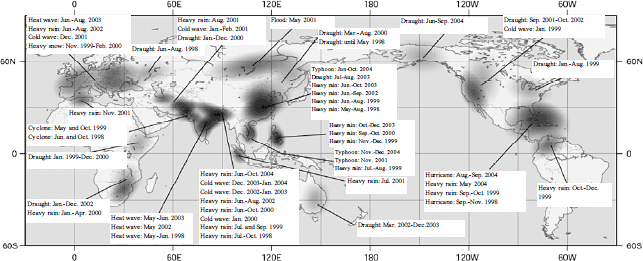
Figure 1-2-16 Distribution of main climate disasters in the world (1998-2004)
Note:
Areas reporting heavy rain, typhoon / hurricane, drought / forest fires,
heat waves and cold waves are colored in green, yellow ocher, red and blue,
respectively.
Source:
Japan Meteorological Agency "Extreme Weather Report
2005" (October 2005)
There is a connection between the conditions in the ocean and the weather in widely separated regions, such as the El Nino currents causing cool summers and warm winters in Japan. Unusual weather is not only a direct threat to the daily activities of humans, but could also attack the foundations of human existence, through desertification, deforestation and a decline in food production.
Japan is a country prone to earthquakes, and the Japanese word "tsunami" is used throughout the world, illustrating that disasters caused by movements of the earth crust have had considerable damage and impact on Japanese society. Following the experience of the Hanshin-Awaji earthquake, research and development of earthquake disaster prevention and earthquake investigation technology should help lessen the damage from future earthquakes and tsunami that are likely to occur in the future, including a strong earthquake beneath Tokyo, Tonankai and Nankai earthquake. It is also necessary for the latest science and technology to be applied for disasters abroad, such as the large earthquake and tsunami in Indonesia and Sumatra at the end of 2004.
There is increasing awareness of the importance of establishing integrated global Earth observation systems. Upon the proposal of Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi at the 2003 Evian G8 Summit, a series of Earth Observation Summits was held and at the Third Earth Observation Summit held in February 2005, the "Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) 10-Year Implementation Plan" (Figure 1-2-17) was endorsed. Japan is now working to promote observation and monitoring systems which integrate satellite, terrestrial and ocean observation in order to contribute to the response to natural disasters such as earthquakes and tsunamis, as well as global warming. The deep-sea Earth drilling project aims to promote R&D to bring to light global environmental changes, the earth’s interior structure, and deep-subsurface ecology by providing the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP) with the "CHIKYU" deep sea drilling vessel which was developed to reach the earth’s as-yet-unexplored mantle. There are also efforts under way to create and publish earthquake forecasting maps, conduct focused study of areas with a high probability of experiencing a strong earthquake, research to greatly reduce the material damage and injury that would occur if a major earthquake occurs within a large metropolitan area, prediction of volcanic activity, floods, landslides and damage from snow and ice, and development of systems to accurately and rapidly provide information on flooding and evacuation warnings.
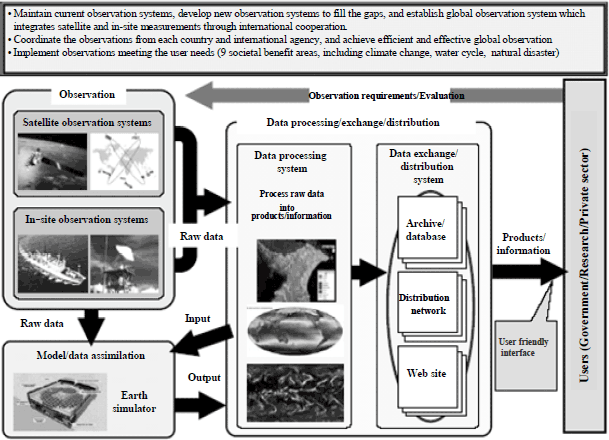
Figure 1-2-17 Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS)
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
● Energy/Resources
As the world population continues to grow and standards of living increase, there is an increasing demand for energy. There is a limit to the fossil fuel resources, such as the petroleum and natural gas that we currently use, and it is reported that their production will hit a peak in the not-so-distant future. It is necessary to continue research and development on energy conservation and energy alternatives to fossil fuels, in order to halt global warming and air pollution, to increase Japan’s stability and independence instead of relying on imports for most of our energy resources, as well as to contribute internationally through advanced technology.
In Japan nuclear power provides about 26% of the total electricity supply (2003 results, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry), but there are limits to the supplies of the enriched uranium used as the fuel. Research and development is proceeding on fast breeder reactors and nuclear fuel cycles, to effectively reuse the plutonium that is created at the ordinary nuclear power plants and make it possible to greatly alleviate the restrictions from the uranium resources. In addition, from the perspective of increasing the range of energy options in the future, research and development is continuing on nuclear fusion energy, which has a minimal impact on the environment, and for which there is an abundance of resources.
Research and development are also continuing in government, industry and academia on the technology for renewable energy and energy conservation. Examples of results include improved conversion efficiencies and lower costs for solar cells, resulting in Japan producing nearly half of all solar cells made in the world. Further research and development is needed in the future to overcome the disadvantages of the higher cost in comparison to current energies, and to promote the widespread introduction and use. Japan is a small country in terms of land area, but has the 6th largest exclusive economic zone in the world.
Development is progressing on ocean exploration systems to search for undiscovered and unused resources in the oceans.
● Serious accidents
An important issue for realizing a safe society is ensuring the safety of the traffic and transportation systems, starting with the prevention of traffic ac-cidents, and including railways and other forms of public transportation. According to a 2005 police department white paper, in 2004 there were 1.18 million people injured in traffic accidents, of which 7,358 died within 24 hours. Among those who died, 41.4% were elderly people aged 65 years or more. In contrast, among the drivers who were the primary parties concerned in fatal accidents (Note 10), 15.7% were aged 65 or more. In 2005 there were many victims of train derailment incidents, one on the JR West Fukuchiyama line in April, and another on the JR East Uetsu line in December. Many Japanese still remember both these incidents.
To prevent traffic accidents, there is research and development being conducted on systems to grasp road and traffic conditions and the circumstances of the surrounding vehicles through the use of various sensors and detecting devices on roads and in vehicles, in order to improve traffic safety through ITS (Note 11). In addition, as a countermeasure to accidents that single vehicle cannot avoid, government, industry and academia are working together on the research and development of driver support systems using telecommunications technologies to relay information between vehicle and between the road and vehicles. In particular, there is progress on (1) Driving Safety Support Systems (DSSS), (2) Automated Highway Systems (AHS), and Advanced Safety Vehicles (ASV).
Further, to prevent accidents due to human error (Note 12) on public transportation, there is development underway on technology to prevent dangerous situations from occurring, by monitoring the mental and physical condition of train operators or drivers in real time, and detecting indications of fatigue or panic.
With regard to major accidents, there are examples of failures in the past that are similar. By analyzing these past examples of failure, in many cases commonalities can be found in the various factors contributing to the failures. Sharing and utilizing the data and understanding obtained from failure experiences can be valuable in preventing the recurrence of failures and in lowering the risk of failure in the development of ground-breaking new technology.
Based on this concept the Japan Science and Technology Agency has been providing public access to a failure knowledge database (http://shippai.jst.go.jp) since 2005.
Note 10:
Primary party concerned: Means the person who is most at fault or
the person with the lightest injuries in cases where fault is shared equally.
Note 11:
ITS: Acronym for Intelligent Transport System. An integrated system
linking people, roads and vehicles using telecommunications technology to solve
road and traffic problems including traffic jams, accidents and environmental
deterioration.
Note 12:
An intentional or unintentional action by a person that
unexpectedly compromises safety. This includes actions based on judgment errors
as well as unintentional mistakes.
● Emerging and reemerging infectious diseases
The World Health Organization (WHO) reported 41 cases of death due to avian influenza during 2005, mainly in Southeast Asia. Emerging and reemerging infectious diseases are usually caused by viruses, which are common to humans and other animals. In the past 30 years, there have been at least 30 emerging infectious diseases, including Ebola hemorrhagic fever and AIDS (Figure 1-2-18).One cause for this is thought to be an increase in the opportunities for contact between people and animals infected with these viruses, as the population increases and forests and jungles are destroyed. In many cases, the virus does not cause a serious disease in the originally-infected animal, but becomes highly lethal in humans or other animals. With globalization, the movements of people now extend over a broad range, and there is concern of expansions of infected areas due to increases in the habitats of insect carriers, like mosquitoes, resulting from the effects of warming.
To deal with these diseases it is necessary, first and foremost, to strengthen coordination and information sharing among relevant agencies and specialists both domestically and abroad, and to quickly and accurately identify the pathogen, carriers, and patients exhibiting symptoms. It is also necessary to identify the characteristics of the pathogen, and develop detection methods, and to enhance and fully support the basic and application research on prevention, diagnosis and treatment, including the development of vaccines and wonder drugs.
However, special facilities, equipment and materials are required to handle fatal and unknown pathogens. Japan is the only G7 nation that does not operate facilities capable of handling this type of pathogen. This means that not only is Japan unable to participate in investigations of pathogens arising in other countries, we also cannot investigate pathogens that arise within our own country. In the past, Japan has relied on the USA for such analyses, but the situation has changed, including terrorism countermeasures that ban delivery of pathogens, creating an urgent need for such facilities. Therefore, it is necessary to thoroughly investigate the nation’s handling of safety assurance and crisis management, and continue to engage in dialog with citizens, particularly those living near a facility site.
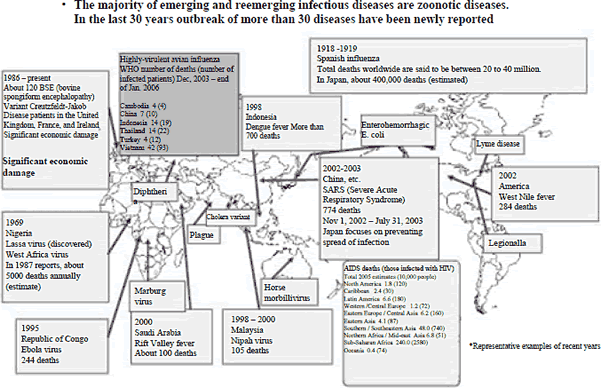
Figure 1-2-18 Expansion of emerging and reemerging infectious diseases
Source:
Created by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports,
Science and Technology based on basic policy expert survey materials, Council
for Science and Technology Policy
● Food safety problem
With the progress of the globalization of society and the economy, as well as mass production and wide-spread distribution, if a problem with food safety should ever occur it would have an impact over a broad range (Table 1-2-19). For this reason, there is development underway on rapid detection methods for harmful microorganisms and chemical substances, and progress on technology development to trace the production history information using radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, etc., to make it possible to easily verify product indications, provide suitable information, quickly discover the cause, and recall defective foods when a problem occurs.
Throughout the long history and civilization of mankind, the substances in our world have been classified as either edible or inedible. During times when careful verification was not possible and information was limited, not eating anything labeled as "not safe" was considered to be a basic strategy for increasing the probability of survival. However, determining whether a given substance is unhealthy depends on the toxicity of the substance and the amount consumed, and any food can have some harmful effect, depending on how it is eaten. In modern society, it is necessary to develop an environment that encourages communication among citizen, manufacturers, experts and government agencies to exchange information and opinions on the dangers of food products, to allow logical and reasonable judgments to be made.
Table 1-2-19 Reasons for anxiety regarding food safety
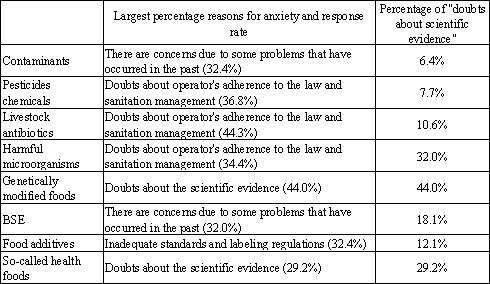
Source:
Created by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports,
Science and Technology based on the results from the Cabinet Office food safety
monitor issue report "Survey of Awareness of Food Safety" (May 2005)
● Terrorism and other crime
Since being shaken by the multiple, simultaneous terrorism attacks in the USA in September 2001, the international community has strengthened alliances and been working on terrorism countermeasures. However, terrorist attacks appear to be more wide-spread, including multiple bombings in London, as well as bombings in Bali in Indonesia. With regard to domestic crime, in 2004 there were about 580,000 crimes, excluding thefts, the largest number after the World War Ⅱ. There appears to be a greater malignancy, skillfulness and organization to crime, including confiscation of record-high amounts of cannabis and synthetic narcotics like MDMA.
In order to deal with this kind of terrorism and crime, it is necessary to improve the technology for customs and immigration examinations, the technology for detection and decontamination of harmful substances, and the technology for collection and analysis of crime information. For this reason, there is development on devices to detect substances associated with criminal and terrorist activity, such as illegal drugs, explosives, and biological agents, which are hidden in the mail, without opening the envelope, etc. (Figure 1-2-20).
There is also development work on portable detectors for biological agents and chemicals, research on the creation of 3-D facial image databases of criminals and automatic matching systems, research on high-speed identification systems for individuals using DNA single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP-s), handwriting analysis, and document forgery detection, and research on detecting areas with a lot of criminal activity using geographic information systems (GIS), and identification of the relationship between area characteristics and the occurrence of crime.
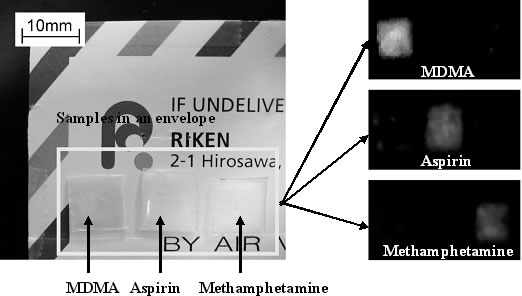
Figure 1-2-20 Devices to detect illegal drugs and hazardous substances without opening the envelope
Furthermore, in order to ensure the safety of children, there are a variety of systems being developed; including systems using cameras and devices mounted at schools entrances, public transportation ticket checkpoints, and on vending machine, to read electronic tags and IC cards carried by the children to track their locations, and notify guardians by email, and emergency information communication systems also used as crime alarms for guardians and local support people (Figure 1-2-21). When this kind of system is used, it has been pointed out that it will be necessary to investigate the issues of children’s safety and privacy, including the interception of radio waves transmitted from the electronic tags.
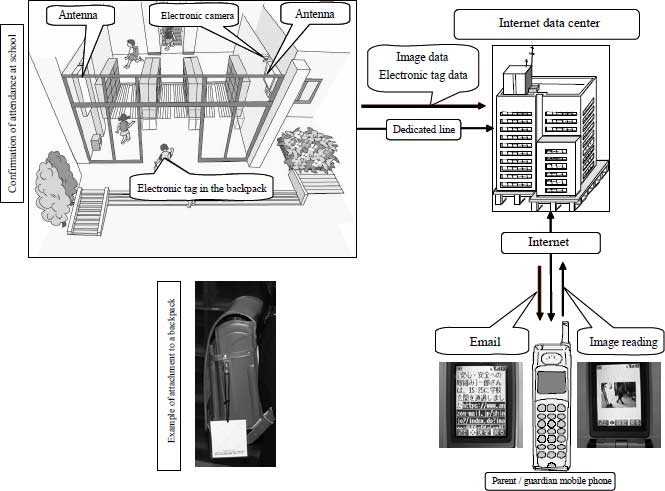
Figure 1-2-21 Summary of tests of electronic tag systems to ensure the safety of children attending school
Source:
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication, Kinki
Bureau of Telecommunication "Study on the Use of Electronic Tags in Public
Fields" (March 2005)
● Information security problems
In 2005 the cyber-crimes using IT investigated by the police nationwide increased dramatically by 51.9% in comparison to the previous year, and exceeding 3,000 cases for the first time. Information security measures are becoming more necessary to deal with the use of new technology for this kind of intentional attack. There is also a need for measures to handle unintentional causes, like human error, and to deal with IT damage due to natural disaster, etc.
The comprehensive research and development needed to ensure the security and reliability of information and communications networks is being implemented, including science and technology to prevent, detect and analyze cyber-crime, verification and cryptographic technology, risk management, communication mechanisms in an emergency, and quantum information communications technology.
Contacts
Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau
(Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau)