3.2 Priority Strategies for Science and Technology
3.2.1 Promotion of Basic Research
Basic research creates human wisdom and is the source of every type of knowledge. It is realized in the steady, serious pursuit of truth and after much trial and error.
Basic research consists of two types: academic research based on the free ideas of researchers in science and technology, including human and social sciences; and basic research that aims at future application based on policies. The former promotes a variety of research activities from the very early stages in the pursuit of universal knowledge from a long-term perspective, aiming to accumulate intellectual achievements to generate new knowledge constantly. Meanwhile, the latter is research activities for policy issues, aiming to create knowledge, a source of discontinuous innovations that can reform the economy and society, toward the achievement of policy goals.
While the results of basic research are not always put into practical use immediately, they are rather accumulated as the common property of all humankind. Therefore, basic research should be widely, steadily, and continuously promoted.
3.2.2 Prioritization of Research and Development in Response to Issues Important to the State and Society
Aggressive and strategic investment in priority sectors and promotion of research and development are essential for ensuring sustained economic development through vitalization of the economy and industry, and for assuring people of safe, secure lives.
The following measures were taken in Fiscal 2005 in line with the Priority Strategies stipulated in the Basic Plan and the “Sectoral Promotion Strategy” (see Figure 3-1-4).
3.2.2.1 Life Sciences
(1) Promotion of Life Sciences
The life sciences aim at elucidating the complex and elaborate mechanisms of biological phenomena produced by living things, and their results contribute greatly to the improvement of people’s lives and to development of the national economy, through dramatic advances in medicine, resolutions of food supply and environmental problems, and other areas.
● Efforts toward Industrialization, etc.
To strengthen efforts toward commercialization of the life sciences, the heads of five ministries and agencies (the Director-General of the Science and Technology Agency, Minister of Education, Minister of Health and Welfare, Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, and Minister of International Trade and Industry), based on the “Basic Strategy for the Creation of Bio-technology Industries (July 1999),” implemented the “Millennium Project” from Fiscal 2000 to Fiscal 2004, in order to promote revolutionary advances in personalized medicine for individual characteristics in response to the Aging Society, and to promote environments that offer prosperous and healthy eating habits and secure living. This project was completed with the provision of final evaluations and advice in July 2005.
Furthermore, the Prime Minister’s Office established the BT (Biotechnology) Strategy Council in July 2002. This strategy council issued the “Strategies for Development of Biotechnology” in December 2002, detailing three strategies focused on 2010, including: (1)revamping research and development; (2)enhancing the process of industrialization; and (3)ensuring public understanding, and specific action plans for achieving those strategies. At the eighth meeting of the BT Strategy Council in January 2006, follow-ups were implemented for the progress in efforts made after the previous meeting was held in March 2005.
● Strategic life sciences fields
1) Genome-related research
On April 14, 2003, the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium, a grouping of six countries and 24 institutions from Japan, North America, Europe, and China engaged in sequencing the human genome containing all human genetic information, announced completion of detailed sequencing of the human genome.
Based on the result, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology started the “Genome Network Project” in Fiscal 2004. This project aims to elucidate basic problems relating to life sciences, elucidate the mechanisms of disease development, and develop new treatment methods by clarifying the network that establishes vital activity mainly through comprehensive analysis of the interactions of biological molecules, etc. In addition, research has been steadily promoted in such fields as the analysis of protein structures and functions related to genome-based drug discoveries, etc., and the development of revolutionary medical tecnologies that make use of individual genome information. In addition, basic research in this sector at universities and colleges has been intensively promoted through the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, and other related programs.
Since Fiscal 2000, the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare has been involved in the Millennium Project, using the elucidation of genes related to dementia, cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure, asthma, and other ailments of the elderly, to promote R&D for the establishment of methods for the prevention and treatment of disease and the development of revolutionary new drugs. Moreover, taking into consideration rapid advances in genomic sciences seen in recent years, research and development has been carried out since Fiscal 2002 into basic technologies (toxicogenomics) that allow rapid and effective prediction of the safety (toxicity, side effects, etc.) of compounds that are candidates for medical products.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, mainly on the strength of the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, had sequenced the full length of the rice genome in the project of the international consortium by the end of Fiscal 2004, while elucidating the functions of various genes through establishment of a method to isolate genes from various organisms. The ministry has also collected many materials and data that are critical for research on elucidation of gene functions. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry commenced a post-genome project entitled “Green Technology Program to Improve Food Supply Capabilities” based on the results achieved in the previous rice genome-related research. In accordance with the program, the ministry is conducting research to improve Japan’s food supply capabilities and to create new industries, by putting together a variety of knowledge in genome informatics and developing and demonstrating the efficient breeding scheme (genome breeding technology) that controls the balance of expression of various genes at the genome level.
Furthermore, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry engaged in genome function research and technology development at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, performed DNA analysis, etc., of industrially useful microorganisms at the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation, and worked through the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization to utilize private-sector vitality to pursue technology development for the analysis of genetic information. In Fiscal 2001, analysis of the complete human cDNA(Notes 1) structure led to the identification of about 30,000 new human genes, and these genes are now distributed by the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation, with analysis of those genes now in progress.
At the Ministry of the Environment, the independent National Institute for Environmental Research is researching the utilization of genome technology in research for the preservation of biological diversity, and also into the health effects of toxic chemical substances.
Notes 1:
cDNA: abbreviation for “complementary DNA (or complementary
deoxyribonucleic acid).” The term denotes DNA synthesized by using reverse
transcriptase in a template for messenger RNA (m-RNA). cDNA consists only
of the gene regions of the DNA, so that a complete cDNA encompasses all information
about a single gene.
a) Promotion of protein structural and functional analyses
Analysis of protein structure and molecular function is one of the most important fields in post-genome research, because the research results can link directly to applications in medicine or to uses in industry.
Toward the goal of developing genome-based drugs in Japan, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology utilized such facilities as the world’s largest NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) facility and SPring-8 (the Large-Scale Synchrotron Radiation Facility) to bring together researchers from industry, academia, and government into the “Protein 3000 Project,” to elucidate the structures and functions of one-third(about 3,000) of the approximately 10,000 basic protein folds known to exist, and to transfer the research results, to include patenting the results to industry in Fiscal 2002. By October 2005, a total of 2,738 structures had been confirmed.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is promoting research and development into the elucidation of the functions and interactions of proteins affiliated with disease, in order to improve prevention and treatment performance for cancer and heart attacks, the two main causes of death for employment age Japanese, as well as for such illnesses as strokes,dementia, and bone fractures that are a major source of demand for nursing care.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has brought researchers from industry, academia, and government to the Japan Biological Information Research Center at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology to engage in “analysis of the three-dimensional structures in biological molecules,” specifically, R&D into the structural analysis of membrane proteins believed to play particularly important roles in the body, and into the “analysis of protein functions” for the analysis of newly discovered human genes using results obtained from analysis of the total human cDNA structure.
b) Promotion of bio-informatics
Recent research into the genome sciences has made available vast volumes of genome-related information, necessitating the appearance of the new field of bio-informatics, an integration of the life sciences and IT (Information Technology) sectors, as a way to utilize this information.
In the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Institute for Bio-informatics Research and Development (BIRD) at the Japan Science and Technology Agency is actively engaged in the upgrading, standardization, and expansion of databases, as well as in the development of genome analysis tools with the cooperation of researchers in both the biology and information technology sectors. The ministry is also promoting the development of the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ), one of the three largest of its kind in the world, under the operation of the National Institute of Genetics, and other genome-related databases. Furthermore, the Special Coordination Fund for Promoting Science and Technology is being utilized to implement programs related to personnel development in the bioinformatics field, with funding targeted at universities and colleges.
In Fiscal 2000, the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry commenced building a H-invitational database (comprehensive database), which includes independently obtained data and advanced search and analysis tools, to enable utilization in research and industrialization of the vast amounts of biotechnology-related data and achievements obtained from the Millennium Project. The database has been made public and further expanded since Fiscal 2004. In addition, the ministry commenced the “Project for Analysis of the Gene Diversity Model” in Fiscal 2000 (based on the supplementary budget) to implement the development of software that will make it possible to conduct efficient searches for genes related to disease, based on micro-satellites, SNPs2, and other polymorphic gene information.
Notes 2:
SNPs: abbreviation for Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms.
It refers both to the expression of base sequences on the genome that vary according
to race or individual (such as the difference between a healthy individual
and a sick person), and to the corresponding area on the genome.
c) Promotion of gene polymorphic research
Various ministries are engaged in the promotion of research and development for the elucidation of the causes of diseases, with the goal to create more effective medicine suited to specific individuals.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, for example, has been conducting the “Project for Realization of Medicine in Response to Individual Genetic Information” since Fiscal 2003. The ministry, with the cooperation of many other medical institutions, performed collection of DNA/serum samples and clinical information from targeted patients for the development of a bio-bank, and, since Fiscal 2005, by using these samples, it has been conducting full-scale research for the elucidation of the relationship between SNPs diseases, drug responsiveness, and side-effects. The RIKEN SNP Research Center made the greatest contribution to the International HapMap Project (Japan, the U.S., the U.K., France, China) among the participating organizations, and released the research results on the JSNP database.
Furthermore, the Center has been promoting research on the elucidation of the causes of diseases, in cooperation with the HapMap Project.
In the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, joint examination of the SNPs data by the Institute of Medical Science of the University of Tokyo and the Bio-Industrialization Consortium (JBiC), in the form of analysis of gene polymorph frequencies (allele frequency analysis), was completed in Fiscal 2002. Currently, data about SNP locations is being issued using the JSNP database.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is promoting searches for gene polymorphs for disease-related genes and drug-reactive genes related to dementia, cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure, asthma, and other ailments.
In Fiscal 2002, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries commenced the development of SNP markers in agricultural crops for the purpose of developing effective crop breeding and nurturing systems that make use of gene polymorphs.
2) Promotion of brain sciences research
Brain science is expected to lead to results that improve the quality of life, as well as to improved medical science and to the creation of new technologies and industries. The resulting efforts have greatly strengthened Japan’s brain sciences research, which is divided broadly into the four fields of “understanding the brain,” “protecting the brain,” “creating the brain,” and “strengthening the brain” through research and development that makes maximum use of the many universities and national research institutions that extend beyond the bounds of individual ministries and agencies.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting research at the Brain Science Institute at RIKEN, through the utilization of Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research and competitive research funds by the Japan Science and Technology Agency, for the priority promotion of brain science research at universities and colleges.Since Fiscal 2005, the ministry has been developing information infrastructure including an enormous amount of research results in brain neurochemistry, while promoting neuroinformatics to provide the results for researchers around the world as part of its international cooperation. In order to clarify the impact that a social and living environment has on peoples’ minds, bodies and language development, the Japan Science and Technology Agency started to collect and analyze the data for infants gained through questionnaires and action observation by experts, in three prefectures: Osaka, Mie, and Tottori..
Activities at other ministries and agencies include the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare’s efforts to promote research on the elucidation of nervous and muscular system disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, and mental system disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, higher-brain dysfunction, schizophrenia, and depression and on the development of methods of treatment, while the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries is engaged in research on brain and nervous system functions in animals, and the Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications is engaged in research into the elucidation and application of info-communication functions in living organisms.
Furthermore, the “Human Frontier Science Program” (HFSP), which was first proposed by Japan at the Venice Summit of advanced nations in June 1987, operates based on the principles of “internationality,” “interdisciplinarity,” and “encouragement of young scientists,” to provide subsidies within an international framework for research that contributes to the elucidation of brain functions and other complex.mechanisms of living organisms
3) Promotion of research on development, differentiation, and regenerative Science
Research into development, differentiation, and regeneration in biological system aims to elucidate the mechanisms, etc. relating to the process in which one cell differentiates into various tissues or organs to form and maintain an individual. This serves as a basis for regenerative medicine, which is expected to lead to treatment for diseases that are now difficult to cure. The research of this field brings about rapid advances in stem cell research and establishment of technology for producing Embryonic Stem (ES) cells in recent years.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is conducting research at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology. Moreover, in Fiscal 2003, the ministry launched the “The Project for Realization of Regenerative Medicine” and has been promoting research towards developing a stem cell bank as research infrastructure in order to provide stem cells for researchers, and applying the results of basic research to clinical areas.
Furthermore, to contribute to the realization of regenerative medicine, the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare is promoting research focusing on clinical aspects in transplant and regenerative medicine.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting development of equipment in support of practical applications of regenerative medicine.
4) Promotion of plant science research
Advances in genome science have also led to progress in the analysis of plant genome structures and functions. Control of plant functions based on these results is expected to lead to the development of plants that can contribute to improvements in eating habits, etc.
Rice genome research is important for laying the foundations for research into the major cereals and other crops. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is currently promoting the Second Phase of the “Rice Genome Project,” which involves the reading of all DNA base sequences for the rice genome, and the elucidation and patenting of the functions of useful genes, which are efforts that have attracted worldwide acclaim.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries commenced post-genome sequence research even as the base sequence readings were continuing. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry launched the “Green Technology Program to Improve Food Supply Capabilities” in order to elucidate the functions of useful plant genes and gene networks, and has been promoting, based on the achievements of that program, the creation of a leading model system for stable food supply, as well as the establishment of technologies for efficient breeding of useful varieties.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting research to improve plant productivity in terms of both quality and quantity, through the genome sequencing of Arabidopsis thaliana etc. at the RIKEN Plant Science Center. Additionally, in plant research, a full-scale foundation for functional analysis, network analysis and metabolome analysis(Notes 3) has been developed, enabling Japan to catch up with the United States and Europe in terms of the level of research carried out.
In order to develop basic technologies to produce useful materials such as industrial raw materials using plant functions, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is implementing the analysis of routes and functions of substance production systems using plants and the development of databases to store the analysis results at the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization.
Notes 3:
Metabolome analysis involves the identification and quantification
of all metabolites generated by enzymes in a cell, and correlating these with
genome functions.
5) Preparation of bioresources
The field of bioresources is not limited to the mere preservation of genetic resources, but also plays an important role in exploring new areas of research. The national interest is served in the development, collection, storage, and provision of bioresources.
In Fiscal 2002, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology instituted the “National BioResource Project” for the purpose of establishing a system facilitating the systematic collection, storage, and provision of bioresources that are of particular strategic importance to the nation, such as experimental animals and plants (such as mouse clones), various cells, and genetic data from various life forms.
At the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation joined to establish a Master Bank (in Fiscal 2001, these two institutions began setting up the Pharmaceuticals Basic Technology Research Facility toward an eventual merger) for the collection and preservation of human and animal-derived cultured cells and genes needed for use in research in medical and pharmaceutical fields. The supply of cultured cells and genes is made through the Japan Health Sciences Foundation to researchers and other personnel. The foundation has also commenced distribution of human tissue with careful consideration for bio-ethics issues. It also collects, stores, and supplies medicinal plants, and breeds and supplies kanikui-zaru monkeys and other animals used for medical testing.
In the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries Ministry, the Gene Bank Project collects, classifies, and identifies all plants, animals, microorganisms, trees, marine life, and other bioresources utilized in the agricultural, forestry, and fisheries industries. The project also conducts evaluations of characteristics, and propagates and preserves specimens. It provides bioresources and information about those resources to the national research institutes, the independent administrative institutions, the private sector, universities, etc. The ministry also promotes maintenance of genome resources that are the results of rice genome research, as well as storage and provision to the private sector, universities and colleges.
In addition, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry established the NITE Biological Resource Center at the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation as Japan’s core bioresource organization for microorganisms, etc. The Center engages in the collection and preservation of biogenetic resources. It also sorts out information related to bioresources (information regarding systematic identification, base sequence, and gene functions, etc.), and project to create a gene resource library for unknown microorganisms, for the purpose of promoting industrial utilization of microorganisms. Furthermore, in order to ensure access to biogenetic resources overseas and thereby promote the industrial utilization of the resources in Japan, the Center has transferred the resources to Japan, in accordance with the Convention on Biological Diversity and based on agreements concluded with other Asian countries concerning the utilization of microorganisms. It is also implementing the development of a system for collecting and utilizing various microorganisms overseas, through promotion of an Asian consortium for preservation and utilization of microbial resources in Asia, as well as enhancement of the system for cooperation with resource-rich countries.
The Ministry of Environment instituted the “Environmental Sample Time Capsule Project” in Fiscal 2002 for the purpose of preserving the cells of wildlife threatened with extinction. In addition, the independent National Institute for Environmental Research is engaged in the collection, preservation and supply of algae, and in building an algae database.
6) Promotion of R&D in food sciences
Building a stable and sustainable production and distribution system for agricultural, forestry, aro-moting the development of functional foods that can contribute to improving the people’s health are essential if Japan is to be able to maintain food security and to guarantee an abundant food supply.For this purpose, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries continues to promote the quality of wheat, soybeans, and vegetables, to improve food self-sufficiency, and as a response to the recent sharp rise in imports of raw vegetables, to develop superior new crops resistant to diseases and pests and rich in nutrition and functional constituents, and new agricultural, distribution methods and processing technologies, as well as to develop cloning and other animal husbandry-related technologies, and technologies for the difficult production of young marine organisms using artificial cultivation. Moreover, to promote food safety and security, the ministry is upgrading technologies for the detection of toxic microorganisms, and developing technologies for DNA identification of species types. For control of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), the ministry is engaged in the elucidation of the shape and characteristics of prion proteins, and in the development of diagnostic technologies. Moreover, the ministry is engaged in the development of basic technologies useful for the diagnosis and prevention of outbreaks within Japan of diseases shared by humans and animals, both to assuage the people’s concerns, and to reduce the effects of such outbreaks on the livestock and poultry industries. Since Fiscal 2005, the ministry has been promoting the development of safe and trusted technologies to produce livestock products for the purpose of reducing the usage of antibiotics, as well as the development of soil conditioning technology for potatoes(Notes 4:) and seed planters for rice, oats, and soy beans, in order to establish an efficient multiple cropping system. In addition, the ministry is accelerating research into the elucidation of bio-regulatory functions through combinations of foodstuffs capable of contributing to the development of new functional foods, as well as supporting the development of technologies for the use of bio-markers (simple biological indices) in the scientific evaluation of food efficacy, and the development of production technologies for food that is efficacious at maintaining health.
With the outbreak of various incidents that threaten food safety and the enactment of the Basic Law on Nutritional Education, people are highly concerned with nutrition, and the guarantee of trusted and safe food products has become an important issue to be addressed. In order to expand, improve, and enhance food safety measures, with regard to additives, pollutants, chemical substances, residual pesticides, microorganisms, Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), health products, and food products derived from modern biotechnology, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has been promoting research on new factors that may cause damage, investigative research to formulate standards, and research and development towards establishing an official method of examination, while reflecting the achievements in risk control measures. Furthermore, the ministry has also conducted research on health risk control including countermeasures against food poisoning and food terrorism.
Notes 4:
Soil conditioning technology for potatoes is a method
for cultivating crops, and contributes to developing an appropriate growing
environment for potatoes and reducing the amount of work on selecting stones
in harvesting by removing the stones from the ground just before planting the
potatoes.
7) Promotion of cancer-related research
Since cancer accounts for about 30% of total deaths in Japan, the “Third Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy for Cancer Control” (ratified by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare in June 1993) was formulated as a new 10-year strategy that started in Fiscal 2004. Based on this strategy, researchers in Japan are promoting the elucidation of the essential elements of cancer, and of new prevention, diagnostic, and treatment methods that utilize these research results.
Under this 10-year strategy, since Fiscal 2004, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has been promoting the “Cancer Translational Research Program” as bridging research to apply the excellent results of basic research relating to cancer immunotherapy and molecular-targeted therapy clinically. Futhermore, the National Institute of Radiological Sciences is acting under this 10-year strategy to perform clinical trials of a heavy ion medical accelerator that is expected to become a revolutionary new treatment method for particularly difficult-to-treat cancers.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, meanwhile, is engaged in the development of a helical CT that will be useful in the early detection of lung cancer, and in the development of safe cancer treatment methods using endoscopes that reduce the burden on the patient.
Since Fiscal 2005, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has been developing molecular imaging equipment to identify changes in cell functions and enable the very early detection of cancer, as well as equipment to combat cancer cells only.
8) Promotion of research on immunologic and allergic diseases
It is necessary to comprehensively promote research in the area of the immune system, allergies, and infectious diseases with the aim of achieving eradication of hay fever, rheumatoid arthritis, and other immunologic and allergic diseases, which many people desire, and coping with infectious diseases, which are still a national health threat.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology engages in research for the basic and comprehensive elucidation of immune systems at the RIKEN Research Center for Allergy and Immunology. With respect to infectious diseases, the ministry has been promoting research and development that targets the suppression of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) and other infectious diseases by utilizing the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry commenced the “Program of Founding Research Centers for Emerging and Reemerging Infectious Diseases” and has been accumulating basic knowledge and fostering personnel to enable the prompt development of countermeasures against emerging and reemerging infectious diseases, through improvement of domestic and overseas research centers and the promotion of joint research conducted mainly at the centers.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is promoting research in the sectors of emerging and reemerging infectious diseases, measures against HIV/AIDS, measures against hepatitis, and immunologic and allergic diseases. The ministry is also conducting research on broad-ranging infectious diseases in a leading, unique and comprehensive manner at the National Institute of Infectious Diseases. In addition, the ministry established a clinical research center at the National Hospital Organization Sagamihara National Hospital, aiming at the elucidation of immunologic and allergic diseases, and the development of treatment methods. The center’s research is currently concentrated on clinical aspects.
Incidentally, the RIKEN Research Center for Allergy and Immunology and the National Hospital Organization Sagamihara National Hospital has made a joint research agreement, and are promoting efficient research through collaboration between the basics and clinical applications.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is promoting comprehensive research on the control of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), highly pathogenic avian influenza (Bird Flu) and other infectious diseases shared by humans and animals at the National Agriculture and Bio-oriented Research Organization.
9) Promotion of research and development in interdisciplinary areas
Since Fiscal 2003, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has been conducting the Cell / Biodynamics Simulation Project, with the aim to simulate the analysis of drug responsiveness and animal tests conducted by using living bodies and cells, based on life information technology and advanced imaging technology.
The ministry commenced the Molecular Imaging Research Program(Notes 5:) in Fiscal 2005, and has been promoting research to establish the world's most advanced molecular imaging technology that will allow people to visually see the quantity and functions of molecules in a living body. In fact, the technology is expected to serve as a tool for the early detection of cancer and other diseases, identification of drug kinetics, and evaluation of drug effects. The ministry aims to establish an innovative method of diagnosing diseases, shorten drug disco very processes, and reduce costs related to drug disovery, through the establishment of a national-scale R&D system.
Notes 5:
The Molecular Imaging Research Program aims to search
candidate substances for drug discovery and to conduct innovative R&D activities
to improve the diagnosis of diseases, through the development of a foundation
to promote molecular imaging research and the establishment of a core research
center for domestic molecular imaging research.
10) Promotion of other research and development
Because living things are generally efficient at energy conversion, consuming little energy for reactions at normal temperatures and pressures, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry has promoted the “Program for Creation of Recycling-Type Industrial Systems Using Bio-Functions” to develop the basic technologies required for effective utilization of bio-functions based on genome information, and for their expanded use in recycling-oriented industrial systems that are energy-saving and eco-friendly.In regard to research on sugar chains, which are believed to play important roles in a vast array of biological functions, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is using the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research and Basic Research Programs to promote sugar chain research at universities and colleges. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting research and development into automatic devices for synthesizing sugar chains as well as structure analysis devices, and of the analysis of functions for the general acquisition of genes related to sugar chain synthesis.
With respect to research and development in life science, basic research is being promoted at universities and colleges, with the provision of Grants-in Aid for Scientific Research Program. Utilizing and strengthening the excellent research capabilities of certain regions can be effective for promoting research and development in the life sciences sector. In this regard, the government’s Urban Renewal Office decided in August 2001, in “Urban Renewal Project No.2,” on the “formation of an international center for life sciences in the Osaka region.” This action was followed in July 2002, in “Urban Renewal Project No.4,” with the “formation of an international center for genome sciences in the Tokyo region.” In line with these decisions, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has promoted research at universities and colleges, and worked to form life science research sites and to build systems that link the research sites with each other. In addition, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is promoting the development of core research institutions in the Osaka region for infrastructure technology toward the development of revolutionary new pharmaceutical products, etc.
The major life science research projects implemented in Fiscal 2005 are shown in Table 3-2-1, by ministry or agency.
Table 3-2-1 Major research subjects in life sciences (FY2005)
| Ministry or Agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| National Police Agency | National Research Institute of Police Science |
Study into a new personal identification system using information obtained from biological samples |
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | Program for Promoting Strategic Information and Communications Research and Development National Institute of Information and Communications Technology |
Research into elucidating and applying the info-communications functions of living organisms Research into a communication-friendly society |
| Ministry of Finance | National Research Institute of Brewing |
Research and development in the manufacturing process for alcoholic beverages. Research into alcoholic beverages. Research into brewing-related microorganisms. |
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | RIKEN (The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) |
Promotion of bioresource projects Promotion of comprehensive research into brain science Promotion of comprehensive research into genome science Promotion of plant science research Promotion of comprehensive research into developmental and regenerative science Promotion of varied genetic research Promotion of immunological and allergy research |
| Japan Science and Technology Agency |
Promotion of bio-informatics Promotion of research using competitive funding |
|
| National Institute of Radiological Sciences |
Promotion of research and development for upgrading heavy particle therapy of cancer |
|
| Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology |
Promotion of Frontier Research System for Extremophiles, etc. |
|
| Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency |
Research into medical science, etc., related to space |
|
| Universities and colleges |
Research into the overall promotion of cancer research Basic research into carcinogenesis and the prevention of carcinogenesis Research into the biological aspects of cancer Diagnosis and treatment of cancer Research into human cancers, and epidemiological research into host factors Strategic and advanced research into cancer Comprehensive genome research toward the elucidation of living systems Genomic analysis of hereditary factors, and the elucidation of abnormal molecule conditions in human diseases New developments in genomic biology toward the elucidation of cellular systems New developments in genome informatics Advanced research into brain science Molecular foundations for the appearance of infection, and host response |
|
| Special coordination funds for promoting science and technology |
Rapid searching of important traits in full-length complementary DNA of rice plants Construction of a comprehensive database of diseases and molecular pathogenesis Strategical prevention with mucosal adjuvant biogenic substances Chaos analysis and science of “pulse diagnosis” in Chinese Medicine Research into alternative medicine, especially multidirectional scientific evaluation methods for Chinese medicine and acupuncture Development of evaluation methods for alternative medicine using gene expression analysis Master of Clinical Biomedical Science Program Course Biomedical Omics Informatics Educational Program Genetic counselor and coordinator Unit Life Information Science Technologist Training Unit Advanced Medical Engineering and Information Science Technologist Reeducation Unit Development of novel SQAG radiotherapy sensitizer Protein Manipulation Development of models for human immune disease in marmosets Construction of Asian international network for cell storage of avian species Development of pluralism and universal norm of bioethics Research and study into database integration of life science Organism elucidation and genomic analysis of virus in wild birds |
|
| HFSP (Human Frontier Science Program) (Note) |
International joint research for the elucidation of the complex mechanisms of living organisms |
|
| Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare | Health and labour sciences research grants |
Third comprehensive research on strategy against cancer Comprehensive research on aging and health Research on the human genome, tissue engineering Research on psychiatric and neurological diseases and mental health Research on emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases Research on HIV/AIDS Research on sensory and communicative disorders Research for the eradication of intractable diseases Research into assuring and promoting reliability and safety of food General research for development of policy drugs Research on allergic disease and immunology Research on proteomics Research on toxicogenomics Research on analysis, support, and alternative medical devices for physical functioning Research on promotion of clinical application of translational research results |
| National Institute of Infectious Disease |
Research into gene recombinant vaccines, etc. Research into the development of vectors related to gene treatment, safety evaluations, etc. Research into AIDS, Hansen's disease, etc. Research into methods for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of SARS and other infectious diseases |
|
| National Institute of Health Sciences |
Research into standard test methods, quality evaluation methods, etc., for pharmaceuticals Research into assuring the safety of food, chemical substances, living environment, etc. Research into safety information on drugs, food, chemical substances, etc. |
|
| National Institution of Industrial Health |
Study on work environment management for irregular work using organic solvents Comprehensive research on occupational stress of elderly workers Research on genetic factors that determine sensitivity to adverse factors in the work environment |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Agriculture and Bio-oriented Research Organization, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, etc. |
Integrated research for providing fresh and delicious "Brand Nippon" agricultural-products Development of technology for reducing the impact on the environment using biofunction Development of technologies for the suppression of Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), and diseases shared by humans and animals Development of safe and secure manufacturing technologies for animal products Development of the techniques for seed production in the Japanese eel and spiny lobster Development of a comprehensive management system of hazardous chemicals in agricultural, forestry and fisheries ecosystem Genome-wide analysis of spatial and temporal gene expression in rice panicle development Development of DNA marker-aided selection technology for plants and animals Development of efficient technology for breeding specific kinds by genome breeding Accelerate research of the livestock industrial genome Insect Technology Research for Utilization of the Greatest Unused Resources of the 21st Century Comprehensive research into food safety and functionality Development of isolation and utilization technologies for useful genes obtained through animal genome analysis Assurance of Safe Use of Genetically Modified Organisms Development of stable production technology of cloned animals by somatic cell nuclear transfer Technical development for the establishment of a high productivity area rotation-of-crops system Elucidation of animal (livestock, insect) behavioral mechanisms, and the development of control technologies Surveys and research into local agricultural methods using special resources Expenses required for the promotion of research into the prevention of invasive insect pests Elucidation of the effects of climate warming on crops and animal husbandry, and the development of technologies to control those effects Evaluation of the effects of organic farming on the soil environment, and the certification of environmental conservation effects Elucidation of the mechanism for outbreaks of mastitis, and the development of preventive technologies Comprehensive research into the creation of new agriculture, forestry, and fisheries products by modifying morphological and physiological functions Development of new weed control technologies that utilize plant metabolism genes Establishment of useful substance production systems using plants, animals, and insects Gene bank project |
| Private sector, universities, etc. |
Development of technologies for assuring food safety and security Development of technologies for the promotion of "Brand Japan" processed food supplies Development of efficient plant breeding and growing systems that utilize genetic information Development of new separation and extraction technologies in the food industry Development of health-oriented food evaluation and production technologies using the life sciences Development of next-generation fermentation technologies in the food industry |
|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry | New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization |
Development of basic technologies for production processes using biological functions Elucidation of useful protein functions, utilizing human genome information and its analysis tools Development of information technology required for DNA analysis, disease prevention, etc. Development of technologies for the synthesis and structural analysis of sugar chains Construction of a gene resource library for unknown micro-organisms based on genome information Development of tools for analysis of biomolecules through the use of nanotechnology Development of high-safety technologies for the differentiation and cultivation of a mass volume of artificial cells and tissues enabling regenerative medicine Analysis of the three-dimensional structures of physiological macromolecules of membrane proteins Development of technologies for the analysis of intracellular network dynamism Development of bioinformatics-related databases Development of technology for model analysis of gene diversity Behavior-based human environment creation technology |
| National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology |
Construction of a neural network and development of new information processing technology based on its functions Age-dimension technology program for creating a healthy and productive society Identification of stress markers and evaluation of its usefulness |
|
| HFSP (Human Frontier Science Program) (Note) |
International joint research for the elucidation of the complex mechanisms of living organisms |
|
| Ministry of the Environment | National Institute for Environmental Studies |
Development and verification of an in vivo model that comprehensively evaluates the effects of environmental pollutants on superior function Studies on application of toxicogenomics for risk assessment of environmental pollutants |
Note:
Funding provided by the Ministry of Education, Culture,
Sports, Science and Technology, and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
● Coordination program for science and technology projects
In post-genome research and research on emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases, the Cabinet Office is implementing the “Coordination Program for Science and Technology Projects,” with the aim to remove the negative effects of sectionalism such as unnecessary overlan and to enhance collaboration among relevant ministries and agencies. In the program, the Cabinet Office has promoted the following research projects that should be carried out as supplementary measures taken by ministries and agencies in fiscal 2005: the “Research and Studies on the Integration of Life Science Database” (for the post genome research); and the “Research on the Migratory Routes of Wild Birds Involved in Spreading Virus, Research on the Pathogenic Organisms of the Wild Birds, and Relevant Database Construction” (for the research on new or revived infectious diseases.)
(2) Efforts for Bioethical Issues and Safety
● Efforts for bioethical issues
Rapid developments in the life sciences in recent years have given rise to expectations of revolutionary achievements in the fields of medicine and elsewhere.Therefore, to cope with these issues appropriately, the Expert panel on Bioethics , established under the Council for Science and Technology Policy (CSTP), are now engaged in surveys and examinations of specific important issues concerning bioethics, while the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and other ministries are preparing the relevant laws, regulations, and guidelines and conducting other activities.
Regarding human cloning technology, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has taken measures prohibiting the production of human clone individuals under the Law Concerning Regulation Relating to Human Cloning
Techniques and Other Similar Techniques (Year 2000, Law No.146) and prohibiting the creation and utilization of human clone embryos for the time being under the guidelines based on the said law.
The Expert Panel on Bioethics under the CSTP has discussed the handling of human fertilized embryos and cloned human embryo since August 2001 according to the provisions of the said law. Consequently, in July 2004, the CSTP compiled a statement of opinions to related office and ministries concerning the “Basic Conceptual Approach Relating to Treatment of Human Embryos.” This statement permitted, for research purposes and with limitations, the creation and utilization of human clone embryos and human fertilized embryos, and requested the development of a framework to ensure the proper treatment of embryos. In response to this, the Working Group on the Studies and Utilization of Human Clone Embryos established under the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is examining the treatment of human clone embryos. The Expert Committee on Medical Technology for Reproductive Treatment and the Expert Committee on Research on Human Embryos, established respectively under the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, is holding discussions on the treatment of human fertilized embryos for the purpose of research into assisted reproduction technologies at joint committee meetings.
In the area of human Embryonic Stem (ES)(Notes 6) cell research, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has conducted examination of research plans under the guidelines formulated in 2001 and has reviewed compliance with the guidelines for one derivation plan and 32 utilization plans so far.
Elsewhere, in the areas of human genome and gene sequencing research, epidemiological research(Notes 7) or clinical research, respect of human dignity and suitable management of personal information are required. Therefore, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry are cooperating for the appropriate promotion of research based on the guidelines(Notes 8).
In August 2005, the Special Committee on Guidelines in the 21st Century for the Life Science and Bioethics, Science Council of Japan announced the results of examining various issues related to bioethics, in the form of the“On the foundation for the respect for ‘life’ and the respect for ‘mental well-being’ -a social system to develop a new set of bioethical values -.”
Notes 6:
Human Embryonic Stem (ES) cells: these primordial
cells have attracted high expectations for medical applications because of their
capability of differentiating into all parts of the human body. At the same
time, however, sacrificing human embryos would raise ethical concerns.
Notes 7:
Epidemiological Research: scientific research that clarifies causes
of a disease by investigating the frequency and geographical distribution of
disease incidence and other factors related to human health
Notes 8:
Ethical Guidelines for Human Genome and Gene Analysis, Ethical Guidelines
for Epidemiological Research, and Ethical Guidelines for Clinica Research
● Efforts to ensure safety in the life sciences
Recombinant DNA technology is applied to a broad range of fields, from basic biological research to the production of pharmaceuticals and improvement of agricultural crops, however, one of its characteristics is its application of new properties to living organisms. For this reason, the ensuring of appropriate use of living modified organisms, etc. has been aimed at based on the Law Concerning the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biological Diversity through Regulations on the Use of Living Modified Organisms (Year 2003, Law No. 97), which stipulate the measures necessary to prevent adverse effects on biodiversity due to the utilization of living modified organisms. As some organizations illegally utilized living modified organisms after the Law was enforced, written warnings were issued to the organizations, and briefing sessions were held, aimed at thorough compliance with laws and ordinances.
For clinical research aimed at the establishment of gene therapy(Notes 9), the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare are making efforts for the appropriate promotion of research based on the Guidelines for Gene Therapy Clinical Research.
Notes 9:
Gene therapy: a treatment method that involves the insertion
of genes, or cells containing genes, into the bodies of patients for the purpose
of treatment of disease. It is not an established method of treatment at present,
but is practiced as one aspect of clinical research
3.2.2.2 Information and Commnications
Promotion of research and development in the information and communications sector not only brings about innovative results in many other areas of research and development but also contributes to the creation of new industries and development of existing industries. In addition, as can be seen from the dissemination of mobile phones and computers, information and communications technology has become essential for a wide variety of activities in our daily life, and is an important foundation that enables people to live safely, comfortably and with confidence.
● A society served by ubiquitous networks, and building a High-Speed, Highly Reliable Information Communication System for the creation of a world market
Society demands that Japan swiftly return research results to society and to the economy by constructing a “high-speed, highly reliable information communication system” with unified hardware and software and strong cooperation among industry, academia, and government ahead of the rest of the world, centered around superior technologies (information appliances, mobile, optical, device technologies, etc.).
For specific research and development topics, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is engaged in “R&D on ubiquitous network technologies,” involving research and development into technologies for real-time verification from extremely large numbers of terminals, and into technologies for the control of network channels.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting the “R&D project for Basic Technology Supporting Safe Ubiquitous Society,” established to conduct research and development on the following basic technologies supporting an ubiquitous environment that allows people to exchange information safely and with peace of mind: electronic tags equipped with security functions of higher performance and larger capacity; and built-in basic software that ensures safety.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is engaged in the “business grid computing project,” which aims for the development of infrastructure software allowing multiple network-linked computers or memory devices to function as if they were a single computer, toward the realization of the goal of a highly reliable, safe-to-use social IT infrastructure.
● Information and communication technologies that lead to next-generation breakthroughs and the seeds of new industries
Society demands the promotion of research and development into advanced information and communication technologies carried out in cooperation with interdisciplinary sectors, like next-generation human interface technologies, next-generation information and communication technologies that make use of quantum engineering and other new principles and technologies, such as space development (communications),nanotechnology, and bioinformatics.
In order to exceed the limit of existing supercomputing technologies, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting the “R&D Project for Elemental Technologies for Future Supercomputing” to conduct research and development on basic technologies that relate to hardware with large spillover effects and that require future breakthroughs.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting a variety of projects such as: the “Project for the Practical Application of Next-Generation Robots” to conduct demonstration tests, at the 2005 World Expo Aichi, on nine types of robots (project for promoting the development of practical systems) and 65 types of prototype robots (project for promoting the development of prototypes) in areas of living and welfare; the “Project for Practical Application of Human Support Robots” to implement the development and demonstration testing of technologies for the practical application of robots, which are designed to serve a specific person and are required to have high-level safety and operative flexibility; and the “Project for the Development of a Common Basis for Next-generation Robots” to develop a common interface connecting parts and systems with the aim to expand the robotics industry through the modularity of basic parts that is essential to develop robots efficiently.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport plan to work together, in cooperation with the private sector, to conduct research and development on a quasi-zenith satellite system that will be able to provide highly accurate positioning services to virtually 100% of the country without being affected by narrow mountain valleys or tall buildings.
● Infrastructure technologies for research and development
Society demands the development of science and technology databases, an area in which Japan lags behind Europe and North America, the development and equipment of technologies for supercomputer net-works, and virtual research institutes that allow joint research over long distances by linking research institutions with universities via high-speed net-works.
In the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, specific research and development topics being carried out include the “R&D Project for Innovative Simulation Software,” which involves the research and development of world-class multiscale multiphysics simulation software that enables the development of drugs tailored to individual differences with the use of the Earth Simulator(Notes 10) and other ultra-high speed computers.
The main research topics in the information and communications sector during Fiscal 2005 are as shown in Table 3-2-2.
Notes 10:
The Earth Simulator, a supercomputer owned by the JAMSTEC’s
Earth Simulator Center, is able to simulate global climate and the mechanism
of crustal movements.
Table3-2-2 Major research subjects in the information and communications sector (FY2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | National Institute of Information and Communications Technology |
Research and development for Sophisticated Use of RFID Research and development on ubiquitous sensor network technologies Research and development on the next generation of image contents production and distribution support technology Promotion of transition to Internet IPv6 Research and development into Asian broadband satellite infrastructure technologies Comprehensive research and development into network human interface technologies R&D on time-stamping platform technologies Promotion of research and development into information security measures Comprehensive support for the development of electrical communication systems that form the foundation for the merger of communication and broadcasting services Research and development into quantum information communication technologies Research and development of photonic network technologies Comprehensive research and development of IPv6 for (digital) Information consumer electronics, etc. |
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Universities, Japan Science and Technology Agency, National Institute for Materials Science, RIKEN (the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research), Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (Japan Atomic Energy Agency), National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, National Institute of Informatics, etc. |
Research and development project for innovative simulation software Research and development project of fundamental technology for supporting a safe ubiquitous society Establishment of software technology infrastructure to support electronic storage and utilization of intellectual assets National Research Grid Initiative (NAREGI) Comprehensive software development for e-Society infrastructure Priority research and development project for realization of the world's most advanced IT nation e-Science realization project |
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Agriculture and Bio-oriented Research Organization, etc. |
|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry | New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization, Information Technology Promotion Agency, etc. |
Semiconductor application chip project Business grid computing project Development of an Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) exposure system Digital information device interoperability infrastructure project Development of efficient organic device technology Development of photonic network technology, etc. |
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Engineering Affairs Division, Minister's Secretariat National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management |
Development of circulation analysis technology for urban space utilizing four dimensional GIS data |
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport |
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency New Energy and Industrial Development Organization |
|
3.2.2.3 Environment
The field of the environment is an essential area of science for the preservation of the natural environment, including ecological systems with their diverse forms of life, for the maintenance of human health and the preservation of the living environment, and for maintaining the foundations for the future survival of mankind. At present, there is an increasing need for efforts in science and technology to resolve global environmental problems, and Japan is actively moving ahead in this area, through the research and development projects detailed below.
(1) Research into Earth Observation and Change Forecasts, and Other Solutions for Global Environmental Problems
In recent years, global warming and other globalscale environmental issues have become imminent, and these issues urgently require international cooperation in their resolution.
In response to the “science and technology for sustainable development” action plan agreement reached in June 2003 at the G8 Evian Summit in France, the First Earth Observation Summit was held in the United States in July 2003.Following that, the Second Earth Observation Summit was held in Tokyo in April 2004, and a framework for a 10-year implementation plan for the establishment of Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) was adopted with the participation of 43 countries. Based on those results, the 10-year implementation plan was adopted at the Third Earth Observation Summit in Belgium in February 2005.
In regards to global warming issues, the Kyoto Protocol, which incorporated commitments to reduce the amount of greenhouse gas emissions in advanced nations and other countries, went into effect in February 2005. In December 2004, the Tenth Conference of Parties to the Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP 10) was held in Argentina to give consideration to the steady introduction of the Implementation Plan for the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS).
● R&D and related measures for understanding phenomena on a global scale
Since phenomena relating to global environment problems go beyond national borders, global cooperation is crucial in promoting research and development. Therefore, Japanese researchers are participants in the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP), and other international research programs, continuing to advance joint research.
Promoting the international sharing of global observation information is important for the elucidation of various global-scale phenomena. Japan hosted the Second Earth Observation Summit in April 2004, and is an active participant in and contributor to the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) and the Integrated Global Observing Strategy Partnership (IGOS-P).
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting research and development into the highly trustworthy projection of global change using the “Earth Simulator” system, one of the world’s fastest supercomputers. The “Earth Simulator” won the “Global 100 Eco-Tech Award” at the 2005 World Expo Aichi, as a “technology for new development” which greatly contributes to resolving global environment problems and benefits the 21st century. As research and development using the “Earth Simulator,” the ministry implemented the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which provides scientific information regarding climate change and the “Project for Sustainable Coexistence of Humans, Nature and the Earth,” which aims to achieve high-precision predictions of global warming that will contribute to the Fourth Assessment Report (AR4) and the forecast of water resources and water-based disasters in the future. In addition to contributing to the 10-year implementation plan prepared by the Earth Observation Summit, the ministry established the Earth Observation Promotion Committee under the Council for Science and Technology, in accordance with the Basic Strategy for Efforts Regarding Future Earth Observation (December 2004).
The Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology is promoting research on global environment prediction, including climate variation research, hydrological cycle research, global warming research, atmospheric composition research, ecosystem change research, and integrated modeling. In addition, regarding research on global environment observation, the agency is promoting observation of climate change, observation of the hydrological cycle, observation of global warming and observation of ocean general circulation. Moreover, research cooperation with the United States is carried out at the International Pacific Research Center (IPRC) located at the University of Hawaii, and the International Arctic Research Center (IARC) at the University of Alaska.
The Japan Science and Technology Agency’s Basic Research Programs promote research and development related to the “Mechanism of Global Change” and “Hydrological System Modeling and Water Resources System.”
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications’ National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) is currently engaged in international joint research with the United States, primarily with the University of Alaska, within the framework of the Japan-U.S. Science and Technology Cooperation Agreement, to promote comprehensive research into technologies for the observation and measurement of the arctic atmosphere.
Japanese Antarctic Research Programs are centered at the National Institute of Polar Research, affiliated to the Headquarters for the Japanese Antarctic Research Expedition (JARE) (Chairman: Minister of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)), and are operated in cooperation with relevant government agencies. In Fiscal 2005, the 46th winter expedition and the 47th expedition carried out routine observations of ocean and atmospheric phenomena around Showa Station, and also performed monitoring observations, etc., for the purpose of bringing to light environmental changes on a global scale. In January 2006, they conducted ice sheet excavation activities at Dome Fuji Station and succeeded in collecting ice cores from a depth of about 3,029 meters.
● Earth Observation Technology Using Satellites
Satellite-based observation of the Earth is an extremely effective method for repeated and continuous acquisition of varied information covering wide areas. Japan is currently engaged in comprehensive promotion of this activity toward the resolution of global environmental problems, in cooperation with related organizations in Japan and abroad.
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) is promoting the development of a Superconducting Submillimeter Wave Limb Emission Sounder (SMILES) mounted on the exposed facility of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM; also known as “Kibo”) on the International Space Station. NICT is also studying technology to enable the measurement of global environmental changes from space.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) processes the data collected from a Precipitation Radar (PR) mounted on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS (AMSR-E) mounted on the NASA Earth Observing System (EOS) Aqua satellite and other satellites to provide the data for researchers and users. JAXA launched the Advanced Land Observation Satellite “DAICHI” (ALOS) in January this year and plans to begin routine operation of the satellite in September. JAXA is also developing, in cooperation with relevant agencies, the Greenhouse Gas Observing Satellite (GOSAT), the Global Precipitation Measurement/Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (GPM/DPR), and the Global Change Observation Mission (GCOM).
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is currently engaged in joint operations with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency for the operation of the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflectance (ASTER) radiometer, a resource exploration sensor mounted on the NASA global observation satellite (Terra), and for the development of the next-generation Phased Array Type L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR), to be mounted on ALOS. It is also engaged in the development of the ground-based processing and analysis technologies required for the observation data obtained from the satellite sensors.
The Japan Meteorological Agency procured the Multi-functional Transport Satellite (MTSAT-1R) and launched it on February 26, 2005, as a follow-on satellite to the Geostationary Meteorological Satellite-5 (GMS-5).
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries has created a database of imaging data obtained from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) mounted on Terra and Aqua NASA global observing satellites, and has made it available on the Internet.
The Ministry of the Environment is using valuable observation data on the ozone layer and other phenomena obtained from the Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer-Ⅱ (ILAS-Ⅱ) mounted on “MidoriⅡ” (ADEOS-Ⅱ) to promote observation, monitoring, and research of the global environment, and is cooperating with JAXA and the National Institute for Environmental Studies for development of the greenhouse gas monitoring sensor mounted on GOSAT.
To promote the use of the data obtained in this way from satellites, JAXA’s Earth Observation Research and Application Center is promoting the development and operation of satellite data information systems that promote the use of satellite data in Earth observations, disaster monitoring, resource management, etc., the mutual utilization of data, and research into data analysis and utilization. Furthermore, the agency uses a web page to publish satellite data, etc., to deepen peoples’ understanding of the current status of the global environment.
● Ocean observation technology
The oceans occupy about 70% of the Earth’s surface, and are strongly related to many global-scale phenomena on earth, so that the elucidation of the roles that they play is an important issue. To advance knowledge in this area, the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology promoted research and development into ocean observation technologies, including the next-generation JAMSTEC-Compact Arctic Drifter (J-CAD) and Argo float for establishing a global ocean intermediate water observation system.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications developed an extended-range marine radar, which realizes continuous long-term observation of the flow field of the Kuroshio Current, etc. at the shore at the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, and started observing the flow field of Kuroshio Current in the south of the East China Sea by installing the radars at Ishigaki Island and Yonaguni Island.
To observe the global ocean in real time, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport have been engaged in the development of an Advanced Ocean Observing System (Japan ARGO(Notes 11)). In this project, an array of 3,000 mid-depth floats are being deployed with international cooperation all around the world to measure temperature and salinity to an ocean depth of 2,000m.
In addition, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting research on the mechanism for CO2 circulation in the Pacific Ocean.
The Ministry of the Environment is promoting research into the utilization of satellite remote sensing technology, a special method for monitoring the ocean environment, as a part of the Northwest Pacific Regional Ocean Action Program (NOWPAP) promoted by the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) in the Sea of Japan and part of the Yellow Sea.
Notes 11:
ARGO is named after the ship of the Greek mythic hero
Jason, which is the name of the related earth observation satellites series.
● Technology development to restrain the emission of carbon dioxide accompanying energy use
Carbon dioxide accompanying energy use accounts for about 90% of the total emission of greenhouse gases that cause global warming. Therefore, it is necessary to develop, practically apply, introduce and disseminate technologies for restraining the emission of carbon dioxide.
In Fiscal 2004 the Ministry of the Environment started promoting development for practical application of basic mitigation techniques and development of mitigation techniques that can be commercialized in a short period of time.
Incidentally, the major research subjects conducted during Fiscal 2005 are as shown in Table 3-2-3.
Table 3-2-3 Elucidation of various global-scale phenomena, and major research topics in the earth sciences and technology sector (FY2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | National Institute of Information and Communications Technology |
International joint research on advanced electromagnetic technology for the global environment Research and development of technologies for the measurement of subtropical Earth environments Research on global environment measurement and forecasting technology, using 3-D high-resolution imaging radar Research of prediction techniques Promotion of international information networks for conservation of the Earth's environment |
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology |
Aeolian dust experiment on climate impact International research project on the interaction between the sub-vent biosphere and geo-environment Unzen Volcano: International cooperative research with scientific drilling for understanding eruption mechanisms and magmatic activity |
| National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention |
Study on extreme weather events and water-related disasters due to Climatic Change Research on earthquake and volcanic eruptions |
|
| National Universities and Other Institutions |
International cooperative research project on the arctic environment Academic research into earthquake and volcanic eruption prediction systems |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences |
Assessment and mitigation techniques of global warming effects on the agriculture, forestry and fisheries sector |
| National Institute for Rural Engineering, National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute |
Assessment of the impact of global-scale change in water cycles on food production and alternative policy scenarios |
|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry | National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology |
Evaluation of long-term carbon dioxide absorption, based on the analysis of intermediate- and deep-ocean water in the Pacific Ocean |
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department, Japan Coast Guard |
As part of activities of Hydrographic and Oceanographic department, comprehensive ocean research in jurisdictional sea areas, marine geodesy using satellites, geomorphological and geological surveys of sea bottoms for the detection of volcanic eruptions, and observations of water temperatures, ocean currents, waves, and other aspects of the Western Pacific ocean region |
| Meteorological Research Institute, Japan Meteorological Agency |
Comprehensive projection of climatic change around Japan due to global warming Development and improvement of a materials circulation model and research on assessment of the effect on the global environment Observational study of radiative process in the atmosphere |
|
| Geographical Survey Institute |
Study on geodynamics using precise Earth measurement technology Plate motion and deformation in the East-Asia and Pacific region Technical development of precise determination of the geoid and the gravity field variations in the Northwest Pacific from dedicated satellite gravity data |
|
| Port and Airport Research Institute |
Use of tide-level observation to monitor rising sea levels Research into the change of characteristics for the occurrence of high water due to global warming |
|
| National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management |
Research into supporting technology for energy conservation with better performance of existing residences |
|
| Ministry of the Environment | Global Environment Research Fund |
Development of greenhouse gas sink and source control technologies, through the utilization and preservation of land ecological systems -- mid- and long-term policies toward the stabilization of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Research into the maintenance of sustainable national territories for island nations formed from coral atolls Elucidation of the dynamics of global-scale ocean pollution caused by toxic substances, and research into their prediction Research into gene migration due to the release of gene recombinant organisms, and evaluation of the impact on biological diversity Integrated study for the terrestrial carbon management of Asia in the 21st century based on scientific advancements Research on the explanation of long-term trends, and prediction of future change ozone layer Comprehensive assessment of climate change impacts to determine the dangerous levels of global warming and the appropriate stabilization target of atmospheric greenhouse gas concentration Study on the process of the transport and transformation of aerosols and their precursors from Asian Continent |
| Global Environment Research Coordination System |
Research into the mechanisms for the carbon dioxide cycle in ocean surface layers, using radioactive nuclides as multi-tracers Evaluation of the impact of carbon dioxide marine isolation on the ocean material cycling process |
|
| Technology Development Program for Mitigating Global Warming (competitive funding) |
Development toward practical application of basic technology to restrain emission of carbon dioxide |
|
| Open-Type Project to Subsidize Development of Technologies Directly Connected to the Marketing of Competitive Global Warming Mitigation Measures |
Development of technologies to restrain emission of carbon dioxide, which can be commercialized in a short period of time |
(2) Research into Building a Sound Material-Cycle Society
In order to secure sustainable growth of Japan’s economy and society in the future, it is absolutely essential to carry out research and development for creating a sound material-cycle society that promotes the 3Rs through effective utilization of resources and restriction of the generation of wastes, etc.
Efforts for the utilization of biomass will be improved in accordance with the Biomass Nippon General Strategy (decided by the Cabinet in December 2002).
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is currently engaged in the “The Project to Design a Sustainable Management and Recycling System for Biomass, General and Industrial Wastes,” a tie-up between industry, academia, and government for the promotion of the detoxification disposal or recycling of wastes, and also for research and development into the impact and safety assessments and design of social systems, to encourage the commercialization and dissemination of recycling.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is working on automobile recycling measures, measures for articles difficult to recycle, and development of technologies for construction materials recycling measures, and is also implementing practical application support projects to disseminate these technologies and develop an intellectual basis for surveys concerning dissemination of recycle technologies and recycled products.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is promoting the development of recycling and utilization technologies for biomass, the development of system technologies for the efficient recycling and utilization of local biomass resources, and the development of new energy production technologies that utilize organic resources in place of fossil fuels. In addition, the ministry started development of technologies to reduce production costs for biomass plastic in Fiscal 2004. Furthermore, the ministry is engaged in the development of technologies for the sorting and transport of recycled foodstuffs, an area that has long been a bottleneck, preventing the promotion of foodstuff recycling, as well as the development of reproduction and conversion technologies, and of constituent and quality evaluation technologies, needed for the promotion of advanced uses.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport is promoting the development of new geo-materials made from various wastes, and research into the applications of these to port and harbor facilities, the development of methods for strategic stock management of housing and social infrastructure capital, the development of technologies for the restricting and recycling of wastes generated during construction projects, the formation of logistic systems that promote the utilization of recycled resources, and research into the recovery of biomass from sewer sludge, livestock manure, etc.
The Ministry of the Environment is carrying out the research and development of processing technologies for the detoxification of toxic chemical substances generated in the course of waste processing, of technologies for the safe recycling of plastics, etc., and technologies for the proper management of final disposal sites, research into elucidation of the mechanisms for the generation of micro-pollutants at waste disposal facilities, etc. and control of their emissions, as well as research on the control of risks attendant with micro-pollutants. In addition, the ministry is promoting research for the establishment of a sound material-cycle society, including assessment of social systems to promote formation of a sound material-cycle society, ideal cost burden, studies on promotion methods, and research into recycling and reduction in waste generation.
The Fire and Disaster Management Agency of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is implementing research and study on safety measures for fire prevention in relation to the utilization of biomass energy.
The major research subjects conducted during Fiscal 2005 are as shown in Table 3-2-4.
Table 3-2-4 Major research subjects for building a recycling-oriented society (FY2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology |
Development of an integrated urban liquid and solid waste treatment system incorporating technologies for transforming kitchen garbage to biodegradable plastics |
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Agriculture and Bio-oriented Research Organization, Private sector, universities, etc. |
Development of new technology for the treatment and local recycling of biomass Development of technology for assessments of and countermeasures for effects on agriculture, forestry, and fisheries by global warming Development of technology for reducing the production cost of biomass plastics |
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry | New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization, Private sector, universities, etc. |
Development of fundamental technologies for manufacturing environmentally harmonious hyperfine steel particles Development of technologies for the detoxification and materials recycling of aluminum impurities Development of recycling technology for iron and plastic compounds, using an electric furnace technology Development of maintenance technology for extending the life of structures Support of 3R for practical uses (Request for Proposal) |
| National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology |
Development of reduction technology for the final disposal amount in urban areas Development of chemical products and production technology from biomass Research on evaluation design for environment-conscious local measures Development of production technology for biomass liquid fuel |
|
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Technology Research Division, Minister's Secretariat |
Development of housing and urban infrastructure management technology for sustainable society and safe environment Development of management technology for infrastructure and building stocks Development of evaluation method and technical measures of environmental impact throughout a building's life cycle |
| National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management |
Research recycling systems for construction waste reduction |
|
| Public Works Research Institute |
Research into social infrastructure development using new materials, unutilized materials, and recycled materials Research into technology for effective utilization of plant waste materials as green materials Study on technology for the exploitation of resources and the recycling of organic waste materials utilizing sewage sludge Study on a method for efficient use focused on inorganic characteristics of sewage sludge ash |
|
| Building Research Institute |
Research and development into the effective utilization of existing buildings Quality management of structural recycled coarse aggregate from river sands and gravel as the original material, and study on blend and quality evaluation of concrete using the recycled coarse aggregate Development of production technology for reprocessed shaft materials from wooden buildings and evaluation technology for performance |
|
| National Maritime Research Institute |
Research on application of environmental label to ships using method of life-cycle-assessment (LCA) Development of systems to evaluate and rate ship's life cycle value (LCV) |
|
| Port and Airport Research Institute |
Research into recycling technology in coastal areas Research into life cycle management (LCM) of facilities for harbors, airports, etc. |
|
| Civil Engineering Research Institute of Hokkaido |
Experimental study on developing a regional system of biogas-derived hydrogen energy supply, including the technology for such a system |
|
| Ministry of the Environment | National Institute for Environmental Studies |
Evaluation of policies for the promotion of resource recycling from the lifestyle perspective Research into methods for the analysis of recycling systems' local adaptability |
| Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research of waste disposal, etc. |
Study on construction of systems for optimal resource recycling in the region |
(3) Research Related to Building a Society that Co-Exists with Nature, Research Related to the Comprehensive Management of Chemical Substances, and Research Related to Other Sectors
● Research and development related tobiological diversity
With the extinction of wildlife species proceeding at a speed never seen before, the “Convention on Biological Diversity,” which is aimed at conserving the diversity of living things on Earth and their habitats and conducting sustainable use of biological resources, and the National Strategy of Japan on Biological Diversity, which is based on the said convention, call for the promotion of basic surveys for the purpose of scientific and objective data collection and facilitation regarding the current state of the natural environment and how it is evolving over time, the expansion of ecological and taxonomic knowledge of living things, and basic research for the purpose of elucidating the structure and maintenance mechanisms of ecosystems.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) is participating in the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), which is an international scientific cooperation project. The aim of this project is to distribute biodiversity data scattered in countries and utilize it worldwide via the Internet. MEXT is now advancing the creation of a biodiversity online database in Japan as part of the project.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is promoting research into the development of biofunction-based technologies for reducing the burden on the environment, the analyses of the mechanisms that enable plants to resist environmental stress, and research and development of technologies that encourage human coexistence with wild animals and birds, while reducing their damage to agriculture and forestry.
The Ministry of the Environment is promoting research into the prediction of and countermeasures against the effects of a decrease in biodiversity, by using the Global Environment Research Fund.
● Research and development related to antipollution measures
In the area of pollution prevention, the government is promoting the priority of research and development that utilizes pollution prevention testing and research funding. In recent years, in order to contribute to measures for mitigating environmental risks posed by chemical substances such as dioxins and endocrine disrupters, the relevant ministries and agencies are currently actively engaged in surveys, research and development, and establishment of an intellectual basis, including the development of methods for testing and measuring these substances and the collection and provision of information on chemical substances.
In the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Japan Science and Technology Agency is promoting research and development into endocrine disruptors in its Basic Research Programs.
● Other
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is promoting research into an international information network technology for the protection of the global environment, to facilitate the effective distribution of global environmental data.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is promoting research into assessment methods based on environmental accounting systems, in order to enable the comprehensive evaluation of agriculture’s diverse functions, and of the positive and negative influence on the environment, and is also engaged in the development of nature-friendly control technologies for the hydrological cycle, and for agricultural, forestry, and fishery ecologies in drainage basins, to encourage agriculture, forestry, and fisheries industries that co-exist with nature.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport is promoting the development of drainage basin restoration and recovery technologies that take the entire drainage basin into account for comprehensive hydrologic cycle management, as well as the development of land and infrastructure technologies offering co-existence with nature.
The Ministry of the Environment is promoting research into the design and presentation of scenarios for coexistence with nature in major cities and drainage basins, in relation to the “topic of technologies for the rejuvenation of drainage basins and major cities that are co-existent with nature” funded by the Environmental Technology Development Fund.
Incidentally, major research subjects conducted during Fiscal 2005 are as shown in Table 3-2-5.
Table 3-2-5 Major research subjects for research related to building a society that co-exists with nature, research related to the comprehensive management of chemical substances, and research related to other sectors (FY 2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute |
Development of flue-gas radiation treatment |
| Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare | Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants |
Research into the safety and health effects, etc., of dioxins and other microscopic chemical substances, and of microorganisms |
| Research Project on Health Science |
Research on water purification/pipeline technology that contributes to the formation of a circulation system of safe water |
|
| Research Fee for Water Supply Facility Improvement Project |
Consideration of projects and measures that contribute to the conservation of water supply sources |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, National Institute for Rural Engineering, Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute, and others |
Development of comprehensive management system of hazardous chemicals in agricultural, forestry and fisheries ecosystem Development of technologies for the management of agricultural and forest ecologies to reduce damage to agriculture and forestry by wild animals and birds Development of symbiotic management technology of water circulation/agricultural, forestry and fisheries ecosystem in the basin zone |
| Project for the Development of the Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries Industry, Foodstuffs Industry, and Other Advanced Industrial Technologies |
Development of technology for recycling-based use of marine resources using advanced technology Development of low-cost basic technologies for the production of organic fertilizers, etc. |
|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry |
Environmental technology development Development of technology for CO2 fixation and effective utilization Development of environmentally friendly processing technology Development of materials that put low stress on the environment Development of environmentally friendly recycling technology |
|
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Technology Research Division, Minister's Secretariat |
Development of thermal environment evaluation and countermeasure technologies for urban space |
| National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management |
Study on risk evaluation of chemical substances in water environment Wetland restoration project for urban area Proper reuse of treated wastewater Research on the influence of soil and groundwater contamination on the watersheds Strategic planning and adaptive management on environment restoration in coastal zone |
|
| Geographical Survey Institute |
Geoecological research and survey using airborne LIDAR data- Case study in Shirakami Mountains |
|
| Public Works Research Institute |
Research on evaluating water quality risks Research on techniques for conserving the ground environment Research on comprehensive hydrologic models for rivers Research on techniques for controlling water quality and soil at dam reservoirs and in the downstream sections of rivers Research on techniques for controlling water quality and soil at dam reservoirs and downstream sections of rivers Research on techniques for treating bottom sediment in enclosed water areas Research on evaluating heat island phenomena reduction alternatives |
|
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Building Research Institute |
Improvement on quantification of the intensity of pollutant emission and air ventilation methods for indoor air Research on aquatic conservation technology through high-grade combined treatment of existing individual sewage treatment tanks Development of symbiosis technology between humans, cities, and nature |
| National Maritime Research Institute |
Research on systems to injection carbon dioxide on sea for carbon dioxide sequestration in deep waters Research on technologies for reducing environment adverse effects from ships Japan-France joint research on detection of oil spills, etc. using fluorescence radar Research on technologies to observe marine pollutants in heavy weather Research on risk assessment method for elucidating environmental adverse effects from ship's anti-fouling substances |
|
| Port and Airport Research Institute |
Research on the assessment of the effect of toxic chemical substances in the coastal area and measures to mitigate those effects Research on oil-spill cleanup technology for the coastal area Comprehensive environmental monitoring of the Tokyo Bay and research on the environmental forecasting model |
|
| Ministry of the Environment | Global Environment Research Fund |
Research into the selection of coral reef biodiversity preservation districts The study for methods and measures of invasive alien species risk assessment |
| Environmental Technology Development Fund |
Research into the restoration of hydro and material cycles that co-exist with nature in cities and drainage basins, and the development of ecology evaluation standards Research into the development of methods for diagnosing the degradation of multidimensional functions in natural drainage basin environments, and of integrated modeling for the effective evaluation of the soundness of restoration policies |
|
| Research Funding for the National Research Institute engaged in Environmental PollutionResearch |
Theoretical research for appropriate lake utilization that takes the mutual interactions of life-forms into account, toward integrated protection of lakes |
|
| Survey and Research Funds for the National Organization for Pollution Prevention |
Research into elucidation of changes and behavior in the natural environments of world natural heritage districts |
|
| National Institute for Environmental Studies |
Research into the evaluation of technologies for natural restorations of marshland ecologies Assessment of the possibility of recovering the marshy ecosystem by the re-routing of rivers flowing into the Kushiro Wetlands Assessment of the lake environment based on organic linkage and preparation of a scenario for improvement |
3.2.2.4 Nanotechnology and Materials
Nanotechnology and materials are key technologies for rapid developments over a wide range of scientific and technological areas. Nanotechnology is expected to become a major support element of all science and technology fields in the 21st century, and to lead to a new industrial revolution in the 21st century.
(1) Materials Fields
Based on the “Basic Strategy for Promotion of the Nanotechnology and Materials Sectors in the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (interim report)” prepared by the Council for Science and Technology (Subdivision on Research and Development Planning and Evaluation)” in June 2002, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology generally and widely promotes basic and fundamental R&D for materials science and technology, including “structural materials for the 21st century” and “superconducting materials.” Research into materials science and technology is also being promoted through the administration of the “Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology,” and other similar programs including “Creative Research for Evaluation Science and Technology Program of the Japan Science and Technology Corporation (JST)”, and the Frontier Research System, at RIKEN. The ministry is also encouraging the development of creative and advanced materials research at universities and independent administrative entities, as well as providing the “Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research Program” for basic research into materials science and technology, in order to promote creative science research at universities and in others, so that they can serve as sources of free imagination and research inspiration for researchers.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is using “Insect Technology Research for Utilization of the Greatest Unused Resources of the 21st Century” to engage in research and development for the wider utilization of biomaterials such as fibroin, a silk protein, as a new material with active anti-thrombosis properties, or the development of materials utilizing the compound capabilities of the bone constituents of silk to form artificial bone or artificial ligaments.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting the Program to Create an Innovative Components Industry to strengthen the international industrial competitiveness of Japan while sufficiently using the functions and characteristics of substances to establish a high-value added material industry that creates new markets and employment. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry implemented the Project for Developing Manufacturing Process Technology for Advanced Titanium Alloy, which aims to develop innovative technology for manufacturing processes in which material creation technology and processing technology are integrated, the Production, Analysis and Measurement System for Microchemical Technology Project, which aims to speed up the process from the research and development stage to the production stage, and the Next-Generation Semiconductor Nanomaterials Advanced Evaluation Project, which aims to achieve efficient searching for the optimum combination of multiple materials.
(2) Nanotechnology
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is engaged in the research and development of optical functional devices and information memory elements, etc., as basic research on information communications. In addition, under the “Strategic Information and Communications R&D Promotion Programme,” the ministry started the Research and Development on Ultrahigh-Functional Network Technology Utilizing Nanotechnology in Fiscal 2003 as well as promoting research and development on new information and communications functions and device technologies. Moreover, the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology is promoting Research and Development of New Functions and Extreme Technologies, and thereby implementing basic research into ultra-compact, ultra-high speed, and ultra-low power consumption information and communications devices, including the development of optical devices for the high-speed control and processing of large-capacity signals.The Fire and Disaster Management Agency of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is promoting development of methods of assessing corrosion and deterioration for dangerous facilities, and preparing the necessary databases for creating an environment for developing and introducing methods of assessing corrosion and deterioration for dangerous facilities.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has established research centers and a research system of the industry-academi a-government cooperation in order to promote research and development of novel interdisciplinary fields based on nanotechnology and materials expected for technical innovation. In addition, the ministry is promoting, in its R&D projects (Leading Project) for economic revitalization, the “development of artificial organs and artificial sense organs using nanotechnology,” the “development of nano measurement and processing technology,” etc., through cooperation between industry and academia in sectors where the life sciences, information and communications, environment, and energy sectors merge together, and in technologies in which they share common foundations. In addition, the “Nanotechnology Comprehensive Support Project” provides broad, cross-cutting and integrated support that goes beyond the bounds of existing research institutions and sectors, such as fostering human resources through seminars and international exchanges of young researchers, offering opportunities for the utilization of large and special facilities and equipment to outside researchers, collecting and publishing relevant information, and convening symposiums.
In addition, the Japan Science and Technology Agency implement the research and development of “virtual laboratories by nanotechnology field” from mid- and long-term viewpoints, in close cooperation with researchers by nanotechnology field” utilizing the Basic Research Programs.
The National Institute for Materials Science is engaged in the development of new materials for nano-devices, research into nano-scale materials for energy and environmental applications, and other nano-materials research. RIKEN is engaged in basic research, which will form the foundation of nano-science technology for future generations. This includes the measurement and control of nano-level properties and functions, simple quantum manipulation toward the development of new information processing devices, and space-time function materials for manufacturing auto-changing, auto-reacting materials, and materials that can change over time. Moreover, many universities and colleges and independent administrative institutions are engaged in basic research spanning a wide range of fields. Furthermore, various research funding support programs, including the ministry’s Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, and the “Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research Program,” are being used for nano-technology research themes.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is utilizing information about biological functions obtained at the molecular and cellular level, and cooperation from industry, academia and government, as well as from different technology fields, to promote the development of revolutionary new functional materials through the use of nano-level structural controls, the development of technologies for the utilization of innovative biological functions, and the construction of a micro-bioreactor..
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is also promoting the “Nanotechnology Materials Program” to establish the technological foundation that contributes to the sustainable economic development as a source of industrial competitiveness of Japan, through intensive development of “nanotechnology” that may bring about innovative development in the broad areas of industrial technologies, as a source of Japan’s industrial competitiveness. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry conducted the “research and development on nano-tech/advanced materials for practical use” to promote research and development conducted through cooperation with users by using innovative nanotechnology, for the purpose of developing devices for new materials that enable the creation of new industries, such as information appliances and fuel cells.
The Ministry of the Environment is implementing the development of environmental technologies that make use of the nanotechnology merits of miniaturization and improved function. In Fiscal 2005, the ministry started the development for thermoresponsive hydrophobic chromatography to reduce organic solvent waste.
The major research topics in the nanotechnology and materials science and technology sector con-ducted during Fiscal 2005 are shown in Table 3-2-6.
Table 3-2-6 Major research subjects in the nanotechnology and materials sectors (FY2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, etc. |
Research and development of ultra functional network utilizing nanotechnology Research and development on new functions and ultimate technologies |
| Fire and Disaster Management Agency |
Development of methods of assessing corrosion and deterioration of dangerous facilities |
|
| Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology | Special coordination funds for promoting science and technology |
Combinatorial computative chemistry for the revitalization of Japan Kyoto University personnel development unit for computative materials researchers Development of new crystal material for the terahertz range Use of nano-boundary control for the manufacture of magnetic recording materials Development of next-generation display media using self-organization of molecules Research and development into generation of high-polymer particles using micro-chemical reactors SNDM strong dielectric probe memory Development of SiO2 glass-metal slope function material as a light source Comprehensive research on nano devices for elucidation of the structures and functions of chromosomes Establishment of appraisal method of materials/tissues in tissue engineering Standardization of lithium-ion cells for storing electrical power Research study on promotion of the social receptivity of nanotechnology Formulation and fostering of human resources of human environment medical engineering through collaboration of medical science, dentistry, and engineering Nanomedicine fusion education unit Creation of glass photonic element with innovative functions Research on high-reliable boundary surface for ferroelectric memory Development of nano micell type siRNA delivery system Development strategy of an observation robot system for the Asian hydrosphere Supercritical hybrid QD imaging and treatment Development of original hole detection system and ultrasensitive biosensor using magnetic nanobeads |
| National Institute for Materials Science |
Development of novel materials for nano-devices Nanosynthesis and nanostructural materials for energy and environmental applications R&D of new superconducting materials High Temperature Materials 21 Project for the promotion of biological materials Ultra-Steel Products for New High Safety Infrastructures Combinatorial Materials Exploration and Technology (COMET) Development of virtual experimental platform for material design using computational science and technology Development of a carrier material for an innovative nano drug delivery system (DDS) |
|
| RIKEN (The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) |
Nano-scale science and technology Study on the genesis of matter Advanced technology research (physical science research) Material science research (Quantum Materials Research ) Spatio-Temporal Function Materials Research Single Quantum Dynamics Research Research on exotic particle beams Electron complex matter science research Extreme photonics research Development of high-sensitive poison gas detector using nanotechnology processed thin film |
|
| Japan Science and Technology Agency |
Creation of ultra-fast, ultra-power-saving high-performance nanodevice systems, creation of bio-elements and systems utilizing medical-oriented chemical and biological molecules, and other projects for the promotion of strategic creative research Project for the promotion of nano-space, spin superstructures, and other creative science and technology |
|
| New Century Priority Research Creation Plan (RR2002) |
Nanotechnology Researchers Network Center |
|
| Research and Development Project for Economic Revitalization (Leading Project) |
Development of measurement, analysis, and evaluation equipment leading to next-generation science and technology Development of artificial organs and artificial senses using nanotechnology Development of devices operating on new principles based on nanotechnology Commercialization of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light source technology and other advanced semiconductor manufacturing technologies Next-generation fuel cell project |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences |
”Insect technology project” in order to utilize the most untouched natural resources of the 21st century |
| National Food Research Institute |
Development of nanotechnology and materials technology for the innovative utilization of biological functions |
|
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport | Technology Research Division, Minister's secretariat |
Development of performance assessment method of novel structure buildings using innovative structural material such as high-tension steel, etc. |
| Policy Bureau |
Research on the reduction of the effects on the environment in the transportation field utilizing nanotechnology |
|
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry |
R&D of nanometry technology Precise macromolecule technology Nanometal technology Nano coating technology project Nano processing technology using a next generation quantum beam Development of low-temperature forming/integration technology of nano level electroceramics material Technology for creating a standard substance used for assessment of 3D nanometer Forming/processing technology of metallic glass Development project of semiconductor for efficient UV light-emitting device Development of ultra-pure metallic material for power-generating plants Development of ceramic reactors Creation/processing technical development project of high-tech titanium alloy R&D project of putting nanotechnology/tip material into practical use |
|
| Ministry of the Environment |
Environmental technology development and promotion operations utilizing nanotechnology |
3.2.2.5 Energy
The “Basic Energy Plan” (by the Cabinet in October 2003) based on the Basic Law on Energy Policy (enacted in June 2002) revealed the energy R&D policies meriting priority promotion for the long-term comprehensive, planned promotion of policies related to energy supply and demand. The Plan states that intensive effort should be made by the government to ensure a stable energy supply and to resolve environmental problems based on important political significance.
(1) Research, Development, and Utilization of Nuclear Energy
Research, development and utilization of nuclear energy in Japan have been carried out strictly for peaceful purposes, in accordance with the Atomic Energy Basic Law. The Atomic Energy Commission formulated the “Framework for Nuclear Energy Policy (hereinafter referred to as “the Framework”)” on October 11, 2005, and the Cabinet decided to respect the Framework on October 14 as a basic principle for nuclear energy policy and to promote research, development and utilization of nuclear science and engineering. In accordance with this decision, the government is steadily promoting research, development and utilization of nuclear energy.
Today, nuclear power generation plays an important role in energy supply as a major source of energy accounting for more than one-third of electric power supplies and also as an energy source that contributes to mitigating global warming. Moreover, accelerators and other achievements in atomic energy science and technology continue to provide new knowledge in basic science sectors, and offer essential research tools for the life science and nanotechnology and materials sectors. In addition, the use of radiation has spread to a wide range of sectors, including medicine, agriculture, manufacturing, and environmental protection. Thus, nuclear energy has greatly contributed to assuring stability in the nation’s energy supplies and improving the lives of the people.
Meanwhile, in regards to the atomic energy R&D structure in Japan, the “Reorganization and Rationalization Plan of Public Corporations,” adopted by the Cabinet in December 2001, called for abolition of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, and for their merger through the establishment of a new incorporated administrative agency for the comprehensive implementation of atomic energy research and development. In response to these, the Law for the Japan Nuclear Energy Research and Development Organization was enacted at the 161st extraordinary Diet session, and the ministry is currently engaged in promoting operations toward the establishment of the new entity in October 2005. In October 2005, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was established.
● Ensuring safety, and emergency preparedness
Safety is the indispensable prerequisite for the research, development, and utilization of nuclear energy. Enforcement of stringent regulations and safety management, and execution of safety research, are essential to ensuring safety. Moreover, in recognition of the impossibility of eliminating the occurrence of accidents to 0%, there is also a need to prepare countermeasures in the case of an accident to ensure that damage to the lives and health of local residents, etc., is held to the absolute minimum.
Because of these viewpoints, the government imposes stringent safety regulations on nuclear facilities in the design, construction, and operation stages of nuclear energy research, development and utilization, to a degree unseen in any other industrial sector in Japan. In addition to regulations, the government also has adopted various kinds of measures to ensure safety, such as environmental radiation monitoring and emergency preparedness.
Regarding the ensuring of safety at nuclear facilities, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and other related administrative organizations submitted a bill to the 162nd session of the Diet to amend the Law for Regulation of Nuclear Source Materials, Nuclear Fuel Materials, and Reactors, with the aim to strengthen the system to protect nuclear materials, introduce the clearance system(Notes 12) and enhance the regulation system concerning the dismantling and abolition of nuclear facilities. The bill was passed and approved in May 2005, and the amended law was enforced on December 1, 2005.
Regarding nuclear emergency countermeasures, efforts to expand and strengthen nuclear disaster measures are now being promoted based on the Special Law of Emergency Preparedness for Nuclear Disaster established in 1999, including the dispatch of the Senior Specialists for Nuclear Emergency Preparedness, designation of base facilities for emergency measures in urgent situations (off-site centers), etc., preparation of radiation measurement equipment and other necessary materials and equipment, preparation of disaster prevention plans for nuclear energy companies and implementation of emergency drills.
For surveys of environmental radiation, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and other relevant ministries and agencies, prefectural governments, and atomic energy enterprises continue to conduct radiation surveys in areas surrounding nuclear energy facilities. In addition, surveys of environmental radioactivity level in Japan are conducted, as well as radiation surveys of nuclear-powered military vessels when they enter port.
Enterprises engaged in handling radioactive materials reacted to the simultaneous multiple terrorist attacks that occurred in the United States in September 2001 by strengthening their controls of radioactive materials and reviewing their emergency communication procedures.
To introduce the international standard value (lower limit of the subject of regulations) set by the Interntional Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and streamline the regulations of radioactive isotopes along with their introduction, the Law for the Prevention of Radiation Sickness Caused by Radioactive Isotopes,(Notes 13) amended in 2004, was enforced in June 2005.
Also, in ensuring nuclear safety, it is important to promote safety research because serves as a technical basis for safety regulations, etc. To this end, the Nuclear Safety Commission is coordinating the “Five-Year Safety Research Program (Fiscal 2001 to Fiscal 2005)” and the “Priority Safety Research Program,” thereby promoting safety research on a well-planned basis. Specifically, the following safety research projects were conducted for each sector at research institutes.
In the area of safety research related to nuclear facilities, JAEA and other organizations conducted research on a variety of issues such as: improvement of probabilistic safety assessment methods; safety evaluation on high burn-up of fuel for light water reactors, soundness evaluation on highly aged equipment and structures; safety of criticality and confinement at nuclear fuel facilities; evaluation on accident prevention, mitigation, and evaluations in Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs).
For safety research related to environmental radiation, the National Institute of Radiological Sciences and other organizations conducted safety research on the dose evaluation of radiation exposure, as well as basic safety research into radiation effects.
Concerning safety research for radioactive waste management, safety research including near surface disposal and geological disposal, as well as clearance level verification technology, was conducted by JAEA and other organizations.
Notes 12:
Clearance: Excluding radioactive materials, of which
radiation level is sufficiently small compared to the radiation levels in the
natural world and of which effect on human health is negligible, from the subject
of regulations of radiation protection as “those which do not require treatment
as radioactive materials”
Notes 13:
The following amendments were made through amendments to the Law
for the Prevention of Radiation Sickness Caused by Radioactive Isotopes in 2004:
(1) creation of a system of design certification by the equipment
manufacturer
(2) rationalization of sales and leasing services from a license system
to a notification system
(3) creation of a regular confirmation system to improve the safety of
establishments
(4) creation of a regular training system to improve the ability of radiation
protection supervisors
(5) preparation of provisions concerning disposal of waste by burial.
● Efforts for assuring trust and coexistence with communities
In order to promote the smooth research, development, and utilization of nuclear energy, it is extremely important to obtain public confidence in the government and nuclear power operators. For this purpose, nuclear power operators must build up a record of safe operations, and strive to obtain public understanding. To this end, public hearings and public relations programs are being promoted to ensure two-way communication and transparency, as well as activities to further their understanding, such as support for education about nuclear energy or lending out simplified radiation detectors.
Furthermore, to promote coexistence between nuclear power research facilities and regions where there nuclear facilities located, the Power Source Grant program, of which use was expanded to non-construction projects, is being utilized in response to the needs of the regional communities.
● Nuclear power generation and the nuclear fuel cycle
1) Nuclear power generation
With nuclear power generation being an important energy source for ensuring stable energy supplies in Japan, and also a superior energy source in terms of protection of the global environment, since it emits no carbon dioxide or nitrogen oxides in the course of power generation, its research, development, and utilization is being steadily promoted, predicated on the assurance of safety and on peaceful utilization.
For the light water reactors that are the main form of nuclear reactor currently in use in Japan, the government, electrical power companies, manufacturers of atomic power equipment, etc., have been cooperating to improve working efficiency, and reduce employee exposure to radiation on the premise of securing the safety of light water reactors by Japan’s own technologies. In view of operational experiences to date, the parties have striven to make the lightwater reactor technology more economical, while maintaining high levels of reliability and safety.
2)Research and development of the nuclear fuel cycle
Japan, which must rely on imports for the vast majority of its energy resources, is steadily promoting efforts to establish the fuel cycle through effective utilization of the recovered plutonium, etc., from the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel, in order to secure long-term energy supply stability in view of the future energy supply and demand in the world, and to reduce the load on the environment. It is important, therefore, to continue to promote research and development on the nuclear fuel cycle, and to steadily develop the Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant, the plutonium utilization program in light water reactors, and the interim storage of spent fuel.
In promoting plutonium utilization, Japan strives to ensure the transparency of plutonium use by disclosure of information regarding plutonium inventories, not only from the viewpoint of rigorous management of nuclear materials, but also in clear observation of the principle of never holding excess plutonium that is not required to implement current programs, so as to avoid arousing international concerns regarding the proliferation of nuclear weapons. Specifically, Japan adopted international plutonium guidelines for improving the transparency of its plutonium use, and annually announces its plutonium management state through the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Concerning the enriched uranium used as fuel in nuclear power generation, Japan is promoting the development of domestic uranium enrichment projects to secure independence over the entire nuclear fuel cycle, and endeavoring to maintain economy.
While some reprocessing of spent fuel from nuclear power plants is conducted at JAEA’s Tokai Reprocessing Plant, most is consigned by contract to reprocessing by British Nuclear Fuel Limited (BNFL) and COGEMA, the French nuclear fuel company.
In view of the principle that spent fuel should be reprocessed domestically in Japan, construction is underway on a private-sector reprocessing facility (with an annual reprocessing capacity of 800 tons) in Rokkasho-mura, Aomori Prefecture, and a series of tests are currently underway toward a planned date of operation commencement of August 2007. The aim is the firm establishment of reprocessing technology on a commercial scale through the successful construction and operation of a private-sector reprocessing plant, toward the eventual establishment of the nuclear fuel cycle.
In this regard, the Tokai Reprocessing Plant, which had been reprocessing spent uranium fuel used in light water reactors under contracts with electrical power companies, completed this work in March 2006. As a result, about 1,100 tons were reprocessed in total.
Intermediate fuel storage is important as a means to provide flexibility for the whole nuclear fuel cycle because the time period until the fuel is reprocessed can be adjusted through the storage. A law concerning intermediate storage was enacted in 1999, and utility companies are preparing for the facilities to be commissioned by 2010. The “Fugen” advanced thermal reactor, which was undergoing independent development as a nuclear reactor with the ability to flexibly and efficiently utilize plutonium, recovered uranium, and other fuel, terminated its operations in March 2003, and the project ends as of 30 September 2003 with the completion of a report summing up the project results. The research and development necessary for decommissioning is now in progress.
3)Radioactive waste management
One of the most important issues from the viewpoint of executing coherent policies for the promotion of nuclear power utilization, and of obtaining the people’s understanding and trust, is the management of the disposal of radioactive waste, and the decommissioning of nuclear facilities. Since radioactive waste varies in radioactivity and the types of radioactive materials contained in it, radioactive waste is now classified not by its sources, but by its disposal methods, and specific measures are taken.
JAEA, acting as the core institution working in close cooperation with the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and university-affiliated research institutions, is now engaged in research and development on the disposal of high-level radioactive waste. In addition, JAEA is developing two underground research laboratory programs in Mizunami, Gifu Prefecture (crystalline rocks) and in Horonobe, Hokkaido Prefecture (sedimentary rocks) as key facilities for promoting its research and development.
Under the Law on Permanent Disposal of Special Radioactive Waste, enacted in May 2000, the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan was established as a waste disposal contractor in October of that year. In December 2002, as part of the process for selecting a disposal site, the organization invited municipalities from throughout Japan to consider volunteering as candidates for exploring the feasibility of it constructing disposal facilities in their area.
Low-level radioactive waste generated at nuclear power plants has been disposed of at the Japan Nuclear Fuel, Ltd.’s Low-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Center in Rokkashomura, Aomori Prefecture since December 1992, with about 36,400000-liter drums of waste already having been transferred to the center as of the end of January 2006.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry established the Nuclear Energy Division under the Electricity Business Subcommittee of the Comprehensive Investigation Committee on Resources and Energy in July 2005, and has been considering the preferable method of disposal of radioactive wastes (TRU wastes) including transuranic nuclide.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, in November 2005, established the Working Group on Radioisotope and Research Institute Wastes under the Panel for R&D on Nuclear Energy at the Research Planning/Evaluation Committee of the Council for Science and Technology, and has been considering specific candidates for disposal contractors.
With respect to regulation-related laws and ordinances, the “Law Concerning Prevention from Radiation Hazards due to Radioisotopes, etc.” was amended to add an article about near surface disposal of solidified radioisotope wastes in June 2004. In May 2005, the Law for Regulation of Nuclear Source Materials, Nuclear Fuel Materials, and Reactors was also amended to reinforce provisions concerning the introduction of the clearance system and the dismantling and abolition of nuclear facilities. In addition, ministerial ordinances related to the Law were amended, and the Law Concerning Prevention from Radiation Hazards due to Radioisotopes, etc., amended in June 2005, was enforced.
JAEA has continuously researched and developed decommissioning technologies of nuclear fuel cycle facilities including the “Fugen” reactor.
● Research and development of fast breeder reactors and related nuclear fuel cycle technology
FBRs and related nuclear fuel cycle technology can greatly boost the efficiency of uranium resource utilization. When this technology is put to practical use, it will become possible to continue using nuclear energy for several hundred years even if we only depend on the uranium resources known today to be technologically and economically utilizable. The use of FBR cycle technology could further reduce the environmental burden by minimizing longlived radioactivity in high-level radioactive wastes. In terms of preparation for assurance of an effective future energy option, development effort in this area is plainly important.
The “Monju” prototype fast breeder reactor uses technology based on MOX fuel and sodium cooling, the most advanced of the FBR cycle technologies, and it is the only fast breeder reactor plant with power generating capabilities in Japan. “Monju” is positioned in the Nuclear Energy Policy Outline as the core for Japan’s research and development into fast breeder reactor cycle technology
“Monju” ceased operations following a sodium leak accident in December 1995. In response to this situation, JAEA decided to implement plant modifications to increase safety toward resuming operations and obtained government approval. In February 2005, the agency obtained approval for the commencement of the plant modifications from Fukui Prefectural government and Tsuruga City municipal government, and has been implementing plant modifications since September 2005.
However, regarding an administrative suit initiated by the local residents to cancel the construction license of “Monju,” the Supreme Court of Japan dismissed the high court decision and ruled in favor of the government through the dismissal of the appeal of the plaintiffs in May, 2005.
In addition, since July 1999, JAEA has been collaborating with electric power companies to conduct a “Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems,” to propose, by around 2015, appropriate concepts for FBR cycle technology to be commercialized in the future and develop research and development plans toward its realization. In Phase Ⅱ (Fiscal 2001 to Fiscal 2005), the agency was engaged in research and development in order to improve safety and economic efficiency, to reduce the burden on the environment, and to clarify the commercialization candidates for fast breeder reactor cycles in consideration of nuclear nonproliferation. The agency announced the final results of Phase Ⅱ at the end of Fiscal 2005.
● Promotion of nuclear fusion research and development
Promotion of nuclear fusion research and the development of nuclear fusion are important because they expand available energy options for the future and increase the feasibility of fusion energy. In Japan, fusion research and development is promoted by JAEA, the National Institute for Fusion Science, and universities and colleges through mutual cooperation. In addition, bilateral and multilateral international cooperation is being actively promoted.
JAEA has been promoting R&D on a tokamaktype reactor(Notes 14) toward the realization of a practical reactor. In particular, JT-60 as large tokamak device has achieved significant results, which led the physicccs R&D toward the implementation of ITER(Notes 15), and demonstrated the feasibility of a steady-state fusion reactor. Further research is being promoted to achieve the long pulse operation of high pressure plasma through the improvement of plasma confinement performance.
The National Institute for Fusion Science constructed the large helical device(Notes 16) (LHD) that is based on a unique idea originating in Japan and is the largest helical device in the world. Its research into new plasma regions leads the world. In addition, the Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University, other universities and in-dependent administrative institutions, etc., are engaged in basic research into various magnetic confinement and inertial confinement methods, and in research into essential technologies related to reactor engineering The ITER project is an international cooperation project that aims to demonstrate the scientific and technological feasibility of nuclear fusion energy with the participation of Japan, China, the EU, South Korea, Russia, the United Sates and India. Japan promotes this project actively. After the ITER ministerial meeting, held in Moscow in June 2005, it was decided that the ITER site would be in Cadarache. The Director-General Nominee of the prospective ITER International Organization was appointed in November of the same year. In addition, inter-governmental talks for the establishment of the ITER International Organization were concluded at the vice-ministerial-level meeting held in Tokyo in April 2006, thus remarkable progress is being made toward the realization of the project.
When the construction site for the ITER facility was decided, it was also decided that the Broader Approach, a complementary R&D project to be conducted in parallel with the ITER project under the cooperation between EU and Japan, would be implemented and Japan would assume an important role along with EU, the host of the ITER project.
Notes 14:
The Tokamak-type reactor is a machine confining plasmas
by producing a donut-shaped magnetic field. It has a circular magnetic field
produced by external coils and confines plasmas in a stable manner by creating
a spiral magnetic field with the toroidal electric current. Research institutions
around the world have constructed and studied this type of plasma experimental
device for its excellent confinement performance.
Notes 15:
“ITER” means “(long) way” in Latin.
Notes 16:
Helical devices are different from tokamak devices which pass electric
current through plasmas. They confine plasmas with a donut-shaped spiral magnetic
field produced by external coils.
● Promotion of nuclear science and technology
Nuclear science and technology mainly contributes to two sides. One side is the application to basic and fundamental research using “quantum beam technology(Notes 17)” which is innovated by the technologies of accelerators and high intensity lasers. Quantum beam technology supports research on the basic principles of nature and gives new valuable knowledge and results in life science and material fields. The other side is research and development for offering options of stable energy supply in the future addressing needs of the economy, society, and consumers by the development of nuclear fusion and innovative nuclear reactors.
With respect to the quantum beam technology, JAEA and the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) have been jointly promoting the High Intensity Proton Accelerator Project (J-PARC(Notes 18) project), which aims at new developments over a wide range of research fields, including life science, material science, nuclear physics and elementary particle physics by generating and utilizing proton beams with the highest beam power in the world. The project was evaluated in August 2000 by the Advisory Committee on Evaluation of the High Intensity Proton Accelerator Project, which had been established under the Atomic Energy Commission and the Science Council’s Accelerator Science Subcommittee. In view of the evaluation results, the construction of accelerators laid down in the plan commenced in fiscal 2001 and the project is in progress towards the commissioning in fiscal 2008.
RIBF is the accelerator facility for generating beams of all types of radioactive isotopes (RI), from hydrogen to uranium, with the highest intensities in the world. To launch some experiments of the RI Beam Factory (RIBF) during fiscal 2006, RIKEN (The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research) is currently engaged in construction and development.
Moreover, basic research in nuclear science and technology creates the seeds that lead to diversification in nuclear power usage and future technological innovation, and contributes to research projects in the field of nuclear energy and the development of other science and technology sectors.
JAEA is making efforts to conduct fundamental research for the renewed development of nuclear energy, with advanced basic research into the science in radiation fields being conducted at the Advanced Science Research Center, the development of the X-ray laser and other advanced laser scientific research being conducted at the Kansai Research Establishment (in Kansai Science City,) and synchrotron radiation scientific research using a large synchrotron radiation facility (SPring-8) in Harima Science Park City, Hyogo Prefecture. Furthermore, national scientific research institutions under the control of each office and ministry are promoting cutting-edge basic research in the four areas of fundamental technology, i.e. substances and materials, biological and environmental effects, computation technologies, and disaster prevention and safety. In addition, the Nuclear Energy Fundamentals Crossover Research(Notes 19) is being conducted by organically combining the capabilities of incorporated administrative agencies, universities, national experimental research institutions and other research institutions through their active cooperation in research.
The outlook for the 21st century is for innovative new reactors with excellent economy and safety that are suited for thermal utilization and other diversified energy supplies, and to the spread of nuclear reactor use, as well as for the advent of innovative nuclear fuel cycle systems that can alleviate the problem of how to dispose of spent fuel and radioactive wastes and also improve the nonproliferation situation.
Beginning in Fiscal 2002, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has entertained various new ideas, using links between industry, academia, and government to perform research and development into public canvassing methods for selection between proposals related to innovative nuclear power technologies. Since Fiscal 2005, the ministry has been carrying out the R&D Project for the Nuclear Energy System Design using the competitive funding system.
Since Fiscal 2000, the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry has been conducting research and development for innovative, creative, and practical nuclear power technologies by inviting proposals, to ensure that there will be a variety of choices regarding future nuclear power generation and the nuclear fuel cycle.
JAEA has been conducting a rise to power test for the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to establish a high-temperature, gas-cooled reactor technology that explores the possibilities for diversification of energy supplies, such as high-temperature thermal supplies, and to promote research and development in hydrogen production and other heat utilization. In April 2004, JAERI succeeded in removing high-temperature gases of 950, which marked the highest temperature of an outlet of a nuclear reactor in the world.
Notes 17:
“Quantum Beam Technology” means the technology which
consists of generating and controlling electromagnetic waves such as high-strength
and high-quality photons, and synchrotron radiation, and particle beams such
as neutron radiation, electron beams, and ion beams, etc. using accelerators,
high power laser devices, facilities and high flux research reactors for research
purposes.
Notes 18:
J-PARC:Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex
Notes 19:
The Nuclear Energy Fundamentals Crossover Research is positioned
as comprehensive experimental research on nuclear energy and consists of a variety
of technical elements for which individual research institutions, by themselves,
have a difficulty in making achievements promptly.
● Promotion of radiation utilization
One use for nuclear energy is the application of radiation in a wide range of sectors from basic research to utilization in medicine, engineering, agriculture, and other sectors; promotion of research and development toward the widespread use of radiation is also important.
As for the state of radiation utilization, the medical sciences already make wide use of diagnostic technology employing X-ray Computerized Tomography (CT) and X-ray or gamma ray radio-therapy for the treatment of cancer, while research is being conducted on the use of protons and heavy ion beams, etc., for the treatment of cancer. In particular, the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) is engaged in research on cancer therapy using heavy ion beams, which was approved as highly-advanced medical treatment by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Fiscal 2003 with high expectations for its clinical effectiveness against cancer.
In addition, the institute is promoting research to downsize equipment in accordance with the Third Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy against Cancer. In universities, as well, such as at the Tsukuba University’s Proton Medical Research Center, research is progressing into the diagnosis and treatment of cancer using proton beams. In the agricultural sector, radiation is used for the improvement of crop varieties, the eradication of vermin without recourse to agricultural chemicals, the prevention of budding in potatoes, etc. In the industrial sector, radiation is used for non-destructive testing of industrial products, for industrial measurements, and for quality improvements of rubber, plastics, and other polymer materials. In the research area, research using ion beams and gamma radiation is being conducted at JAEA for the creation of new functional materials and biotechnology useful for preserving resources or cleaning up the environment, and using electron beams in environmental protection technologies for the elimination of toxic substances from smoke emissions.
● Nuclear non-proliferation policies and international nuclear energy cooperation
To smoothly carry on with nuclear energy research, development, and utilization requires that Japan clearly explain to international society its stance underlying nuclear power policies, and to obtain their understanding and trust. In addition, in order to resolve international concerns related to nuclear energy, such as the issues of nuclear safety and disposal of radioactive wastes, it is important that Japan actively make use of its technology and experience in cooperation with international society, so as to obtain the understanding and trust of the international community.
1) Nuclear non-proliferation policies
In order to ensure smooth implementation of the peaceful use of nuclear energy, the maintenance of the international nuclear nonproliferation regime, along with safety assurances, is extremely important. Several international frameworks, including the Treaty on the Nonproliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT), the comprehensive safeguards by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) based on the NPT, and the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), have been established. In addition to these frameworks, Japan reinforces the international nuclear nonproliferation regime with its technologies and skilled personnel in relation to the peaceful utilization of nuclear energy.
Japan is promoting the development and utilization of nuclear energy strictly for peaceful purposes, as stipulated in the Atomic Energy Basic Law. For many years, Japan has accepted “safeguards” to ensure the peaceful use of nuclear materials, based on the Safeguards Agreement with the IAEA, and implemented “physical protection” to prevent theft of nuclear materials or attempts to sabotage nuclear facilities. Japan is also promoting the necessary technology development for the implementation of the above measures. In 2004, the IAEA concluded that there was no indication of the diversion of nuclear materials placed under safeguards and no indication of undeclared nuclear materials or activities for Japan as a whole. Since then, the Integrated Safeguards, which are efficient safeguards that enable a reduction in the number of inspections, have been implemented.
In order to implement effective, efficient safeguards toward the commercial operation of the Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant, an important facility to be safeguarded, the government is engaged in system development, including the establishment of safeguards, measures, and the foundation of the Rokkasho Safeguards Analytical Laboratory and the Rokkasho Safeguards Center. The government also organized an international training course for the improvement of technologies for nuclear materials accounting.
In addition to responsibilities imposed under the NPT, it is important for Japan to ensure transparency by employing rational and consistent plans, while adhering strictly to the principle of non-possession of surplus plutonium. Therefore, in line with international plutonium guidelines designed to boost transparency of the nuclear fuel cycle program, Japan discloses through the IAEA the conditions of its plutonium management, and independently discloses more detailed data, to ensure that transparency is maintained at as high a level as possible. Furthermore, Japan actively promotes the development of technologies related to non-proliferation policy, and undertakes research and development activities with full consideration of nuclear non-proliferation in fields such as advanced recycling technologies.
Additionally, Japan in July 1997 swiftly ratified the CTBT banning all nuclear weapon test explosions and all other nuclear explosions, a historic step towards a world that is free of nuclear weapons, and is now engaged in development of an international monitoring system toward the treaty’s eventual enforcement.
2) International nuclear power cooperation
In the area of international nuclear cooperation, it is important to promote international cooperation activities for common issues or R&Ds, such as those for the research, development and utilization of nuclear non-proliferation, as well as to respond positively to the expectations of developing nations.
Japan participates in the Generation Ⅳ International Forum (GIF), members of which are the United States, France, and eight other countries and one institution. In February 2005, the governments of five countries, the United States, France, the United Kingdom, Canada and Japan, concluded a framework agreement related to the development of next-generation nuclear energy technology (as of December 2005, the number of countries participating in the agreement was seven due to the addition of Switzerland and Korea.)
For nuclear cooperation with Asian countries, exchanges of information, opinions, and technology are being promoted under the framework of the Forum for Nuclear Cooperation in Asia (FNCA) for the peaceful utilization of nuclear energy, in such areas as research reactors and the medical utilization of radiation. The sixth FNCA Ministerial Level Meeting was held in Tokyo in December 2005, at which time opinions were exchanged between member nation ministers in charge of nuclear energy on such issues as human resource development, science & technology and nuclear energy.
Japan also participates in the Regional Cooperative Agreement for Research, Development & Training Related to Nuclear Science and Technology (RCA), a grouping since 1978 of IAEA member countries in the Asia-Pacific region hosting study seminars and other events in the industrial, medical, and radiation protection fields, as well as making technology transfers through the dispatch of Japanese experts, providing equipment and materials, offering funding and personnel assistance, and contributing to the social and economic development of developing nations.
For cooperation in nuclear energy with the countries of the former Soviet Union and of Central and Eastern Europe, Japan offers research cooperation for the decommissioning of nuclear facilities, bilateral cooperation for quality improvement of plant operators through training projects, and provision of multilateral support through extra-budgetary contribution funding to the IAEA. In addition, regarding the management and disposal of Russia’s surplus weapons-grade plutonium, Japan is determined to utilize its technologies for the peaceful use of nuclear energy developed over many years in Japan to cooperate in the disposition program of Russia’s surplus weapon-grade plutonium, as part of its contribution to nuclear disarmament and nonproliferation, in close cooperation with the principal countries of the United States and Russia, and with other involved countries. In particular, JAEA is engaged in research cooperation with Russia’s Institute of Physical Energy Research and other institutes, such as the Research Institute for Atomic Reactors and the Institute of Physics and Power Engineering. The agency also started flame tests on 21 fuel assemblies to verify the reliability of the method for producing vibropack fuel and its applicability to fast reactors since fiscal 2004.
Finally, for nuclear cooperation with Europe countries and the United States, Japan exchanges experts and information regarding the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and the receipt and supply of nuclear materials and related services. Specifically, this includes research cooperation by JAEA with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), research cooperation between RIKEN and the U.S. -based Brookhaven National Laboratory, and also with Britain’s Rutherford Appleton Laboratory.
(2) New Energy Research and Development
While new sources of energy can contribute to addressing global warming, and to stable energy supplies, it also faces problems of economy, such as lower energy conversion efficiency and higher electricity generating costs than those of fossil fuels. Research and development into fuel cells, photovoltaic cells, biomass energy, and other forms of new energy need to be aggressively promoted, in order to address these problems and promote the introduction and broader diffusion of these technologies.
● Fuel cells and hydrogen energy utilization
Because fuel cells, which generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, are very efficient and do not emit NOx or SOx, they are expected to be a key energy and environmental technology. While the development of fuel cell vehicles and stationary fuel cell systems is well-advanced, there still remain some hurdles to be addressed, such as durability and performance in order to make them commercially feasible. For this reason, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting the development of innovative new components and materials that can improve fuel cell performance. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry developed a basic, fundamental R&D system on polymer electrolyte fuel cells and established mass production technology for fixed fuel cells. The ministry is also promoting research and development in the demonstration of fuel cell vehicle and hydrogen supply facility areas. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport is also conducting experiments on prototype fuel cells for residential use.
● Photovoltaic power generation
Photovoltaic power generation has been spreading as its price has fallen. Nevertheless, development of technologies that further lower costs is essential for the establishment of a truly independent market. For this purpose, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting the development of technologies that achieve lower costs and higher levels of efficiency, as well as the development of recycling and reuse technologies.
● Biomass energy
Based on the Biomass Nippon Strategy (ratified by the Cabinet in December 2002), the Cabinet Office, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport, and the Ministry of the Environment are promoting research and development into technologies for the efficient conversion of animal wastes, wood residues, organic sewage, food wastes, and other unusable biomass sources into universally acceptable fuel forms, such as methane and other gaseous fuels (gasification), or methanol and other liquid fuels (liquefaction), and into technologies for these fuels’ efficient utilization.
(3) Clean fossil fuel energy R&D
From the perspective of global warming prevention, the promotion of research and development into cleaner and more efficient fossil fuel utilization technologies is a necessity.
● Petroleum
In order to make efforts to further reduce carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and other substances that are generated due to the production and use of petroleum and have an impact on the environment, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting research and development into the more advanced, effective manufacturing processes of petroleum products and the higher quality of fuel for cleaner auto emissions.
● Coal
Coal offers excellent supply stability compared to petroleum and other sources. But since coal emits the highest carbon dioxide of all fossil fuels, research and development is needed to reduce its burden on the environment.
For this purpose, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting the development of highefficiency power generation technologies and other clean coal technologies, such as the high-efficiency power generation technologies by the Integrated coal Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) and the Integrated coal Gasification Fuel cell Combined Cycle (IGFC).
● Natural gas, etc.
Because natural gas has lower carbon dioxide emission than other fossil fuels, the promotion of research and development into its utilization is therefore of importance in order to reduce the environmental burden.
Consequently, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting research into technologies for the manufacture and utilization of liquid fuels (GTL, or Gas-to-Liquid) and dimethyl ethyl (DME), obtained by converting natural gas into liquid fuel, which should lead to the expansion of natural gasuse. The ministry is also promoting the research and development of new exploitation technologies for the utilization of methane hydrates, believed to be available as an energy source in relatively large quantities from the seas around Japan.
(4) Energy Conservation and Energy Efficiency R&D
From the viewpoint of preventing global warming and effectively utilizing limited energy resources, it is important to carry out research and development not only to improve efficiency in specific individual devices, but also to improve the energy supply and utilization efficiency of all energy systems in society, for example by the introduction and use of distributed systems, and the utilization of unused energy. It is also necessary to promote research and development from a point of view of reducing all energy (life cycle energy) that is directly or indirectly consumed in the process of the production, use, re-use, and disposal of products.
To this end, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is strategically promoting research and development of the hydrate slurry air conditioning system(Notes 20) to overcome problems on the demand side in the process from the identification of seed technologies to the practical application thereof with the aim of increasing the effectiveness of development of energy-saving technologies.
In addition, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is promoting research and development into ultra-heat resistant materials for more efficient gas turbines, etc.
Table 3-2-7 shows a summary of the major research topics in the energy sector (excluding nuclear power) implemented during Fiscal 2005.
Notes 20:
Hydrate slurry air conditioning system: A system in
which a multiphase media of hydrate and water solution is used as a heat carrier
to conduct cold latent heat carrying in high density thereby reducing the carrying
power required.
Table 3-2-7 Major research subjects in the non-nuclear energy sector (FY2005)
| Ministry or agency | Research institute or program | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | Fire and Disaster Management Agency |
Consideration of necessary safety measures for installing an outlet within a gas station that supplies fuel cell vehicles with hydrogen |
| Ministry of Education, Cuture, Sports, Science and Technology | National universities and other institutions |
New energy and energy efficiency R&D The Project to Design a Sustainable Management and Recycling System for Biomass and General and Industrial Wastes Next-generation fuel cell project |
| National Institute for Materials Science |
New century heat-resistant materials project Research into the development of highly efficient advanced structural materials with superior processability |
|
| Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries | National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, etc. |
Assessment and mitigation techniques of global warming effects on the agriculture, forestry and fisheries sector Development of new technology for the treatment and recycling of biomass |
| Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry |
Photovoltaic power generating technology Development of technologies for the stabilization of wind power generating systems Biomass energy technologies Hydrogen energy technologies Fuel cell technologies GTL and DME-related technologies Development of methane hydrate technologies Research and development into clean coal technologies Development of entrained bed coal gasification power plants Development of energy conservation technologies - SiC and other power electronics -Technologies for the analysis of the optimum utilization of energy between multiple industrial users (pinch technology) -Development of high-efficiency white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) -Research and development into high-efficiency organic EL technology Development of technology for distributed energy network systems Development of technology for performing the comprehensive evaluation of energy systems |
|
| Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport |
Promotion of technology development for the introduction of fuel cells and other new energy sources into residences Development of a new energy system to reduce CO2 emissions, as well as the development of optimization technologies to adapt the system to houses and buildings R&D on the evaluation of positive effects on the urban environment from adding greenery to building sites |
|
| Ministry of the Environment | National Institute for Environmental Studies |
Development of technologies for the manufacture of hydrogen from bioresources and biowaste, etc. Development of technologies for the manufacture of hydrogen using offshore wind power generation |
|
Global Environment Research Fund -Study on development and spread ofhousehold energy saving technologies and lifestyle Development of technologies to prevent global warming -Development of energy-saving technologies for practical use -Development of practical-use technologies to introduce renewable energy -Environmental Model Project for Urban Redevelopment |
3.2.2.6 Manufacturing Technology
Manufacturing technology is the source of Japan’s economic power and can even be called its lifeline, standing at the highest levels in the world. These technologies will continuously need to be advanced further, and the development of innovative technologies will be important. Based on this recognition, the Science and Technology Basic Plan positioned manufacturing technology as one of the eight areas meriting special priority.
To actively promote the fundamental technologies for manufacturing that support the growth of the manufacturing industry, the Manufacturing Fundamental Technology Promotion Basic Plan was adopted in September 2000, based on the Basic Law to Promote Fundamental Technologies for Manufacturing (1999 Law No.2), and comprehensive and planned implementation of measures for promoting such technologies is now in progress (see Section 3.3.6.6).
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is engaged in the development of next-generation fundamental technologies. For example, RIKEN is promoting the development of an “Integrated Volume-CAD System Using Advanced IT”, based on technologies for utilizing the new concept of “volume data(Notes 21)”, for the purpose of integrating geometric modeling, simulation, testing, manufacturing and other kinds of information technologies in production engineering, and is also engaged in the development of an advanced measurement technology that utilizes a multidimensional quantum detector, toward the goal of establishing a cutting-edge measurement technology based on new detection technologies.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting various projects, including the “MEMS Project,” which aims to strengthen international competitiveness in key devices in the information and communications sector and other sectors by establishing manufacturing technology for MEMS ((Micro Electro Mechanical System)), the “Project for a Computer Aided Engineering System for MEMS,” the “Advanced Machining System Development Project,” which aims to develop advanced machine tools through improvement of production efficiency, accuracy and energy efficiency, the “Development of Eco-Management Production System Technology,” which contributes to the improvement of production efficiency and energy efficiency in the manufacturing industry, the “Digital archive of human body properties,” which promotes the development and designing of products through accumulation of data concerning the measure and shape of the human body and development of an automatic measuring system, and the “Knowledge support system for field operators at oil refinery,” in which support system using ergonomic techniques is developed to conduct the maintenance and checkup of oil refineries during operation efficiently and with high reliability.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries was engaged in the establishment of local brand food products through industry-academia-government cooperation and the development of technologies for the export of food, in order to strengthen competitiveness in the food industry. The ministry was also engaged in the development of technologies that ensure safe and trusted foods in response to consumer demand and the development of functional foods to improve peoples’ health, as well as the development of functionality evaluation technology.
Notes 21:
Volume data-digital data describing a material body
which maintains geometry, internal structure and distributed physical properties,
all in a unifiedform
3.2.2.7 Infrastructure
Infrastructure is a basic sector that supports people’s lives. In order to achieve a prosperous, secure, safe, and comfortable society, research and development is promoted to reduce the risks inherent in society, and to improve the people’s conveniences so they can achieve a quality life.
(1) Science and Technology for Disaster Prevention
In order to mitigate the potential damage from natural disasters, it is important to be able to fully utilize scientific and technical knowledge to prevent disasters before they happen, limit the spread of damage when disasters actually occur, and recover from disasters. The major scientific and technological research issues on disaster prevention at each ministry and agency are shown in Table 3-2-8. The contents of the research are wide-ranging. In particular, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is conducting the “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation In Urban Areas” that focuses on earthquake disasters. With the completion of construction of a three-dimensional full-scale earthquake testing facility (called “E-Defense”) in March 2005, the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED) has been performing full-scale experiments to improve earthquake protection since Fiscal 2005. In addition, universities and research institutions are conducting research into the prevention or mitigation of damage from various types of natural disasters other than earthquakes. With respect to snow damage caused by heavy snowfall in the 2005-2006 winter, relevant ministries and agencies, cooperating with research institutions and universities, implemented research and studies including emergency survey research using Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology (SCF).
In the area of international cooperation, Japan is taking part in bilateral research on science and technology for disaster prevention within the framework of science and technology cooperation agreements with the United States, Russia, Italy, and others, and the “U.S.-Japan Cooperative Program in Natural Resources” (UJNR). In addition, in the Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 formulated at the U.N. World Conference on Disaster Reduction held in January 2005, Japan was requested to provide support for the improvement of capacity for risk assessment, monitoring and early warning systems.
Table 3-2-8 Major research subjects in (natural) disaster prevention science and technology (FY2005)
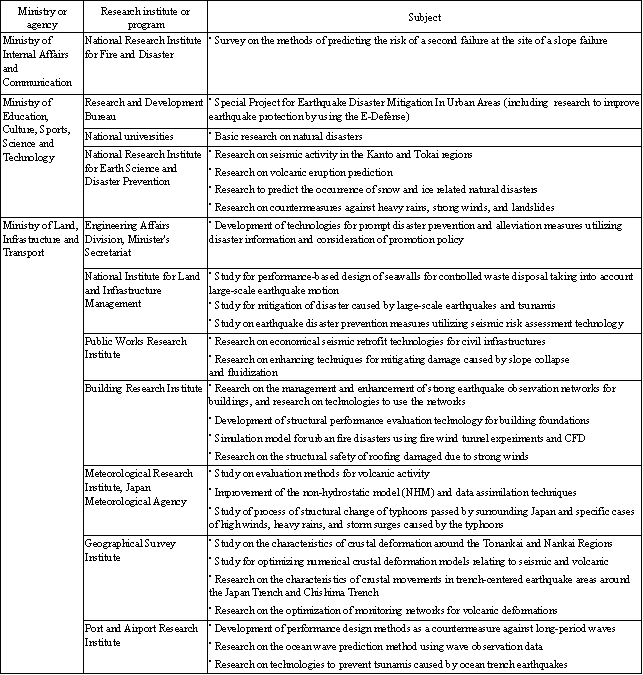
(2) Earthquake Surveys and Research
Under the Special Measure Law on Earthquake Disaster Prevention, established after the occurrence of the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake in 1995, the Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion (Chairman: Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology) were established to clarify the system of responsibility for earthquake surveys and research that should impinge directly on administrative policies and to promote comprehensive earthquake prevention measures throughout Japan. A Policy Committee and an Earthquake Research Committee was also established under the Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion, and based on “The Promotion of Earthquake Research-a basic comprehensive policy for the promotion of earthquake observation, measurement, surveys and research,” adopted in April 1999, the Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion serves as the point of contact and cooperation between relevant ministries and agencies for the promotion of earthquake surveys and research (Figure 3-2-9).
Figure 3-2-9 The structure of the headquarters for earthquake research promotion
The Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion, putting together the matters examined at the Policy Committee, formulated the “Focused Research and Observation Program in the Future” in August 2005. This stipulates the methods and targets for focused research and observation, as well as additional and complementary research on active faults.
The Earthquake Research Committee holds monthly meetings and extraordinary meetings. The extraordinary meetings are held when relatively large-scale earthquakes occur. At monthly meetings, the committee made comprehensive evaluations of earthquake activities in Japan by collecting information and results of analysis related to them and publishes them immediately to ensure their use in disaster prevention activities. In addition, extraordinary meetings were held to analyze the occurrence of an earthquake with an epicenter in the sea near Miyagi Prefecture on August 16, 2005, in order to prepare evaluations.
On the other hand, the Earthquake Research Committee performs a series of long-term evaluations of the probabilities of future large earthquake occurrence (site, scale (magnitude), and occurrence probability) as well as strong ground motion estimations, and published the results for 98 major active fault zones throughout the country and subducion-zone earthquakes in 7 sea areas around Japan. In March 2005, the committee published the “General Seismic Hazard Maps” based on these results (Figure 3-2-10).
Figure 3-2-10 Probability Seismic Hazard Map (Distribution map of probabilities of having an intensity of 6 Lower or greater※ quakes in the next 30 years)
Notes 1:
Regarding figures for the classifications of the “high”
possibility having an intensity Lower or greater quake in the next 30 years,
it is shown that 26% will experience an earthquake about each 100 years on average,
6% about each 500 years, and 3% about each 1,000 years, respectively.
Notes 2:
Base date: January 1, 2005
The major measures related to earthquake research and surveys of related ministries and agencies are as shown in Table 3-2-11.
Based on the policies laid down by the Headquarters for Earthquake Research Promotion, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) promotes additional or complementary research on active faults, and focused research and observation into ocean trench earthquakes in the Tonankai and Nankai earthquake zones, etc. and the Itoi River-Shizuoka fault line. In addition, as part of the “Special Project for Earthquake Disaster Mitigation in Urban Areas”, it also promotes the research and survey into the crustal structure in major metropolitan areas. The National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED), acting in accordance with the “Fundamental Seismic Survey and Observation Plan,” is promoting the development and operation of high sensitivity seismic observation stations and of broadband seismograph network, and is also engaged in collecting data from earthquake observation networks, and in processing and disseminating that data. The institute is also engaged in research into methods for the preparation of general seismic hazard maps. In addition, the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) is promoting the development of a comprehensive real time deep sea-floor observation network system. The Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) promotes research into the mechanism and prediction of occurrence of earthquakes caused by active faults. The Geographical Survey Institute (GSI) operates 1,231 (as of March 2006) continuous GPS stations throughout the nation as well as Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) and other advanced survey technologies, to make observations and analysis of crustal deformation and plate motion. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) establishes and operates observation facilities, while providing earthquake information with centralized observation data including other relevant institutes. The agency is also working together with NIED to conduct research and development towards practical application of the emergency earthquake information reports (EEIR), which aim to provide information including the hypocenter and magnitude of an earthquake before the strong motion occurs in order to mitigate the earthquake’s damage. The Japan Coast Guard promotes seafloor geodetic observation, bathymetric survey and the research for the evaluation of earthquake activities. National universities conduct basic research into earthquakes.
The national research for earthquake and volcanic eruption prediction is comprehensively promoted according to the plan based on “The Second New Program of Research and Observation for Earthquake Prediction” adopted in July 2003 by the Council for Science and Technology as a five-year promotion plan (2004-2008) and “the Seventh Program for Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions,” with universities, the National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention, the Japan Meteorological Agency, and other institutions proceeding in the spirit of cooperation while utilizing their particular functions and capabilities.
Table 3-2-11 Measures for earthquake surveys and research (FY2005)
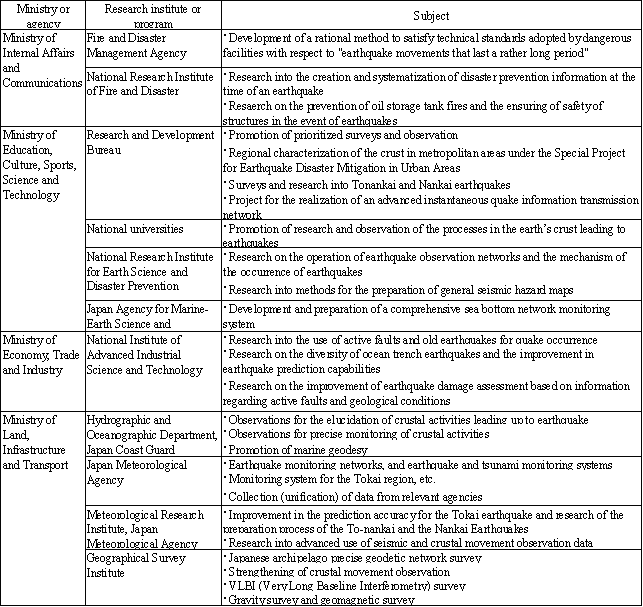
(3) Aviation Science and Technology
R&D in aviation science and technology is knowledge-intensive and makes use of advanced technologies. As a result, it not only brings about the development of air transport, but also spills over into many other sectors.
In Japan, technology has accumulated through the independent development of the YS-11 commercial transport aircraft and other projects, international joint development of the Boeing 787 and other aircraft, and international joint development of the V2500 jet engine for commercial aircraft. The nation’s technology is steadily increasing its role in the world’s aviation industry. In particular, Japan’s application of composite materials and other advanced materials in its structural design and manufacturing technologies is recognized as top-class around the world.
To actively promote the development of aircraft and their engines, it is necessary to even further improve the technological levels. In the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Council for Science and Technology decided the “Policy to Promote Research and Development on Science and Technology for aeronautics” in Fiscal 2003, thereby indicating desirable ways of research and development. In addition, in the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Aircraft and Space Industry Committee’s Aircraft Subcommittee under the Industrial Structure Council is holding discussions on the possibility of joint international development of domestic aviation aircraft and engines, and on other directions in aircraft industry policy.
In response to the above-mentioned promotion policy, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology is intensively promoting R&D that can contribute to the development of a domestic aircraft and domestic jet engine, and R&D into transportation safety and environmental protection under the leadership of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. Elsewhere, the agency is promoting research into numerical simulations and basic technologies for assessment of advanced composite materials. The agency also develops wind tunnels, engine testing facilities, and other large-scale testing and research facilities, encouraging their joint use by other institutions, to play a leading role in improving the level of aviation science and technology in Japan.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry is promoting research and development for low-cost small domestic aircraft with a limited burden on the environment and environmentally-friendly high-performance small aircraft that demonstrate the entire integration technology(Notes 22) for domestic engines, as well as research and development of engines for environmentally-friendly small aircraft. In addition, the ministry is promoting the development of civil aircraft using technologies for supersonic aircraft and the Defense Agency’s aircraft, and the development of technologies for manufacturing and processing next-generation structural parts and materials, which realize reduced cost and increased reliability of composite materials for aircrafts and magnesium alloy parts and materials, as well as the development of next-generation technologies related to additional accessories and functions, such as incorporating maneuvering and air conditioning into electrical operation.
The Electronic Navigation Research Institute under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport has been conducting research in the field of communications, navigation, monitoring and air traffic control to develop technologies for securing and facilitating air traffic safety. This research is expected to be important for the further advancement of air transportation.
Notes 22:
verall integration technology: technology for producing
entire completed airframe
(4) Development of Other Social Infrastructure
Society as a whole is becoming increasingly complex, with advancing urbanization and the general improvement of society through the development of transport, shipping, and communications systems, etc. On the other hand, however, rural communities face problems of population outflow and aging, reduced vitality in industry and society, a decline in public transport and shipping functions, and a general multifaceted decline in such important functions as land conservation, water source cultivation, and conservation of the natural environment. Moreover, in order to achieve a higher quality for people’s lives, where leisure and prosperity can be experienced, the development of the socio-economic infrastructure has come to be demanded.
In this sector, a number of documents have established priorities for the promotion of research and development, including the “Basic Plan for the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport Technology,” adopted in November 2003 by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport, the “Basic Plan for Research and Development in Information and Telecommunications,” adopted in February 2000 by the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications’ Council for Telecommunications Technology (Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications), and the “Items Related to Pollution Prevention that Require Experimental Research Priority,” adopted in April 2003 by the Ministry of the Environment.
Specifically, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport and other ministries and agencies are promoting comprehensive land use through the development of advanced national land use management technology, and research and development into disaster prevention evaluations and countermeasure technologies in city renewal projects, and into other local disaster prevention activities. The ministry is also promoting research and development into technologies for a superconducting magnetically levitated train, and of other advanced transport and shipping systems.
The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications and other ministries and agencies are promoting research and development into ultra-high speed network technologies, advanced information resource transmission and accumulation technologies, and other advanced information and communication systems, as well as research and development for fire fighting and disaster prevention, including research on technologies for alleviating damage by disaster and disaster response technologies.
In addition, the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries is engaged in the development of technologies for the restoration and improvement of agriculture, forestry, and fisheries ecologies, and of methods for managing drainage basin environments.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry promotes research and development of “human lifestyle engineering for quality life” for the development of universal design products and systems.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport offers subsidies and other support for the Railway Technical Research Institute to promote research and development toward the practical realization of a superconducting magnetically levitated train, for the objective of high-speed transport in the future. In addition, based on the “Development Vision for Technologies Related to Deep Underground Use,” the ministry is promoting the development of technologies with broad general applications for projects that require traversal of the deep underground.
The major research topics in Fiscal 2005 for socioeconomic infrastructure, safety assurance, etc., are as shown in Tables 3-2-12 and 3-2-13.
Table 3-2-12 Major research subjects in the improvement of the socioeconomic foundation area (FY2005)
Table 3-2-13 Major research subjects in the safety area (FY2005)
3.2.2.8 Frontier Science
(1) Space Development and Utilization
Space development and utilization not only brings about the “accumulation of intellectual property common to all humankind” through acquisition of commonly applicable knowledge regarding the origin of the universe and various phenomena occurring on Earth, but also contributes to development of critical and strategic national technologies, which serve as a basis for sustainable development of the nation, thereby contributing to national security in a broad sense. It is extremely important because the expanded use of space contributes to the “expansion of the socioeconomic infrastructure” through global environment observing and disaster monitoring, weather forecasting, and satellite-based communications and broadcasting activities, and to “pioneering advanced technologies” that may result in the creation of new technologies in various fields and of new industries with much additional value, so-called “spining-off”.
Since the successful launch of Japan’s first satellite “Ohsumi” in 1970, Japan had launched 113 satellites as of the end of March 2006. Table 3-2-14 shows the major satellites planned and/or prepared for future launch by Japan and their objectives.
The Council for Science and Technology Policy issued in September 2004 the “Basic Strategies for Space Development and Utilization in Japan.” This describes action plans for all space development and utilization in Japan.
The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology directed the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to promote research and development in a strategic and concentrated way in accordance with the “Long-Term Plan for Space Activities” in September 2003, based upon discussion in the Space Activities Commission. JAXA, learning from troubles in the past, has been making efforts to establish reliability, and succeeded in the No. 7 H-ⅡA launching in February 2005, and has continued to make successes in the following five rockets launches by the end of March 2006, that is, three H-ⅡA launches and two M-V launches.
Furthermore, in accordance with the basic principles of overall space development and utilization in Japan, the Space Activities Commission holds discussions on the long-term plan for space development and examines safety in rocket launches. The commission also conducts investigation into the causes of accidents or malfunctions.
Table 3-2-14 Satellites and payloads planned to be launched
| Satellite/payload | Weight (kg) | Orbital altitude (km) | Launch vehicle | Launch date (fiscal year) | Major objectives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JEM Japanese Experiment Module |
Approx. 26,800 | Approx. 400 | U.S. Space Shuttle | 2007 | Expansion of Japan 's space activities, promotion of leading science and technology development, and contribution to the advancement of international cooperation |
| WINDS Wideband Internetworking engineering test and Demonstration Satellite |
Approx.2,700 | Geostationary orbit | H- ⅡA | 2007 | Development, etc., of ultra-fast high-capacity satellite communications technologies and other world-leading technologies, and experiments/ demonstrations thereof |
| SELENE SELenological and Engineering Explorer |
Approx.2,900 | Orbit around the moon (Approx. 100) |
H- ⅡA | 2007 | To research the origin and evolution of the Moon, collect data for a Moon-use feasibility survey, etc. |
| SOLAR-B 22nd scientific satellite |
Approx.900 | Sun synchronous orbit (Approx. 600) |
M-V | 2006 | Detailed observation of the structure and motion of micromagnetic fields on the solar surface, to elucidate the components of solar magnetism and the source of solar activity |
| GOSAT Greenhouse gas Observing Satellite |
Approx.1,500 | Sun synchronous orbit Approx. 650 |
H- ⅡA | 2008 | Continuous observation of physical Earth quantities, to contribute to the elucidation and forecast of global warming, climate change, changes in the ozone layer, etc. |
| GPM/DPR Global Precipitation Measurement/Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar |
Approx.3,000 | Approx. 400 | H- ⅡA | 2010 | To develop the Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) for monitoring precipitation, as part of international cooperation in the Global Precipitation Measurement Program (GPM) |
| HTV H- Ⅱ Transfer Vehicle |
Maximum supply weight: Approx. 6,000 |
(Approx. 350-460) | H- ⅡA | 2008 | To use a Japanese transport system that can contribute a fair share of material supplies to the Space Station |
| PLANET-C 24th scientific satellite |
Approx.480 | Orbit around Venus (Approx. 300-80,000) |
M-V | 2010 | To explore Venus' atmosphere, and solve riddles in the basic principles of planetary weather and the evolution of atmospheres |
| LUNAR-A 17th scientific satellite |
Approx.540 | Orbit around the moon (Approx. 200) |
M-V | To be determined | Elucidation of crustal structure and thermal structure of the moon |
| Bepi - Colombo Mercury Exploration Project |
Approx. 200 (MMO) |
Elliptical polar orbit around Mercury (Approx. 00-12,000) (MMO) |
Soyuz Fregat 2B | 2012 | To observe the magnetic field, magnetosphere, the inside and surface of Mercury from many directions through international cooperation with the ESA (European Space Agency). Japan is in charge of the Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (MMO). |
Note:
The launch dates above are as of March 2006 and could be
changed in the future.
● Earth Observation and Earth Science
This is described in 3.2.2.3.
● Space Science and Lunar Exploration
JAXA plays the core role in the field of space science in Japan, launching science-mission satellites with the participation of researchers from various universities or academic institutes nationwide.
“Hayabusa” the 20th Science-mission Satellite (MUSES-C) was launched in May 2003 for the purpose of performing an engineering test for a mission to take rock samples from an asteroid and bring them back to Earth. The microwave discharge ion engine mounted on “Hayabusa” marked a total operating time of 26,000 hours, and “Hayabusa” arrived at the asteroid “Itokawa” in September 2005. “Hayabusa” observed the vicinity of the asteroid after the arrival, and left the area in November. “Hayabusa” is the first satellite in the world that succeeded in landing on and taking off from an asteroid, and is now making preparations for its return to Earth.
Launches scheduled for Fiscal Year 2005 include “Suzaku” the 23rd Science-mission Satellite (ASTRO-E Ⅱ) for the observation of X-rays emitted from active galactic cores and galactic clusters, aimed at investigating the structure and evolution of the universe, and “Akari” the 21st Science-mission Satellite (ASTRO-F) that is aimed at clarifying the process of formation and evolution of galaxies, stars and planets through infrared observation.
There are other projects now in development, such as the 22nd Science-mission Satellite (SOLAR-B), which is aiming to investigate the origins of the solar atmosphere and the causes of solar activity, and the Moon orbiter SELENE to gather data for investigation on the origins and evolution of the moon and to clarify the feasibility of the lunar resources utilization.
● Communications, Broadcasting, and Positioning
Utilization of satellites for communications, broadcasting, and other purposes offers a broad range of benefits in terms of wide-area use, broadcast simultaneity, durability following disasters, etc. In Japan, the private sector has already been deeply involved in satellites for communications and broadcasting, such as for satellite broadcasting. To further promote these private-sector efforts, the government is promoting development in advanced and underlying technologies where the risks are too big for the private sector, and the development of pioneering technology for the future utilization of space.
Furthermore, in order to ensure autonomous technologies in space development and utilization and to contribute to technological innovation, the government is engaged in the R&D and testing of new space technologies as well as underlying technologies to promote space development and utilization.
1) Engineering Test Satellite Ⅷ (ETS-Ⅷ)
JAXA, cooperating with the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, is developing the Engineering Test Satellite Ⅷ (ETS-Ⅷ) with a targeted Fiscal Year 2006 launch. The purpose is to develop and demonstrate large-scale satellite bus technologies, large-scale deployable antenna technologies, mobile multimedia satellite broadcast system technologies, and fundamental technologies related to satellite positioning systems utilizing high-accuracy clock standards.
2) Wideband InterNetworking engineering test and Demonstration Satellite (WINDS)
JAXA, cooperating with the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, is developing the Wideband InterNetworking engineering test and Demonstration Satellite (WINDS) with a targeted Fiscal Year 2007 launch. The purpose is to establish a satellite-based communications technology that enables ultra-high speed Internet and large-volume data communications, and to demonstrate ultra-high speed networking technology using satellite communications.
3) Quasi-Zenith Satellite System
The quasi-zenith satellite system will consist of multiple satellites placed in quasi-zenith orbits to ensure that one or more satellites are always visible at the zenith in the skies over Japan, and are expected to achieve virtually 100% land coverage without being affected by narrow mountain valleys or tall buildings. On March 31, 2006, the Cabinet decided the basic principles for the future at the meeting of the Council for Promotion of GPS and GIS. Based on the principles, the Ministry of Intnal Affairs and Communications, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport plan to conduct, in cooperation with the private sectors, research into the quasi-zenith satellite system with a targeted Fiscal Year 2009 launch, in order to provide such high-accuracy positioning services.
● Manned Space Technology
The International Space Station (ISS) program is an international cooperative project being carried out jointly by five countries and regions, namely Japan, the United States, Europe, Canada and Russia, to construct the space stations in low Earth orbit. Japan is carrying out the development of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM; also known as “Kibo”) and the H-Ⅱ Transfer Vehicle (HTV), as its contributions to the ISS.
In July 2005, astronaut Soichi Noguchi participated in the Space Shuttle Discovery’s flight, and accomplished the important mission including three extra-vehicular activities.
In September 2005, the United States notified the results of its ISS program review to the international partners. In consequence of discussion, it was confirmed that the Japanese module “Kibo” will be delivered to the ISS by space shuttle flights as previously planned. On the other hand, it has been decided that “Centrifuge,” a biology research laboratory developed by Japan for the United States to offset the Space Shuttle launch services for “Kibo,” was canceled for it’s flight.
1)Kibo
The development of “Kibo,” the Japanese first manned space experiment module, is almost finished, and functional tests and maintenance are being conducted as preparation for its operation.
2) HTV
To support the ISS operation, it is necessary for Japan to transport various cargos to the ISS. In addition, severe safety, rendezvous technology and orbital transfer technology are required for approaching and berthing to the ISS as a manned facility. In order to acquire these technologies and to deliver necessary supplies in the future, Japan is developing the HTV unmanned transfer vehicle and will demonstrate its flight.
● Promotion of Space Environment Utilization
It is expected to promote research and development that contributes to society through the various kinds of experiments and observation, by utilizing the unique conditions of the space environment such as microgravity and a high vacuum.
As for preparation for utilization of “Kibo,” JAXA is conducting microgravity experiments at a microgravity experiment facility (drop tower) and by aircraft (parabolic flights), and experiments of the High-quality Protein Crystallization, by using the ISS's Russian service module, as well as the Three-Dimensional Photonic Crystallization. To promote diversification for the ISS utilization, JAXA also provides space education events such as communication between high school students on the ground and ISS crew, and contests for the aircraft-based microgravity experiments conducted by university students.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) developed a next-generation Unmanned Space Experiment Recovery System (USERS) to promote the utilization of the space environment. It was launched in September 2002 and the part of the space vehicle containing the results of the test experiments was successfully returned to Earth and retrieved on May 30, 2003. Analysis of the samples obtained in a large-scale superconducting materials crystallization growth test using a microgravity space environment is now in progress. In addition, to encourage the broad use of Japan’s well-developed industrial technology in commercial satellite production processes, and to rationalize their design, procurement, and manufacture, etc., the Space Environment Reliability Verification Integrated System (SERVIS) satellite program was used to develop guidelines and the necessary intellectual infrastructure for the transfer of industrial technologies to space-related devices and the use of databases of private-sector components for space-related devices, and the satellite was launched in October 2003. The private-sector components worked well in the tests, and various data is being obtained in accordance with the plan.
● Space Infrastructure
For autonomy of national space development in the international community, it is important for Japan to acquire the capability for transporting necessary materials and equipments to a specific location in space whenever needed. For this purpose, Japan is engaged in the research and development of space transportation systems. Japan is also developing an advanced inter-satellite communication technology that targets the acquisition of space network operations technology.
1)H-ⅡA Rockets
For the launch of large-scale satellites, etc., JAXA has developed a two-stage rocket with liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen-fueled engines for both the first and second stages (H-ⅡA) (Table 3-2-15) and employs it to launch large-scale satellites. H-ⅡA rockets are positioned as Japan’s key rocket and are planned to be used appropriately through steady implementation of technology upgrades and improvements to reliability. Moreover the H-ⅡA standard type is to be transferred to the private sector to ensure the improvement in product quality through shared manufacturing liability.
The development of H-ⅡB rockets (capacity-enhanced H-ⅡA) is being promoted jointly by the public and private sectors to ensure the launch capability of the H-Ⅱ Transfer Vehicle (HTV) and to enhance international competitiveness. In September 2005, JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. concluded a basic agreement on the development of H-ⅡB rockets, to stipulate a framework for joint development between the public and private sectors. In Fiscal Year 2005, the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS), also known as "Daichi", and the Multifunctional Transport Satellite 2 (MTSAT-2),also known as "Himawari-7", operated by the Ministry of Land Infrastructure and Transport and the Japan Meteorological Agency, were launched and successfully entered their planned orbits.
Table 3-2-15 Main specification of vehicles used to launch satellites
2)M-VSeries Rockets
JAXA launches science-mission satellites usually by using the M-V rockets that use solid propellant for all stages. In Fiscal Year 2005, JAXA launched the X-ray Astronomy Satellite "Suzaku" (ASTRO-E Ⅱ) using M-V rocket No. 6 and the Infrared Astronomy Satellite “Akari” (ASTRO-F) using M-V rocket No. 8. These satellites successfully entered their planned orbits.
3)GX Rocket
The GX rocket is a rocket designed to launch small- or medium-size satellites, which has been developed under private initiative. Public-private sector joint research and development is now progressing toward the first launch in Fiscal Year 2008. JAXA will conduct a flight test of the LNG-fueled propulsion system in a GX rocket.
4)Optical Inter-orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite (OICETS) "Kirari"
In August 2005, the Optical Inter-orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite (OICETS) "Kirari," designed to conduct orbital experiments on basic technologies needed for communications in inter-satellite communication systems was launched using a Dnepr rocket designed in Russia and Ukraine. With this launch, JAXA was the first in the world to succeed in a bi-directional optical link, which is a feat achieved through communications with the Advanced Relay and Technology Mission Satellite (ARTEMIS) of the ESA, and demonstrated optical inter-orbital communications technologies in space. In March 2006, JAXA also achieved the world's first success in non-military laser-optical communications, accomplished by communications with the optical ground-based station (Koganei City, Tokyo) of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology.
5)Data Relay Test Satellite (DRTS) "Kodama"
JAXA is advancing preparation for an inter-satellite communications demonstration between the Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) "Daichi", which was launched in January 2006 and the Data Relay Test Satellite (DRTS) “Kodama”.
● Fundamental and Advanced Research on Satellite and Launch Vehicle Technology
JAXA and research institutes of related ministries and agencies conduct fundamental research on launch vehicle and satellite technology. They also work in a number of advanced research areas, including an unmanned winged reusable space vehicle and a space plane.
● Promotion of International Cooperation in Space
In recent years, the need for international cooperation including with Asian countries in space activities has expanded, because satellite-based Earth observation contributes to solve global issues, such as environmental problems, disasters, which are getting much more serious, and space activities have become international activities with the globalization in society and the economy. Therefore, the need for Japanese contribution in space activities such as mitigating disaster damage utilizing satellites has become greater ever than ever before.
Japan promotes multilateral cooperation through the activities in the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS), in which nations discuss the international order on exploration and utilization of space, and on the promotion of international cooperation, the Asia Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF) hosted by Japan, a place for discussing concrete international cooperative projects in the Asia Pacific region for the development of space technology and applications for the future, and the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS), a place for coordinating technical matters and information exchange. Particularly in Asia, Japan promotes multilateral cooperation with space agencies and disaster management organizations for establishing ”the Disaster management support system in the Asia Pacific region,” a network system for sharing disaster information.
Japan participates in the International Space Station (ISS) program as the largest international cooperation project in space development, and is developing the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM: ”Kibo”) and the H-Ⅱ transfer vehicle (HTV). Japan has close cooperation with all participating partners for the construction and utilization of the ISS.
As bilateral cooperation, Japan promotes cooperation in space activities with the USA concerning “Cross-Waiver of Liability for Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Space for Peaceful Purposes.” With European countries, Japan maintains close cooperation, through annual administrative Japan-ESA meetings, etc. Moreover, with Russia, Japan promotes cooperative relations through a periodic Japan-Russia joint Committee on Cooperation in Outer Space.
(2) Ocean Development
The development and use of the ocean, which contains an abundance of resources, including biological and mineral resources, as well as vast space, is an important issue for a country as physically small and confined by the sea as Japan. Furthermore, because the ocean plays an important role in global environmental changes, and the movements of oceanic plates are believed to be a major factor of earthquakes and volcanism, elucidation of their mechanisms is urgent. In the light of these conditions, the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) and the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) called for the implementation in the early 1990s of the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS), which aims to build a system for the conduct of comprehensive observations and research of ocean phenomena on a worldwide scale. The GOOS project is now being promoted in co-operation with the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
This plan was also incorporated into the Agenda 21 that was adopted by the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also called the Earth Summit. Based on these international efforts, it is crucial for Japan to promote ocean research related to global environmental issues, and to promote other research and development into ocean sciences and technologies. Furthermore, in order to shed some light on ocean phenomena occurring on a global scale, the relevant ministries and agencies have joined with universities, etc., to actively participate in international ocean research programs such as GOOS. Also, Japan has taken a leading role in cooperation with China, South Korea, and Russia to promote the North East Asian Regional-Global Ocean Observing System (NEAR-GOOS) as a regional pilot project for GOOS.
Japan’s ocean development adheres closely to the report of the Council for Science and Technology, and research and development is being promoted with the co-operation of relevant ministries and agencies according to their various situations. In “Basic Concepts and Promotion Measures for Ocean Development from the Long-Term Viewpoint (report),” subdivision responded in August 2002 to an inquiry by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, by noting that “it is important to carefully balance knowing, protecting, and using the ocean for the policies for future ocean development when presenting strategic policies and promotion policies toward realization of sustainable utilization.”
Moreover, the Inter-Ministerial council was established to promote and coordinate surveys for the establishment of the outer limits of the Japanese continental shelf. The council recognizes that it is important for the government to firmly implement these surveys.
At the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication, the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology conducts research into high-resolution three-dimensional microwave radar and shortwave ocean radar to facilitate the establishment of methods for the measurement of marine oil pollution, currents, and waves, etc., and the prediction of changes in the global environment, and implements joint observation in cooperation with universities and other research institutes.
At the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, research Institutions including the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) are promoting advanced and basic research and development into ocean sciences and technologies. These institutions cooperate with related ministries and agencies, universities, etc., to promote comprehensive projects.
The Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology conducted marine observation using Triton buoys(Notes 23), Argo floats(Notes 24), and an oceanographic research vessel “MIRAI” with the aim of investigating the interactions between the atmosphere and the ocean, such as El-Nino events, as well as the effects they have on global climate change. In addition, the deep sea research vessel “KAIREI” was used for ocean surveys for research into the dynamics of oceanic plates. In addition, the agency conducted geological, biological, and geochemical studies at sea on board the “YOKOSUKA,” the support mother vessel for a manned research submersible “SHINKAI 6500.” For the deep-sea Earth drilling project(Notes 25), construction of the “CHIKYU” deep sea drilling vessel, which had started in Fiscal 1999, was completed in July 2005, and a test voyage carried out. Furthermore, the Project for Research on Marine and Extremophiles Biology promoted research for the elucidation of the physiological adaptability of deep-sea organisms existing in extreme environments.
In addition, Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, is at the center of continuing ocean-related scientific research, including basic research related to GOOS for the purpose of building a comprehensive observation system for the elucidation and forecast of changes in the ocean environment, and for its preservation, participation in joint surveys of the Western Pacific region, and research into ocean flux(Notes 26), which can contribute to the elucidation of physical cycles in the ocean. In addition, other national universities are engaged in research into marine ecosystems and conducting observations of changes in the atmosphere and oceans.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries elucidated ocean surface layer ecologies to facilitate the rational utilization and management of organic marine resources, and also elucidated the structure of deep sea ecologies and the relationship between mechanisms of change, and changes in surface layer ecologies.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry continues to implement surveys for reserves of oil and other resources, prediction of effects on the marine environment and surveys of the ocean bottom in cooperation with Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology and other organizations.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport promoted research and development on next-generation coastal ships (Super Eco-Ship), and expanded the Nationwide Ocean Wave Information Network for Ports and Harbors (NOWPHAS) in cooperation with the Port and Airport Research Institute. The Japan Coast Guard is engaged in research into upgrading water channel measurement and marine condition monitoring technologies, and into the development of seabed monitoring technologies and upgrading of the accuracy of current flow forecasting. The Japan Meteorological Agency continues to conduct investigation and research on the ocean, such as the oceanographic and marine meteorological observations and elucidation of El Nino phenomena, in order to improve the information about monitoring and forecasting of marine phenomena and climate change. Moreover, the National Maritime Research Institute is carrying out research into safety and environmental protection in the field of maritimetechnology. In relation to the NEAR-GOOS project, the Japan Meteorological Agency and the Japan Coast Guard operate a system for promoting the exchange of oceanic data for NEAR-GOOS area, in order to better promote oceanographic research. In addition, the Geographical Survey Institute conducts basic research of coastal sea areas for the purpose of providing the basic information needed for the formulation of comprehensive development, utilization, and protection plans for coastal sea areas.
At the Ministry of the Environment, the Global Environment Research Fund is being used to conduct research into cross-border air pollution including acid deposition, and marine pollution, including pollution from chemical substances on global-scale.
Table 3-2-16 summarizes the main research subjects undertaken in the ocean sciences and technology sector by various ministries and agencies in Fiscal 2005.
Notes 23:
The Triton buoy is an oceanographic observation buoy
that is deployed mainly in the tropical regions to automatically monitor and
report wind, atmospheric temperature, humidity, precipitation, solar radiation,
seawater temperature, salinity, and tides.
Notes 24:
The Argo float is a float that automatically rises and sinks between
the water’s surface and a depth of about 2,000 meters in order to monitor and
report water temperature and salinity.
Notes 25:
The deep-sea Earth drilling project aims to promote R&D to bring
to light global environmental changes, the earth’s interior structure, and
deep-subsurface ecology by providing the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP)
with the “CHIKYU” deep sea drilling vessel which was developed to reach the
earth’s as-yet-unexplored mantle.
Notes 26:
The Research into ocean flux aims to elucidate the circulation
velocity of various matter within the ocean interior or crossing between the
ocean and other reservoirs (atmosphere, solid earth, etc.), as well as the
factors determining the velocity. The flux refers to the rate of flow of materials
per unit area.
Table 3-2-16 Major research areas in marine science and technology (FY2005)
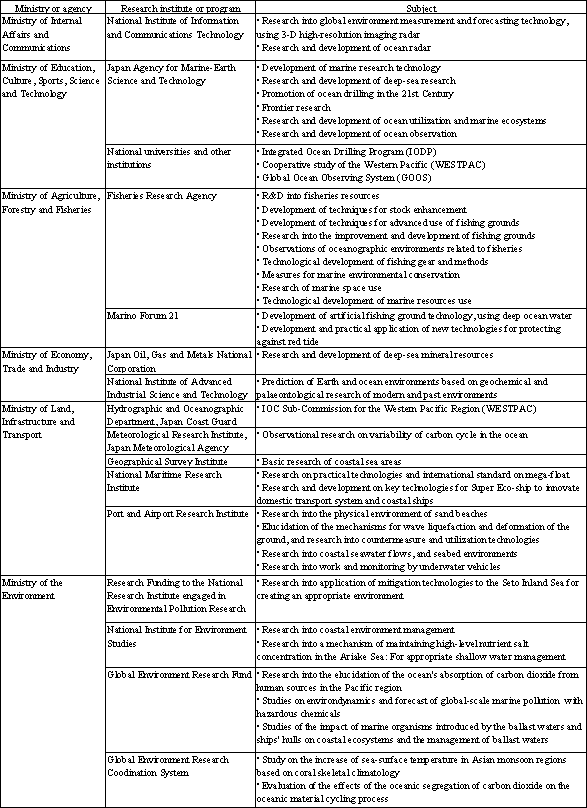
3.2.2.9 Promotion of Science and Technology for Safety, Security and Spiritual Enrichment
Toward realization of the concept of “Protect nation's health and safety” offered in the 3rd Basic Plan as a principle that Japan should aim for, as well as of the policy goal of being “the world's safest nation,” the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in April 2006 established the Committee on Science and Technology for a Safe and Secure Society under the Council for Science and Technology Subdivision on R&D Planning and Evaluation and is holding discussions on fields to be addressed to develop a safe and secure society, technical issues, and specific measures for the promotion of research and development. In addition, the “2nd Japan-U.S. Workshop on Science and Technology for a Secure and Safe Society” was convened in March 2005 to discuss how Japan and the United States can cooperate in the fields of science and technology in response to the various risks and threats that society faces, and is extending cooperation in areas of shared concern.
In addition, research and development utilizing competitive funding, such as the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology and the Project for Promotion of Strategic Creative Research (Japan Science and Technology Agency), is being conducted in order to promote research and development on the creation of unique digital content, as well as human resources development.
Contacts
Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau
(Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau)