1.2 Science and Technology to Create a New Society
1.2.3 Science and Technology Contributing to Building a Spiritually Wealthy Society
Summary
In an aging society with fewer children the average lifespan is increasing. If it is possible to extend the healthy lifespan (meaning the period of time of healthy independence, in terms of the quality of daily life and health of both mind and body) through science and technology, this is expected to lead to a society in which people can live a long life of health and wealth. Furthermore, there is a growing percentage-e of people who feel that "from now on there should be an emphasis on a life of spiritual wealth and ease." The things that create a sense of spiritual wealth differ depending on the individual, but it is no exaggeration to say that cultural arts and crafts, sports, and intellectual curiosity are important. Contributing to the realization of a "spiritually wealthy society" that enables appreciation of cultural arts and crafts, participation in/viewing of sports and intellectual stimulation is one of the roles demanded of science and technology.
1.2.3.1 Science and Technology Contributing to Achieving Spiritual Wealth
In an aging society with fewer children, if it is possible to extend the average lifespan and increase the healthy lifespan (meaning the period of both mental and physical health, taking into account the quality of daily activities and health) through progress in science and technology, then it is possible to realize a society in which people can live long and productive lives. There is also a growing percentage of people who feel that "since there is already a certain level of material wealth, there should from now on be an emphasis on a life of spiritual wealth and ease." With a longer healthy lifespan and a decrease in annual labor hours, peoples' total disposable time (time which can be used freely) is expected to continue to grow, increasing the opportunities to achieve a sense of spiritual wealth through intellectual and creative activities outside of work. Over 80% of people feel that the progress of science and technology in the future should contribute not only to material wealth, but also to achieving spiritual wealth. Therefore, it is necessary for science and technology to contribute to spiritual wealth in the future (Figure 1-2-39, -40, Table 41).
The things that create a sense of spiritual wealth differ depending on the individual, but it is no exaggeration to say that cultural arts and crafts, sports, and intellectual curiosity are important. Contributing to the realization of a "spiritually wealthy society" that enables appreciation of cultural arts and crafts, participation in/viewing sports and intellectual stimulation is one of the roles demanded of science and technology.
The following section discusses science and technology for the purpose of helping people enjoy a new appreciation of life and spiritual wealth includeng the following:
- Science and technology contributing to the preservation and use of cultural heritage and creation of arts and crafts
- Sports and technology contributing to sports activities
- Science and technology developing intellectual value to satisfy intellectual curiosity
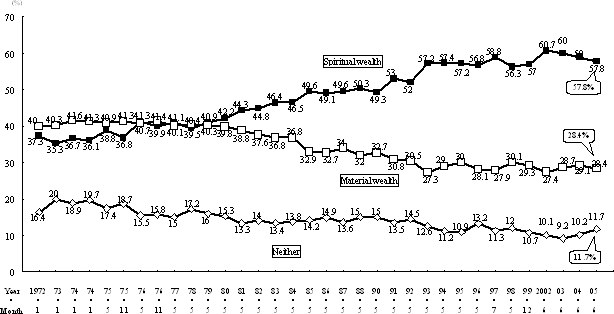
Figure 1-2-39 Trends in the wealth demanded by people
Note:
Spiritual wealth → "Since there is already a certain
level of material wealth, from now on there should be an emphasis on a life
of spiritual wealth and ease"
Material wealth → "Still should
be emphasis on material wealth in daily life"
Source:
Cabinet Office "Public Opinion Poll on Citizens' Lives"
(2005)
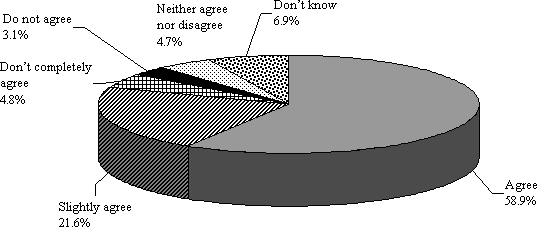
Figure 1-2-40 Science and technology development should focus on spiritual wealth
Note:
Responses to the statement "The progress of science
and technology in the future should not only be for material wealth, but also
directed at achieving spiritual wealth"
Source:
Cabinet Office "Public Opinion Poll on Science &
Technology and Society" (2004)
Table 1-2-41 Increase in total disposable time
|
|
2002 | 2030 | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worker lifetime disposable hours | 183,000 hours (20.9 years) |
205,400 hours (23.4 years) |
Longer healthy life |
Note 1:
Values in parentheses are calculated by dividing total
disposable hours by [24 (hours) 365 (days)]
Note 2:
Assuming the number of annual labor hours in 2030 (2002:
1,954 hours) continues to shift toward the 2002 levels in the west (1,726
hours), the total will be 213,600 hours (24.4 years), an increase of about
17% from the current level.
Source:
Council on Economic and Fiscal Policy's survey report on
"Japan's 21st Century Vision" (2005)
1.2.3.2 Science and Technology to Contribute to Preservation/Utilization of Cultural Heritage and Creation of Arts
● Science and technology contributions to preservation and restoration of tangible cultural heritage
For the preservation and restoration of tangible cultural heritage, preservation and restoration techniques are being developed using the latest science and technology.
For example, inlaid pommels from the Tumulus period (knob on a sword hilt) become corroded while buried in the ground and covered with a thick layer of rust, making it impossible to directly see the inlays. A method to remove the rust only from the surface using a hydrogen plasma technique has been developed, making it possible to see the patterns in the inlaid relics (Figure 1-2-42).

Figure 1-2-42 Pommel inlaid relics
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology,
Council for Science and Technology, Resource Survey Subcommittee report "Promotion
of Science and Technology to Support the Preservation, Use and Creation of Cultural
Resources" (2004)
The establishment of preservation and restoration technology for inlaid relics using plasma, is not only for delicate preservation and restoration; it also has an important role in clarifying history. In this way science and technology development plays an important role in supporting the maintenance of their value as cultural relics.
● Science and technology contributions to preservation and restoration of intangible cultural heritage
Science and technology makes a large contrib.
ution to the preservation and passing down of skills that have historical and artistic value, such as the movements of the human body, as in the traditional techniques of pottery artists, etc.
For the preservation and transfer of the skills of intangible cultural assets, where the value is the action itself, text and diagrams in written documents are not adequate. Recent advancements in 3-D imaging technology have made it possible to make detailed recordings of movements. Specifically, a special camera with two lenses records the hand movements of an artist in 3D video, the movements of the artist's arms and hands are measured using motion capture technologies with magnetic sensors and data gloves, and a database is created. The movements of the artist are regenerated from the database using computer graphics, making it possible to observe even the motions that are ordinarily hid den from view. This kind of technique is valuable as an effective means of recording and preserving intangible cultural assets (Figure 1-2-43).
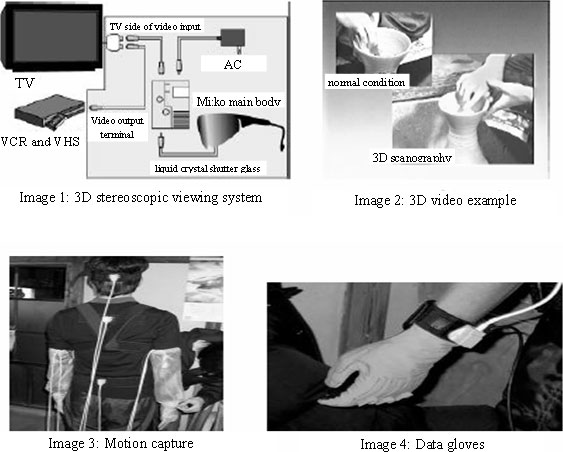
Figure 1-2-43 3D stereoscopic viewing system and images, motion capture, and data gloves
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology,
Council for Science and Technology, Resource Survey Subcommittee report "Promotion
of Science and Technology to Support the Preservation, Use and Creation of Cultural
Resources" (2004)
● Cultural heritage on-line
The Agency for Cultural Affairs and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications are working on the "Cultural Heritage On-line Concept" to actively disseminate information on tangible and intangible cultural heritage of local regions and the nation using broadband technology. Under this plan it will become possible for citizens to easily obtain information on cultural heritage and traditional arts even on a distance basis. Digital archive technology is expected to make a large contribution to the preservation, spread and use of cultural assets and recording of relics (Figure 1-2-44).

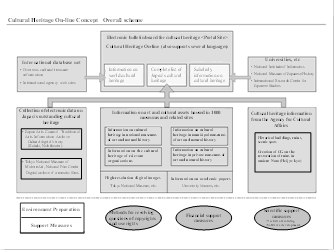
Trial posting of Cultural Heritage Online
Figure 1-2-44 Concept of cultural heritage online
Source:
Agency for Cultural Affairs "Culture Policy in Japan"
(2005)
● Science and technology contributing to the creation, transmission and use of arts and crafts culture
Japan has seen remarkable progress in IT/telecommunications technology, with the now widespread use in computers and broadband connections. This is now an era in which anybody can view the information they want at almost any time. Amidst these developments a new field of art has been created, known as media art, which includes movies, animation, CG (Computer Graphic) art and game software that use the multifunctionality and flexibility pro- vided by the latest digital technology.
In eras when walls and stone were expressive media, ink and paint were actively utilized. In the era of papyrus and paper, paper production technology progressed, and information sharing became common through the discovery of printing technology. With the advances in engineering and precision machinery technology and the appearance of the camera, photographs and movies became a new source of creativity. Subsequently, developpments in electronics technology leading to radio and television further advanced the popularization of media. The appearance of computers and the Internet, has now led to an era in which anyone can view any work they desire at anytime. In the future, it will be easy to not only view, but also to create and release works, through a two-way connection with media and a rapid expansion in the diversity of expression methods. As a result, it will be easier for the public to participate in art creation. The development of digital science and technology has led to an era in which ordinary people can release ideas and content that utilize their own creativity (Figure 1-2-45).
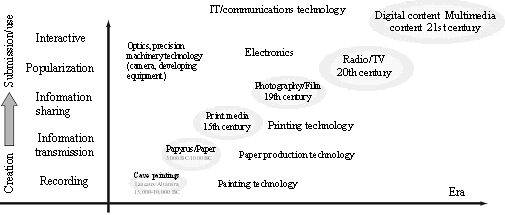
Figure 1-2-45 Art culture development history through media
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology,
Council for Science and Technology, Resource Survey Subcommittee report "Promotion
of Science and Technology to Support the Preservation, Use and Creation of Cultural
Resources" (2004)
Currently research and development is steadily progressing on a variety of expression methods, toward achieving an era in which anyone can create and transmit content. Japan leads the world in research and development on diverse expression methods, producing 2/3 of the new technology programs announced at SIGGRAPH (special interest group on graphics of the US Association of Computing Machinery), the leading computer graphics international conference in the world.
In addition, a variety of devices have been developed for use throughout the many processes involveed right from the creation of digital images to their presentation and display. These devices have been released on the market, but if these are combined at random a good quality image might not be reproduced properly, and the image intended by the creator may not be presented correctly. Therefore research and development has progressed on the establishment of standards to ensure the quality of original digital images in their final presentation (Figure 1-2-46).
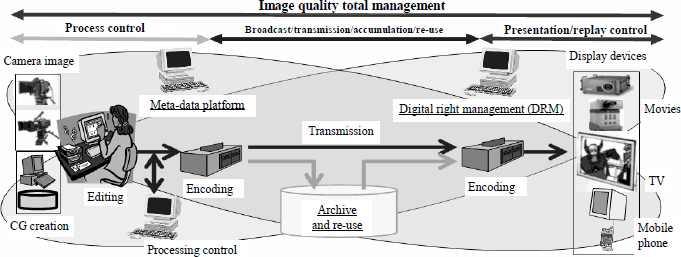
Figure 1-2-46 Research on digital cinema standards technology
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
"Research on Digital Cinema Standard Technology Standards" Project
At the FY2005 Media Arts Festival, a symposium on the fusion of art and technology was held, and the latest technologies were introduced (leading edge technology showcase), drawing a high level of interest (Figure 1-2-47).


FY2005 Media Arts Festival, Agency for Cultural Affairs
Grand
prize winner in the art division
[Title] Khronos Projector
[Summary of
work] When the observer touches the screen the time for the video in the portion
of the screen that is deformed can be changed to move forward or backward. The
image changes in realtime based on the observer's actions, providing a sense
of ability to freely control time.
[Artist] Alvaro CASSINELLI (Uruguay)
Source:
Agency
for Cultural Affairs

From the "Cutting-edge technology showcase" providing future art
expression from the technology perspective
[Title] Invisible Man / Mosaic
Man <Thermokey>
[Summary of work] The color and temperature of the
person are precisely measured and a image is created with the human portion
extracted. The research for this technology was done as a basic technology for
making movies, eliminating the need for the blue screen as in the past. With
the ability to automatically create images in real time for any background this
is a technology that can applied in a variety of ways, including interactive
entertainment, or protection of privacy by automatically applying a mosaic to
the images of people Source: Japan Science and Technology Agency
Basic Research Programs "Foundation of technology supporting the creation
of digital media contents"
Figure 1-2-47 FY2005 Media Arts Festival, Agency for Cultural Affairs
● Sports to provide "spiritual wealth"
Sports are not simply a spectator form of entertainment, but also offer a great deal of enjoyment to those who participate. Participation in sports not only improves health and physical condition through physical exercise, but also contributes to "spiritual wealth" through the sense of pleasure and mental enjoyment, including feelings of exhilaration, accomplishment and connection. Science and technology makes a large contribution to the analysis of the basic principles of sports in order to improve records, as well as to the advancement of related equipment and materials. As science and technology advance, the materials in the equipment change, and more people can enjoy participation in sports.
1.2.3.3 Science and Technology Creating Intellectual Value and Providing Answers to Intellectual Curiosity
The new understanding and discovery arising from the investigation of the human frontiers of space, the earth and life contribute to the shared intellectual assets of mankind and provide answers to the intellectual curiosity of people throughout the world who desire to know the truth.
There is no end to mankind's quest for knowledge. The range of activities of humans and the objects of curiosity cover a range that is not seen in other animals. Human curiosity and activity is not limited to things on land; the range of activity has expanded to the ocean, the air and even space. The driving force has been mankind's ceaseless quest for further knowledge.
● Unraveling the mysteries of space with Hayabusa
The purpose of Hayabusa is to obtain samples from asteroids to investigate the mysteries of the origins of the solar system. Hayabusa is a crystallization of mankind's quest for knowledge in space.
Hayabusa, the asteroid explorer launched in 2003, landed on the asteroid Itokawa in November 2005, approximately 300 million kilometers from earth. An asteroid is a body in space that is like a fossil containing a relatively good record of the time when the planets were born. If the technology to bring back the samples obtained from the asteroid can be realized, this is expected to provide clues about conditions inside the solar nebula at the time the planets were born (Figure 1-2-48).
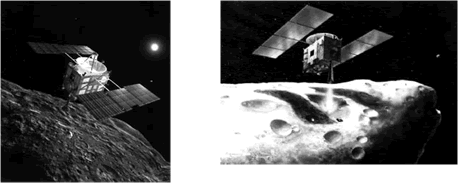
Figure 1-2-48 Asteroid explorer Hayabusa
Source:
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
● Deep Sea Drilling Vessel Chikyu
What is the inside of the earth like? To fulfill the boundless curiosity of mankind, Japan has developped the deep-sea drilling vessel Chikyu. Since major earthquakes occur at plate boundaries, it is necessary to investigate the structure of the plate boundaries in order to learn the mechanism of earthquakes. Chikyu is expected to reach the mantle of the earth and be able to investigate the massive earthquake zones in the ocean trenches.
Chikyu is also being used to track down the origins of life on earth. The first life was born on primeval earth which was characterized by high temperatures, high atmospheric pressure and no oxygen. Even today, deep in the earth there exists an environment that resembles that of primeval earth. In addition, earthquake measurement equipment will be buried in the holes dug by Chikyu to help build an earthquake measurement network system to quickly relay information at the moment an earthquake occurs. This is expected to make a large contribution to future earthquake prediction and disaster preparedness in urban areas (Figure 1-2-49, Figure 1-2-50).

Figure 1-2-49 Chikyu
Source:
Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology
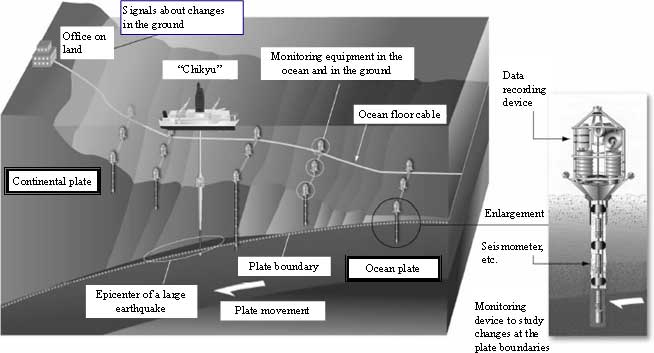
Figure 1-2-50 Chikyu and plate boundaries
Source:
Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology
● Investigation of ancient Egyptian ruins using satellite information
Science and technology is used to understand ancient civilizations. It is said that all of the pyramids of ancient Egypt have not yet been discovered, with many unknown, undiscovered pyramids in Egypt believed to exist. Data about the surface of the earth obtained from earth-observation satellites orbiting several hundred kilometers high in space is being analyzed to look for characteristics similar to pyramid sites that have already been excavated, in order to identify promising locations to discover other as yet unknown pyramid sites. From this satellite information it is possible to investigate the ancient environment and detect ancient cities and ruins that are buried in the sand or jungles.
Analysis of the relationship between the location of pyramids and the changes in water level of the Nile river has revealed that most pyramids are located on land that is not affected by flooding, but nevertheless along the lines of the flood levels, allowing the stones to be transported by boat. Undiscovered pyramids are very likely to be in this kind of location, making it possible to narrow down excavation sites that will lead to new discoveries. This is one of the results of satellite measurement technology (Figure 1-2-51).
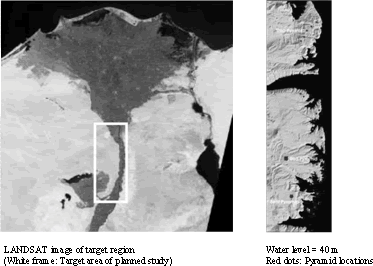
Figure 1-2-51 Satellite photo of the area around Egypt and distribution of pyramids
Source:
Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology,
Council for Science and Technology, Resource Survey Subcommittee report "Promotion
of Science and Technology to Support the Preservation, Use and Creation of Cultural
Resources" (2004)
Contacts
Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau
(Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau)