| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.3 3.3.2 3.3.2.1 | ||
| 3.3.2.1.1Increasing the Dissemination of Information |
To promote the strengthening of coordination between industry,academia,and government,it is essential to bring about a state of common recognition between industry and public research institutes.For this reason,public research institutes are making research results available to the public and pro-viding information in a number of ways,including the presentation of research results,the release of annual reports and other publications,the sub-mission of research papers to various academic societies and journals,and the disclosure of government-owned patents.
To contribute to the creation of new industries,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology utilizes the Japan Science and Technology Corporation to compile databases covering a broad range of R&D support data and research results data,for wide availability over the Internet.Specific examples are the Directory Data-base of Research and Development Technology Activities(ReaD)that compiles organizational data,researcher data,and research theme data from public research institutes,and the JST Science and Technology Research Result Database for Enterprise Development(J-STORE)that brings together and processes research results from national government research projects,etc.,related patent information,and report summaries,for presentation in a readily understandable technology resource format.To provide greater usability,the ReaD database also links to the information system of the National Institute of Informatics(NII),which supplies information from universities,etc..
In addition,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries carries out the digital conversion,etc.,of research results and other information contributing to the technology development,etc.,of the agriculture,forestry,and fisheries industries,for wide availability over the Internet.Specifically,this involves preparation of the Agriculture Information Search System known as Agropedia 74) ,which integrates and serves as a centralized source for the digital full text information database of reports from national and public experimental and research institutions and universities,domestic and international databases of agricultural literature,a database of meteorological satellite images,and a database of research topics under implementation at national research institutes.
| 3.3.2.1.2Promotion of Research Exchanges |
In recent years,research and development has increased in both sophistication and complexity,and has undergone an increase in the number of fields that are either interdisciplinary or are not included in any traditional discipline.To promote creative science and technology,it is critical to actively promote personnel and material exchanges that extend beyond research institutes,in order to promote the development of infrastructures that allow such exchanges to be carried out,and to efficiently and effectively utilize limited research resources.In addition,research exchanges are critical for the transfer of research results from public research institutes to corporations,etc.,and to encourage research by public research institutes which reflects the needs of the corporations,etc.
| 3.3.2.1.2.1Joint Research and Contract Research |
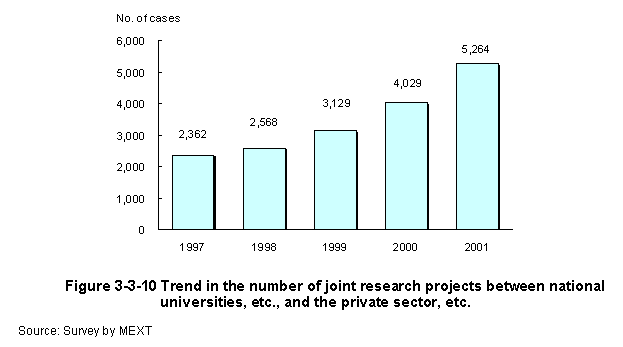
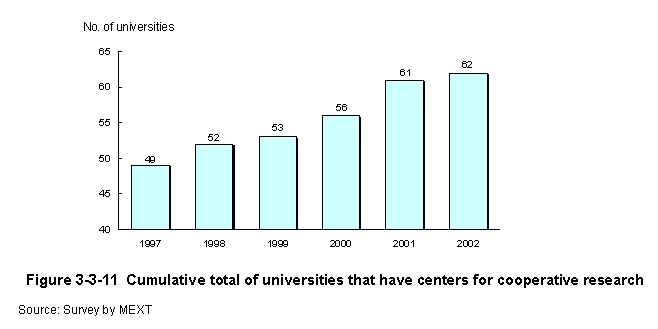
To promote research exchanges between industry,academia,and government,the government ministries implement measures such as joint research programs.The number of joint research projects between national universities and the private sector,etc.,has steadily increased over time (Figure3-3-10) . To promote joint research between the private sector and national universities,etc.,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology implements joint research programs with the private sector,etc.,in which university researchers and private sector researchers undertake joint research themes,contract research programs that commission research from corporations to national universities,etc.,and contract researcher programs in which national universities and inter-university research institutes provide research guidance for researchers at corporations,etc.In addition to implementing joint research and contract research,the Ministry establishes centers for cooperative research at national universities that carry out technical consultations on R&D and training for engineers in the corporations,and also serve as university-wide contact points for coordination and cooperation with industry.Through FY2002,centers for cooperative research were established at a total of62universities (Figure3-3-11) .
Note74)Agropedia:Derived from"Agriculture"and"Encyclopedia."
Government ministries implemented a number of measures to promote joint research through collaboration among industry,academia,and the government.Examples include joint research between industry and academia or industry and government newly begun with the"Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology,"and the"Project for Research Advancement in Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries Utilizing Advanced Technologies"implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries.In addition,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry implements the Plan to Develop Integrated Technology in the Energy and Environmental Fields(New Sunshine Plan),the Program for the Scientific Technology Development for Industries,the Program for Joint Regional Research between Industry,Academia,and the Government for Small and Medium-scale Enterprises,and the Program for Joint Research through Coordination between Government Agencies and the Private Sector.
The Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications implements the"Basic Research21for Breakthroughs in Info-Communications Program,"the"Program for Cutting Edge Research and Development"conducted under the auspices of the Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan(TAO),and the program for"Industry-Academia-Government Development of Advanced Technologies"within the"Program for Promoting Strategic Information and Communications Research and Development."The Ministry of the Environment utilizes the Global Environment Research Fund.The above programs serve to promote integrated project research through coordination between industry,academia,and the government.
Furthermore,revisions to the tax system in FY2002 excluded the research projects commissioned to private universities that require three months or more to perform from the category of"undertaking of subcontracted jobs"and exempted them from taxation.
In addition,measures in the FY2003 tax reforms allow the exemption of a considerable amount of experimental and research expenses for research conducted jointly with or contracted to Japanese universities.
| 3.3.2.1.2.2Development of the Law for Facilitating Governmental Research Ex-change |
Restrictions on research and development by the national government had up to now existed in the form of the Government Officials Program and the Property Administration Program;however,insufficient conditions had been placed on the promotion of research exchanges with individuals from the private sector and from abroad.The Law for Facilitating Governmental Research Exchange was established in order to address inadequacies in the legal system,and a Cabinet decision specified"Basic Policies Concerning the Management of Programs related to the Promotion of Governmental Research Exchanges between Industry,Academia,and the Government,and with Other Countries,"for the purpose of eliminating problems in the management of research exchanges.
In light of the increasing necessity for inter-national contributions in science and technology,as well as the strong push in both Japan and abroad to promote theoretical and creative research,appropriate amendments were made to the Law for Facilitating Governmental Research Exchange,in order to further ease various systematic constraints placed on research activity by the national government.In May1998,a partial amendment was made to the Law for Facilitating Governmental Research Exchange that enabled the joint use of a site in which a joint research facility is erected within the premises of a national university or national re-search institute,etc.To date,this exemption has been applied on three occasions.
In addition,with the promulgation of the Law on the Special Zones for Structural Reform in December2002,special measures in the Law for Facilitating Governmental Research Exchanges were implemented,thereby making it possible to expand the scope of low-cost usage of national experimental research institutions within authorized special district regions,relax the conditions of their use,and simplify usage procedures.
| 3.3.2.1.3Personnel Exchanges |
Currently,there are several programs in place to promote exchanges between researchers.Examples include the Government Guest Researcher Program implemented at various government ministries,the Flexible Employment System for Research Personnel that promotes flexible and creative research activities by researchers at national research institutes,and programs to promote research exchanges such as the Program for Multidisciplinary Exchange implemented by the Japan Science and Technology Corporation(JST).
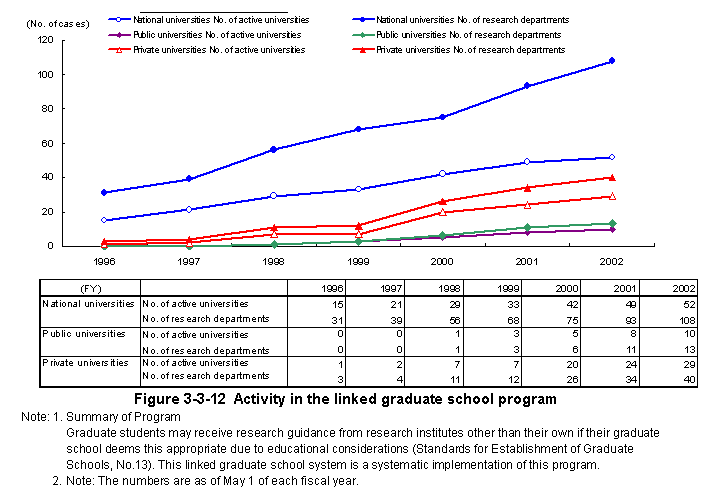
In addition,the Graduate School Coordination Program contributes to the promotion of personnel exchanges that are for the mutual benefit of universities,national research institutes,corpora-tions,etc.This program strives for coordination between graduate schools and both corporations and national research institutes,and is being utilized with increasing frequency (Figure3-3-12) .
To bolster the reforms of the system of collaboration among industry,academia,and government laid down in the Second Science and Technology Basic Plan,in continuation from the previous year,the nationwide"Second Summit on Business,Academia Government Collaboration"was held on November18,2002,sponsored by the Cabinet Office,Keidanren,and the Science Council of Japan,and co-sponsored by the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry.
Taking"Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration Strategies as told by Experts in Their Fields"as the theme,top representatives from progressive overseas enterprises and universities were invited to the summit,where participants participated in practical-minded studies and discussions that included considerations of actual success cases of collaborations among industry,academia,and government that contribute to the competitive strategies of businesses and universities.The participants then adopted the"Joint Declaration of the Second Summit on Business-Academia-Government Collaboration" (Figure3-3-13) .
Furthermore,because of the importance of promoting collaboration among industry,academia,and government in regional areas,the Cabinet Office,the Science Council of Japan,and local business federations sponsored"Regional Summits on Business-Academia-Government Collaboration,"with the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry,and local public authorities of each region that hosted a summit as co-sponsors.In FY2001,summits were held in nine regions across the country,and in FY2002,summits were held in the Chugoku region(Matsue City)and the Chubu region(Nagoya City).
In addition,in order to achieve increased promotion of collaboration among industry,academia,and government,the"First Conference on the Promotion of Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration"was held.Leaders and strategists of enterprises,universities,and public administrations from across Japan attended the conference.Specific working level solutions were put together and reflected in policy.Many people participated in the consultation meetings given by universities,re-search institutions,and TLOs 75) on technology introductions,patent applications,and comercialization.

Moreover,the implementation of research activity for the private sector,etc.,by researchers from national research institutes and faculty of national universities,etc.,contributes to the promo-tion of science and technology in Japan by cooperation between industry,academia and public sector,and serves as an opportunity to demonstrate and build upon the individual capabilities of researchers.For this reason,it is necessary to manage the authorization of side jobs smoothly in which re-searchers employed by the national government are engaged in tasks such as research and guidance for the private sector,etc.,outside of working hours.
Previously,there were few examples in which the authorization of side job were given,such as instructors at private universities.Since FY1996,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry(formerly the Ministry of International Trade and Industry),the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology(formerly the Science and Technology Agency),the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare(formerly the Ministry of Health and Welfare),the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries,the Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications(formerly the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications),and the Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Transport(formerly the Ministry of Transport)have gradually clarified the fundamental permissibility of side jobs outside of working hours,in cases where authorization is obtained from the intended place of work,on the condition that there shall be no transfer of subsidies and that the secondary duty shall have no effect on the performance at the primary place of employment.In the period between FY1996 and FY1999,the number of authorizations for side jobs issued by national research institutes reached in excess of600cases.
Note75)TLO:Technology Licensing Organization
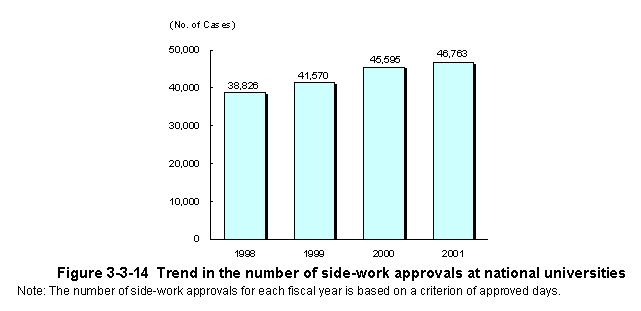
Additionally,since FY1997,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology(formerly the Ministry of Education)has amended the relevant notifications to authorize faculty at national universities,etc.,to engage in side jobs at for-profit enterprises if they are engaged in R&D or in technical instruction related to R&D,or since FY2000,if they are engaged in technical guidance for other enterprises while employed at technology licensing organizations(TLOs),or since FY2002,if they offer counsel management or legal affairs advice for for-profit enterprises while employed at TLOs.For the period of FY1998 to FY2001,the number of authorizations for side jobs issued by national universities,including authorizations in the above new cases,reached in excess of170,000cases (Figure3-3-14) .
The establishment of the National Personnel Authority Regulation in April2000,in accordance with Article103of the Government Officials Act,enables faculty of national universities and research personnel at national research institutes,etc.,to take side jobs as directors and so forth of technology licensing organizations,as directors and so forth of corporations utilizing his research results,and as auditor at stock corporations,etc.In addition,according to partial revisions to the rules of the National Personnel Authority,as of October2002,the authority to approve the taking of side jobs as directors and so forth of TLOs and corporations utilizing his or her research results was transferred from the National Personnel Authority to the heads of the relevant authorities,and was also entrusted again to the heads of national universities. When a researcher needs to concentrate on employment as executive of the enterprise utilizing his research results,the institution may offer the person a leave of absence.So far,this situation has occurred in two cases.
| 3.3.2.1.4Council for Industrial Competitiveness and National Industrial Technology Strategy |
The Council for Industrial Competitiveness con-ducts comprehensive reviews aimed at strengthening the competitiveness of industry through improved productivity.To date,the discussions by the Council have resulted in the implementation of policies such as rebuilding of businesses and possession of intellectual property rights resulted from national contract research to the contractors(enactment of the Law on Special Measures for Industrial Revitalization),support for small and medium enterprises and venture companies(revision of the Basic Law for Small and Medium Enterprises),the drafting of the Millennium Project,and the enactment of the Industrial Technology Enhancement Law,which includes deregulation on the acceptance of executive positions in private sectors by professors or researchers of national universities.
In April2000,the Council for Industrial Competitiveness drafted the National Industrial Technology Strategy,in order to summarize the discussions,proposals,etc.,conducted to that date.
The National Industrial Technology Strategy recognizes the next major direction to take for strengthening industrial technology as"reform of the technological innovation system from a catch-up type to a frontier creation type,"and sets the goals to be obtained as:(1)realization of true collaboration among industry,academia,and government that can create technological innovation;(2)promotion of reforms of universities aimed at gaining international competitiveness;(3)fostering of richly creative researchers and engineers;and(4)restructuring of flexible government systems so that they can respond to world trends in technological innovation.It also specifies programs such as system reforms to achieve the above aims.
Furthermore,the Strategy states that"prioritization of government R&D investment"is inevitable for strengthening industrial technology,and sets prioritized areas as:(1)R&D investments to meet social needs that will lead to market creation;(2)R&D investments in emerging technologies that are particularly innovative and fundamental;and(3)investment in intellectual infrastructure that can be the basis for development of industrial technology and regarded as social capital.
In the Industrial Technology Strategies,goals targeting the year2010were set for each of16sectors by experts from industry,academia,and government,and policies were drawn up for comprehensive strategies.
In addition,the Council for Science and Technology Policy established the Industry,Academia,and Government Collaboration Project under its Expert Panel of S&T System Reformation,for intensive investigation by experts from industry,academia,and government of specific policies for the promotion of cooperation between the three spheres.In June2002,the"Basic Concepts on and Promotion Policies for Collaboration among Industry,Academia,and Government"was pre-pared,and opinions on collaboration among industry,academia,and government were submitted on specific policies regarding the different forms of collaboration,the different sectors,the regional promotion of science and technology,and the construction of collaboration infrastructure.
| 3.3.2.1.5Promotion of the Common Use of Research Facilities |
The public use of cutting edge,advanced R&D facilities at national universities,national research institutes and quasi-governmental corporations to users are crucial to the effective use of the facilities as well as the promotion of the cooperation among them.
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology has begun the public use of the third generation synchrotron radiation facility,SPring-8,as a joint project between the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI)and RIKEN.SPring-8utilizes the light(synchrotron radiation),which is emitted from an electron traveling almost at the speed of light when its path is bent by a magnetic field and it has carried out state-of-the-art experiments in a variety of fields including materials science,life science,information/electronics technology and applications to medical science.Researchers place large expectations on SPring-8since it is expected to contribute to the research results in a wider range of fields.For this reason,the"Law regarding the Promotion of Common Use of the Synchrotron Radiation Facility(SPring-8)"was established in order to promote its use by opening it to the researchers from Japan and abroad.
In addition,based on the"Guidelines for the Effective Utilization and Operation of the Large-scale Synchrotron Radiation Facility,SPring-8"issued by the Council for Aeronautic,Electronics,and other Advanced Technologies,the Ministry has been seeking policies for the efficient use and management of the facility,such as the promotion and upgrade of the facility's use and the effective management system.
In FY2002,the Council for Science and Technology's Subdivision on Research and Development Planning and Evaluation prepared the"Interim Evaluation Report on the Synchrotron Radiation Facility,SPring-8"in September,giving its recommendations on reform of SPring-8's management system.Consequently,the Council is proceeding with reforms to promote strategic re-search.In addition,the Organization for the Pro-motion of Synchrotron Radiation Research adopted approximately990research proposals for implementation between February2002and February2003,promoting a wide range of research.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |