| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.3 3.3.1 3.3.1.2 | ||
| 3.3.1.2.1Universities |
As one of their directives,Japan's universities are entrusted with the task of securing the academic foundation and improving the academic standards of Japan,with a focus on scientific research.The essence of university-level scientific research is to give rise to new and richly creative knowledge based on the unrestricted thinking and independent research activity of researchers.Furthermore,university-level scientific research shall be characterized by the goal of advancement in study carried out over a broad range of fields in the areas of humanities,social sciences,and natural sciences,shall possess a respect for the independent nature of researchers as being essential to such progress,and shall function for the integrated promotion of research and education.
Based on reports and suggestions forwarded by the Science Council,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology strives to provide for Japan's foundation for scientific re-search in a planned and prioritized manner,and to proactively implement a comprehensive policy for the nation by increasing research funding,by improving research facilities and equipment at universities,by nurturing and recruiting exceptional researchers,by prioritizing the promotion of basic research,by creating COEs,by improving the evaluation of research,and by developing and expanding upon the science information infrastructure,in order to develop a scientific research system that is open to the world,and which is capable of flexibly responding to advancements in scientific research.
Expanding the independence of management of national universities and inter-university research institutes in the areas of budget,organization,the National University Corporation Bill was presented in the156th ordinary Diet session with the aim of developing appealing national universities with distinctive identities that actively address education,research,and contributions to society,and establish management structures that are open to public scrutiny.
Furthermore,efforts are being made,primarily by the Cabinet Office,to establish universities in Okinawa with graduate school curricula in science and technology of the highest international standards,and that embrace the new mindset of"internationalism"and"flexibility"as basic concepts,with the aim of getting Okinawa to take part in Japan's and the world's scientific and technological advances,and to develop Okinawa into a region of advanced,concentrated brain power within the Asia-Pacific region.
| 3.3.1.2.1.1Scientific Research at Universities |
Researchers of universities nationwide are making use of research at their universities,departments,graduate schools,research laboratories,and research facilities,as well as joint-use inter-university research institutes,without being tied to a specific university.
In an age of advancements in scientific research that are characterized in particular by the increasing sophistication of research techniques and their large scale,researchers in many research fields are finding it increasingly necessary and efficient to carry out joint research.For this purpose,priority is being placed on the development of joint use infrastructures such as inter-university research institutes,as well as research laboratories and research facilities within universities,in order to expand the infrastructure of research organizations.In addition,efforts are being made to reinvigorate research institutes and give them greater flexibility to respond to the growth of interdisciplinary fields and the existence of social demands,etc.,that have accompanied advancements in scientific research.
The inter-university research institutes make significant contributions to research advancements in a variety of fields by acting as centers for promoting joint research between researchers employed throughout the nation's universities,and by providing a place for the joint use of facilities,equipment,and materials that are unique or large in scale.Projects such as the B Factory project of the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization(KEK)and SUBARU optical-infrared telescope project of the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan(NAOJ)also promote cutting-edge international research.As part of the university education system,the inter-university research institutes carry out research and education in an integrated manner that is typified by the acceptance of graduate students.By the end of FY2002,a total of14inter-university research institutes and17research laboratories had been established.
Research laboratories devoted to research in designated specialized fields have also been established at universities.These research laboratories carry out specialized research in collaboration with education and research carried out at university departments and graduate schools.At the end of FY2002,a total of58research laboratories had been established at the national universities,including19research institutes for joint use for the nation's universities.Research projects such as the neutrino research conducted by the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research(ICRR)of the University of Tokyo have produced research results of the highest international standards.
To secure research funds to promote research conducted at universities,efforts have been made to secure two types of funding,ordinary"fundamental"funds to support basic research activity,and"competitive"funds that are selectively allocated to exceptional research in accordance with appropriate reviews and evaluation of research.
Of these funds,ordinary research expenditures are specifically intended to support research based on the freethinking of researchers.At national universities,such expenses are incurred as educational research foundation schooling expenditures and travel expenditures for faculty research.At private universities,subsidies are provided for operating costs related to ordinary research expenditures and research projects that respond to strong social demand.In terms of competitive funding,Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research are being increased with the aim of achieving significant advancements in exceptional research being carried out in a broad range of fields,and capital investments in the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science(JSPS)are being utilized to implement the Research for the Future(RTTF)program,which prioritizes the promotion of visionary and richly creative research with the potential to produce intellectual assets.
| 3.3.1.2.1.2Expanding Support for Japan's Private Universities |
Roughly80percent of Japan's university students attend private universities,which actively carry out characteristic educational research activity based on the unique spirit upon which each university was created.Accordingly,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology implements the following measures in order to support the private universities.
To support operating costs,the Ministry newly established the"Special Aid to Promote Education,Research,and Upgrades at Private Universities"with the aim of creating world-class universities.This aid provides prioritized assistance according to the state of the university tackling education and research.
To subsidize costs for building research facilities and equipment,the Ministry spent24.3billion yen in FY2002 on such projects as the newly established"Project for Promoting Industry-Academia Collaborative Research"to support research projects with high practicability or seminal research projects that are conducted in collaboration between universities and local businesses in order to contribute to the development of large corporations,venture companies,or local industry,and the"Cyber-Campus Promotion Project"to foster collaboration and exchanges in education and research between universities via the Internet and other media.In addition,the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan finances long-term and low-interest funding in order to offset expenditures incurred by the private universities for the development of research facilities and equipment,etc.
Furthermore,since April1,2002,certain projects related to research commissioned by third parties and undertaken at private universities have been exempted from applicable corporate taxes for profit-earning projects.In addition,measures were taken in the FY2003 tax revisions to fill approval requirements,under certain conditions,for exempting from applicable income taxes for"deemed transfer income"on contributions of spot goods to private universities.
| 3.3.1.2.1.3Deliberations in the Council for Science and Technology |
The Council for Science and Technology con-ducts research and deliberations in response to inquiries posed by the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology regarding matters important to the comprehensive promotion of science and technology and to the promotion of learning in general;it also provides opinions to the minister.The Subdivision on Science was establish-ed within the Council in order to conduct research and deliberations on matters important to the pro-motion of learning that takes place primarily at universities.
In FY2002,the Subdivision on Science put together a report in June on the"Promotion of the Humanities and Social Sciences:Measures for Immediate Promotion in response to their Expected Roles in the21st Century,"and in July an interim report on"Making Joint-Use University Facilities into Corporate Bodies,"based on the making of national universities into corporate bodies.In January2003,the Subdivision put together an interim report on"The State of Attached Laboratories and Research Institutions under the New National University Corporation System."
| 3.3.1.2.1.4Activities of the Science Council of Japan(SCJ) |
Science Council of Japan(SCJ)was originally founded in1949,and is the leading organization representing Japan's scientists both domestically and internationally.The18th term of SCJ started in July2000,and was marked by the following proposals:
1.Proposal of the Japan perspective designed to solve the problems facing the humankind
2.Proposal on creating a new science system based on the current status of science and the relationship between science and society
SCJ is in the midst of mobile and active consideration regarding these two proposals,and is also carrying out research coordination,etc.,in order to improve the efficiency of scientific re-search
| (1)Deliberation Activities |
The Standing Committee on the Status of Science in Japan sorted out some of the problems in Japanese science,such as its"import tendency,"and published"Recommendations for Qualitative Improvement of Japanese Science"in July2002.
In October2002the Committee published"Japan Perspective"the construction of an"Information-Circulating Society Driven by Science"in order to resolve global problems,and in November2002it published"Toward the Scientific Risk Assessment and Risk Management of Techniques for the Disposal of Abandoned Chemical Weapons"in regard to China's abandoned chemical weapons.
Continuing to build upon the opinions submitted on February26,2003,by the Council for Science and Technology Policy on"The Status of the Science Council of Japan,"the SCJ established in March2003the"Committee for the Promotion of Reform of the Science Council of Japan,"and clarified the function and roles that the SCJ should perform within society in the years to come.The SCJ is presently considering reforms to adequately achieve these goals.
| (2)International Scientific Exchange |
| The Science Council of Japan represents Japan through its affiliation with many international scientific organizations,including the International Council for Science(ICSU 70) ).The SCJ actively works with international programs for scientific cooperation,and strives for coordination with other countries |
The Asian Conference on Scientific Cooperation(ACSC 71) ),which gathered scientists from10Asian countries to a conference held in Tokyo on annually until FY2000 for the purpose of collaboration and cooperation among Asian countries in scientific research,was reorganized into a new entity,the Science Council of Asia(SCA 72) ),in which conferences would be hosted by member countries in rotation.The first conference under the council was held in Thailand in May2001,and the second conference in Malaysia in May2002,both with the theme of sustainable development in Asia.
In January2003,the Science Council of Japan hosted the"International Conference on Capacity Building in Science through IT"in Okinawa.Discussions were held at the conference between relevant Japanese and foreign scientists on measures for effectively promoting"capacity building in science"in each country.Specific recommendations were collected.
The Science Council of Japan also obtains approval by the Cabinet to host important inter-national conferences to be held in Japan related to science jointly with relevant scientific research organizations.In FY2002,the council co-hosted eight such conferences.
(3)Open Lectures and Symposiums
Science Council of Japan sponsors open lectures as a way of giving science results back to the citizens of Japan.SCJ also actively sponsors symposiums that engage in various scientific issues.These symposiums center on the activities of the Divisions and the Liaison Committees of SCJ,and draw on the cooperation of various academies and associations.
In FY2002,SCJ hosted two open lectures and a total of133symposiums.
Furthermore,SCJ jointly hosted with the Cabinet Office and Nippon Keidanren(Japan Business Federation)the"First Conference on the Promotion of Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration"in Kyoto in June2002,and the"Second Summit on Industry-Academia-Government Collaboration"in Tokyo in November2002in order to promote collaboration between industry,academia,and government.SCJ also hosted the"Regional Pro-motion Forum"in Kobe in November and in Sendai in December.
| 3.3.1.2.2Independent Administrative Research Institutes,National Research Institutes,and Public Research Institutes |
Independent Administrative Research institutions,National research institutes,and semi-governmental research institutes are assigned with the task of achieving policy targets.It is critical for these organizations to carry out prioritized research and development that centers on basic,pacesetting research to improve in the nation's science and technology level.They should also carry out systematic and integrated research that sets concrete targets in line with policy needs.Public research institutes that belong to local governments shoulder responsibility for carrying out technical development and providing technical guidance that meets the needs of local industry and region.
Note70)ICSU:The International Council for Science
Note71)ACSC:Asian Conference on Scientific Cooperation
Note72)SCA:Science Council of Asia
| (1)Research Activity at Independent Administrative Research Institutions and National Research Institutes |
Independent Administrative Research Institutions,National research institutes including the National Geography Institute and the Hydrographic Department of the Japan Coast Guard promote a variety of specialized research activity.The national research institute expenditures,which consist of the total expenditures including experiment and research expenditures,personnel expenditures,and facilities expenditures,came to496.1billion yen in FY2002.
In addition,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology utilizes the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology to promote the following measures:
1.Development of Centers of Excellence(COEs)at national research institutes.These COEs should possess research environments that bring together exceptional researchers from a-round the world,and produce exceptional research results that are disseminated world-wide.
2.Implementation of flexibility promoting re-search that promotes concentrated research utilizing fixed-term appointment programs at national research institutes,for the purpose of developing a flexible,competitive,and open research and development environment.
Additionally,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology implements the Science and Technology Special Research Fellow-ship Program that is designed to reinvigorate the national research institutes by dispatching young researchers to these organizations.
| (2)Research Activities at Public Corporations |
Research activities at public corporations,the definition of which also includes special authorized organizations,are primarily carried out with the assistance of government capital investments,government subsidies,and capital investments from private enterprise.Together with the national research institutes,these public corporations play an important role as part of the research activities of the national government.Public corporations bring together a broad range of personnel from the public realm and from private enterprise,and are capable of flexible management,as well as being able to accept investments from private industry.These factors make public corporations ideal candidates for efficiently promoting target-oriented research and development.Public corporations play a major role at a time when research and development is characterized by size and complexity.Moreover,based on the"Reorganization and Rationalization Plan of Public Corporations"(Cabinet decision,December2001),public corporations that under-take research activities along with other public corporations will be converted into Independent Administrative Corporations after October2003,thereby putting into place a system in which they can implement more enhanced,effective,and efficient research activities.
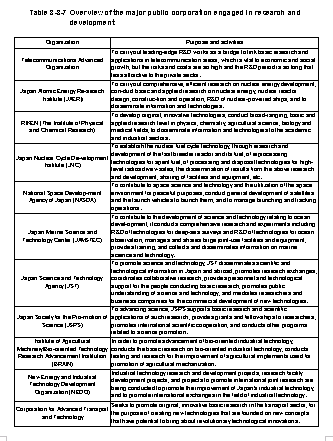
Such a system should be implemented using a comprehensive approach.As discussed in Chapter3.3.1.1.1,Developing a Competitive Research and Development Environment 73) ,public corporations utilize competitive funding to carry out basic research and implement programs such as the Exploratory Research for Advanced Technology operated by the Japan Science and Technology Corporation(JST),and the Frontier Research System of RIKEN.The objectives and tasks of the main public corporations that carry out research and development are shown in Table3-3-7 .
Note73)Refer to3.3.1.1.1Developing a Competitive Research and Development Environment
| 3.3.1.2.3Private Sector Research and Development |
It is critical for the nation to reinvigorate the research and development activities of the private sector,which play an important role together with the activities of the national government.Therefore,it is important for the national government to increase the drive for a broad range of private sector research and development activities,based on the fundamental concept of self-reliance among the private sector.
| 3.3.1.2.3.1Promoting Private Sector Research Activity through the Taxation System |
The measure within the taxation system that aims to promote research and development by the private sector is the Tax Credit for Experimental and Re-search Expense Increments,which provides a certain percentage tax exemption on incremental amounts in the event of increased experimental and research expenses.
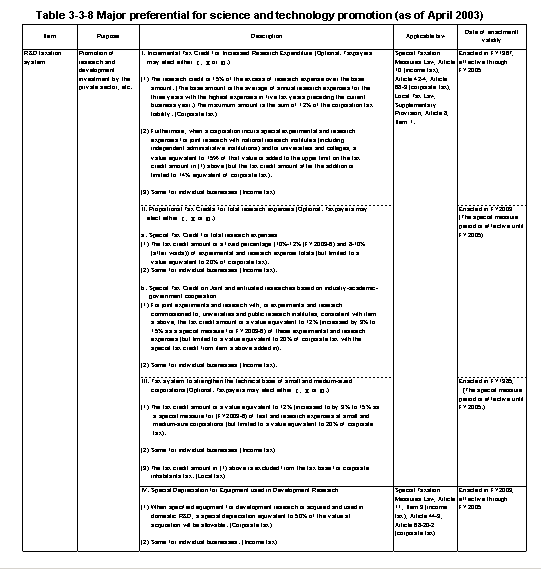
Revisions to the taxation system in FY2003 included-following a fundamental reexamination of the R&D taxation system-a set of special tax exemptions applied to gross experimental and research expenses and to joint research in industry-academia-government collaborations and commissioned research,and special depreciation allowances for equipment used in research and development.In addition,the Tax Credit for Experimental and Research Expenses Increments was extended to FY2005.The Tax System for Promotion of Research Exchanges(special measures concerning the tax base for corporations subject to Article34of the Civil Law that develop facilities on the grounds of governmental institutions specified in the Law for Facilitating Govern-mental Research Exchanges for the purpose of joint research with the relative governmental institution)was extended to FY2004.The tax exemption percentage under the Tax Measures for Strengthening the Technological Foundation of Small and Medium-scale Enterprises was expanded from10%to12%,and term limits were removed.
Table3-3-8 shows the current tax measures through April2003that are related to the promotion of science and technology,including the measures introduced in this section.
| 3.3.1.2.3.2Promoting Private Sector Research Activities through Investment and Loans |
To promote research activities in the private sector,fiscal investment and loan systems for technology development are implemented by the various government-affiliated organizations.The following section introduces some of the main examples.
| (1)Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Association |
The Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Association(BRAIN)was established in October1986with the aim of promoting experimental research in the private sector concerning designated industrial technology of biological systems.Using funds from the Industry Investment Special Account and from private sources,etc.,the Center provides funds and conditional interest-free loans,as well as referrals for joint research.In FY2001,funds from the Industry Investment Special Account totaled3.1billion yen.
| (2)Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research |
The Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research(OPSR)started operating in October1987with the aim of promoting experimental research in the private sector concerning medical products technology and similar matters.Using funds from the Industry Investment Special Account and private sources,the organization provides conditional interest-free loans and funds,and encourages joint research activities.In FY2001,the funds from the Industry Investment Special Ac-count totaled2.1billion yen.
| (3)Other Financial Provisions |
To ensure development of new technologies re-cognized as being able to contribute to a major improvement in the level of Japan's industrial technology,the Development Bank of Japan implements the New Technology Research and Development Loan Program to provide long-term,fixed,low-interest loans to corporations,for development costs related to new technologies.
| 3.3.1.2.3.3Promotion of Private Sector Research Activities through Subsidies |
A system of subsidies is made available to support research and development aimed at commercialization by the private sector.The main subsidies are as follows:
| (1)Subsidies for Pharmaceuticals to Treat Rare Diseases |
To support research and development on drugs,etc.,for diseases that afflict very few Japanese,subsidies are provided for costs related to experimental research for applicable pharmaceuticals,etc.
| (2)Research and Development Project for Advanced Industries in the Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries Industries,and the Food Industry |
To strengthen activities of the agriculture,forestry,fisheries,and food sectors,and to promote the creation of new industries and new technologies that can contribute to economic structural reform,subsidies are being provided to promote private sector research and development in the biotechnology sector,and to promote the practical application of exceptional research results obtained at independent administrative research institutes.
| (3)Technology Development Project for the Creation of Collective Private Agribusiness |
In order to stimulate agribusiness,support is given for research and development that utilizes the potential of universities and independent administrative corporations and is conducted by private-sector enterprises that assume the task of turning research results into practical applications.
| (4)Research and Development Project to Create New Enterprises |
As part of the Millennium Project,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries used joint research groups that bring together private-sector enterprises,etc.,to implement research and development toward realization of functional crops that can protect against lifestyle-related diseases.And in FY2001,the Ministry used the joint research group method to bring together local industry,academia,and government to conduct R&D in such research sectors having local characteristics.
| (5)Technology Developing Project for Strengthening Industrial Infrastructure |
To strengthen the technological infrastructure of Japan's food industry,projects are subsidized after themes have been selected based on the evaluations of outside specialists and experts on specific topics canvassed from enterprises following the government's indication of technological topics.
| (6)Subsidies for Research and Development of Creative Technologies |
From the perspective of technology development and improving the technological capabilities of small and medium-scale enterprises,subsidies are provided for costs related to the development of creative new products,and the research and development of new technologies.
| (7)Subsidies for Cutting Edge Technology Research and Development |
The Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan(TAO)subsidizes the research and development costs for venture enterprises carrying out cutting edge R&D related to telecommunications technologies that will lead to the creation of new business in the future.
| (8)Subsidies for Research and Development into Improvement of Communications and Broadcast Services for Elderly and Disabled People |
The Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan(TAO)provides private sector corporations,etc.,with subsidies for research and development costs necessary to the development of communications and broadcast services for the elderly and disabled.
| (9)Program for Support(Subsidy)of Technology Development for Creation of New Industries |
To support particularly promising research and development from a regional perspective,and to nurture groups of corporations with world-class technological capabilities,subsidies are provided to private sector corporations,etc.,for research and development costs related to technology that contributes to the creation of new industries.
| (10)Program for Support of Research into Private-Sector Infrastructure Technologies |
In order to promote experimental research into infrastructure technologies conducted in the private sector related to the mining,manufacturing,electro-communications and broadcasting industries,public applications are invited for entrustment research contracts.Applications are accepted by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization,for mining and manufacturing technologies,and by the Telecommunications Advancement Organization of Japan,for communications and broadcasting technologies.
| (11)Program for Technology Development Aimed at Practical Use |
To strengthen industrial technology in the private sector,the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization(NEDO)provides financial support on a cost-sharing basis to private sector enterprises for development of practical new technologies aimed at creating new markets or responding to social needs.
| (12)Subsidies and Consignment Expenses,etc.,Conducted under the Small Business Innovation Program |
This program is described under the section entitled,"3.3.2.4,Developing an Environment to Invigorate High Tech Ventures."
| 3.3.1.2.3.4Other |
A number of measures are being implemented to ensure the availability of superior personnel at small businesses,venture businesses,and other corporations that have just started business operations.These measures include the promotion of personnel exchanges between universities and industry,etc.,in order to nurture and produce personnel with an entrepreneurial sprit,to implement model research for courses offered on leading entrepreneurship at universities,etc.,to further promote internships at venture businesses,etc.(student enterprise experience program),and to encourage university graduates to go into venture business operations.
Additionally,to support the creation of new businesses through entrepreneurial activities within corporations or through corporate spin-offs,a share conversion and share transfer program is being implemented to ensure smooth reform of corpora-tion organizations through the use of corporate spin-offs and holding companies,etc.In addition,studies have commenced into development of a legal system for breaking up companies.
The Law for Promotion of New Enterprises is intended to promote the creation of new enterprises that make use of local industrial resources such as technology or personnel,etc.,and offers support for business activities that utilize the new technologies of small and medium-scale corporations,for development of a general support system from re-search and development up to commercialization,and for development of facilities that promote the expansion of businesses that utilize research results.
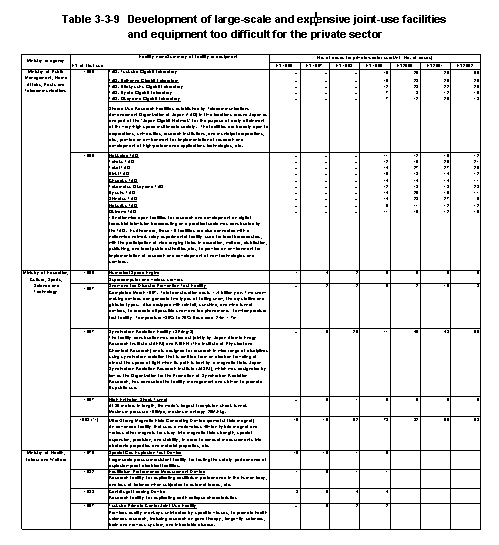
In addition,when preparation by the private sector is difficult because of the need for large-scale and joint-use facilities,the national government is prepared to undertake the preparation of facilities and equipment for joint use with the private sector (Table3-3-9) .
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |