| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.2 3.2.2 3.2.2.3 | ||
The field of the environment is an essential area of science for preservation of the natural environment,including ecological systems with their diverse forms of life,for maintenance of human health and preservation of the living environment,and for maintaining the foundations for the future survival of mankind.For Japan,a country without a great deal of space and possessing few natural resources,the environment sector is important to the nation,and leading the way ahead of other countries in environmental efforts is extremely important.
The New Basic Environment Plan passed by the Cabinet in December2000,based on the"Basic Environment Law,"lists the four concepts of"Environmentally Sound Material Cycle,""Harmonics coexistence,""participation,"and"international activities"as long-term goals toward the transition to a sustainable society,and positions science and technology as one important policy method for practical implementation of these goals.
Moreover,the Strategy for Promotion of the Environmental Sector(drawn up in September2001by the Council for Science and Technology Policy)adds"research into building a society in coexistence with nature"to the Second Science and Technology Basic Plan,to go alongside the already incorporated"research for the resolution of global environment problems,""research into building a recycling society,"and"research into comprehensive management of chemical substances,"and positions these four research areas as priorities.The strategy selects five subjects as meriting particular priority in the environment sector,including:(1)research into global warming;(2)research into zero-garbage and resource recycling technologies;(3)research into drainage basin and urban renewal technologies for coexistence with nature;(4)research into technologies for comprehensive risk management of chemical substances;and(5)research into global scale changes in the water cycle.The strategy also calls for comprehensive rebuilding of the individual research projects taken up by the various ministries,for promotion of scenario-guided initiatives that set the route to a solution that achieves the common policy goals of the government as a whole.
Of these five subjects,the first three were targeted as priority topics for FY2002.Furthermore,the"Biomass Nippon General Strategy"(adopted by the Cabinet in December2002)offers support for utilization of existing com-posting and animal feed conversion technologies,and for the development and commercialization of technologies for the production and manu-facture of value-added products from biomass,including waste products.
In addition,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology established the Committee on Global Environmental Science and Technology under the auspices of the Council for Science and Technology's Subdivision on Research and Development Planning and Evaluation,and in June2002the new committee issued a report,"On Policy for Promotion of Research and Development Related to Global Environmental Science and Technology."
There is an increasing need for efforts in science and technology toward resolution of global environmental problems,and Japan is actively moving ahead in this area,through the research and development projects detailed below.
| 3.2.2.3.1 Research into Solutions for Global Environmental Problems |
In recent years,global warming and other global-scale environmental issues have become imminent,and these issues urgently require international cooperation in their resolution.Japan has established the Council of Ministers for Global Environment Conservation to assure close cooperation between the relevant administrative institutions regarding measures implemented to address environmental problems with severe global effects,and to ensure the effective and comprehensive promotion of these measures.The council is currently actively engaged in these global environmental problems.
For example,the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development(UNCED 10) ,or Earth Summit),held in the Brazilian city of Rio de Janeiro in June1992,ratified the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development,"as well as"Agenda21,"an action program for the principles mentioned in the Declaration.As Japan's response to Agenda21,the Council of Ministers for Protection of the Global Environment Conservation adopted the"National Action Plan for Agenda21."In addition,in June1997,the special session of United Nations General Assembly on Environment and Development(UNGASS)adopted the"Program for the Further Implementation of Agenda21,"to hold meetings of the U.N.Commission on Sustainable Development(CSD 11) )as the venue for following up on the progress of the program.In addition,the World Summit on Sustainable Development(WSSD 12) )was held in Johannesburg,South Africa in August and September2002,at which time the"Johannesburg Declaration on Sustainable Development"and a comprehensive"Plan of Implementation"document to serve as action guidelines for participating countries were adopted.The science and technology section of the"Plan of Implementation"included promotion of organized monitoring of climate change.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is an international treaty that went into effect in1994to address the problem of global warming.The treaty's purpose is to stabilize the density of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at a level where climate systems are not endangered by human interference.Furthermore,the Third Conference of Parties to the Convention(COP3 13) )held in1997adopted the Kyoto Protocol,which incorporated legally binding numerical commitments regarding amounts of greenhouse gas emissions in advanced nations and other emerging market economies,and agreed to institute the so-called Kyoto Mechanism as one method for ensuring the commitments were kept.
In Japan,the Headquarters for Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures drew up a new"Outline for Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures"in March2002,followed by ratification of the Kyoto Protocol on June4,2002.In response,the Headquarters in July drew up"Preparations of a Program for Utilization of the Kyoto Mechanism."In October of the same year,COP8 was held in Delhi,India,where it was decided to seek early ratification of the Kyoto Protocol so that the protocol can come into force at an early date.Regarding research and organized monitoring,the COP8 participants agreed to pro-vide information for international research pro-grams and to study items related to climate change on a regular basis.
Note10)UNCED:United Nations Conference on Environment and Development
Note11)CSD:Commission on Sustainable Development
Note12)WSSD:World Summit on Sustainable Development
Note13)COP:Conference of the Parties
| 3.2.2.3.1.1 R&D and Related Measures for Understanding Phenomena on a Global Scale |
Global warming,ozone depletion,ocean pollution and other global problems are closely related to the social activities of human beings and are likely to make a serious impact on them.For this reason,there is a strong demand that scientific under-standing of these phenomena be achieved and that appropriate measures be taken.
Since phenomena such as global scale environment problems have extensive implications in terms of time or space,and are not confined to a single country,it is of crucial importance to maintain a sense of global partnership in promoting R&D in earth science and technology.Accordingly,it is important that Japan play an active role in the World Climate Research Programme(WCRP 14) ),the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme(IGBP 15) ),and other international research programs,and to promote joint research with research institutions abroad.In particular,in consideration of Japan's geographical position within the Asia-Pacific region and its close economic relationships with the countries of the region,Japan should be promoting research and development that gives priority to this region.
Promoting the international distribution of global monitoring information is important for the elucidation of various global-scale phenomena.Japan is an active participant in and contributes to the Global Observation Information Network(GOIN 16) ),the Committee on Earth Global Observation Satellites(CEOS 17) ),and the Integrated Global Observing Strategy Partnership(IGOS-P 18) ).In addition,the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC 19) )was established in1988to bring together recent scientific information regarding climate change and to provide that information to governments of other countries,and three reports have been filed to date.Japan needs to be more active than it has been in providing scientific knowledge useful in forecasting global warming and evaluating its effects.
The fourth report is expected to be ready in2007.Japan needs to be more active than it has been in providing scientific knowledge useful in forecasting global warming and evaluating its effects.
To promote research on global environmental change for the three major parts of the world,i.e.,North and South America,Europe,and Asia and the Pacific,intergovernmental networks were established.In the Asia-Pacific region,the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research(APN 20) )was established,and Japan has been actively supporting its research activities primarily through the APN Center opened in Kobe,Japan.
For Japan's research and development efforts in this area,the government ministries and agencies make use of their own respective budgets and also utilize such funds as the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology and the Global Environment Research Fund,to combine the research capabilities over a broad range of sectors from national research institutes,independent administrative entities,universities,and even research institutes located overseas,for active promotion of research and development.
Note14)WCRP:World Climate Research Programme
Note15)IGBP:International Geoshere-Biosphere Programme
Note16)GOIN:Global Observation Information Network
Note17)CEOS:Committee On Earth Global Observation Satellites
Note18)IGOS:Integrated Global Observing Strategy
Note19)IPCC:Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Note20)APN:Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research
In FY2002,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology brought together intellectuals from research institutions in industry,academia,and government to launch the"Project for Sustainable Coexistence of Human,Nature and Earth,"which consists of two operating missions,"The'Japan Model'mission for the prediction of global warming"that aims for highly precise forecasts of warming trends,and a"Mission for prediction of hydrological cycle variation"for the purpose of forecasting the extent of water resources and water-based disasters in the future.
At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the"Earth Simulator"system,one of the world's fastest supercomputers,which was developed jointly by the National Space Development Agency of Japan(NASDA),the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI),and the Japan Marine Science and Technology Center(JAMSTEC),was subjected to the Linpack benchmark test(the world's most major method to measure a computation performance of super-computers)in April2002and successfully confirmed the world's highest computation performance.Utilization of this system will be helped to obtain an accurate understanding of global-scale phenolmena,toward realization of highly precise forecasting of global change.
The Frontier Research System for Global Change(FRSGC),a joint project of NASDA and JAMS-TEC,promotes six research programs,including climate variations research,hydrological cycle research,global warming research,atmospheric composition research,ecosystem change research,and integrated modeling.In addition,the"Frontier Observational Research System for Global Change(FORSGC)"performs basic observational research in two research programs,for observation of climate change,and observation of the hydrological cycle,under these projects,two research cooperation with the United States is carried out at the International Pacific Research Center(IPRC 21) )located at the University of Hawaii and the International Arctic Research Center(IARC 22) )at the University of Alaska.
For promotion of strategic basic research,Japan has established such research programs as the"mechanisms of global change"and"hydrological modeling and utilization systems,"to promote basic research toward achievement of strategic goals laid down by the national government.
The Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications'Communications Research Laboratory is currently engaged in international joint research with the United States,primarily with the University of Alaska,within the framework of the Japan-U.S.Science and Technology Cooperation Agreement,to promote comprehensive research into technologies for observation and measurement of the arctic atmosphere,from the troposphere to the thermosphere.
Japanese Antarctic research program,which were begun during the International Geophysics Year of1957,are centered on the National Institute of Polar Research,in cooperation with relevant governmental agencies.The Headquarters for the Japan Antarctic Research Expedition(JARE)has been established within the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology(MEXT)under the chairmanship of its Minister.
In FY2002,the forty-third wintering expedition and the forty-fourth expedition carried out regular observations of ocean and atmospheric phenomena around Showa Station,and also performed monitoring observations,etc.,for the purpose of elucidating environmental changes on a global scale.
Note21)IPRC:International Pacific Research Center
Note22)IARC:International Arctic Research Center
| 3.2.2.3.1.2 R&D of Earth Observation Technology |
In order to collect the information required for elucidation of various global-scale phenomena,satellite and ocean observation of the Earth and research and development into Earth observation technologies is important.
| (1) Earth Observation Technology Using Satellites |
Satellite-based Earth observation is an extremely effective method for repeated and continuous acquisition of various information covering wide areas.Japan is currently engaged in comprehensive promotion of this activity toward resolution of global environmental problems,in cooperation with related organizations in Japan and abroad.
The Communications Research Laboratory(CRL)is promoting development of superconducting submillimeter wave rim radiation sounders mounted on the exposed part of the station's Japanese Experiment Module(JEM 23) ;also known as"Kibo")on the International Space Station.CRL is also studying technology for measurement of global environmental changes from space.
At the National Space Development Agency of Japan,data is currently
being collected from a precipitation radar(PR 24) )mounted
on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission(TRMM 25) )satellite
of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration(NASA),launched in November1997,from
the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS(AMSR-E 26) )mounted
on the NASA Earth Observing System(EOS)Aqua satellite launched in May2002,and
from the Advanced Earth Observing Satellite-![]() (ADEOS-
(ADEOS-![]() 27) )"Midori
27) )"Midori
![]() "launched in December2002.Moreover,the National Space Development Agency
of Japan is currently engaged in development on the Advanced Land Observing Satellite(ALOS 28) ),in
development research on the Global Warming Gas Observation Technology Satellite(GOSAT 29) ),and
is also proceeding in cooperation with the relevant organizations toward development
of a satellite mission for global rainfall measurement,and an international mission
for monitoring cloud cover and radiation.
"launched in December2002.Moreover,the National Space Development Agency
of Japan is currently engaged in development on the Advanced Land Observing Satellite(ALOS 28) ),in
development research on the Global Warming Gas Observation Technology Satellite(GOSAT 29) ),and
is also proceeding in cooperation with the relevant organizations toward development
of a satellite mission for global rainfall measurement,and an international mission
for monitoring cloud cover and radiation.
The Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry is currently engaged in joint operations with the National Space Development Agency of Japan for operation of the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflectance radiometer(ASTER 30) ),a resource exploration sensor mounted on the NASA global observation satellite(Terra),and for development of the next-generation Phased Array Type L-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar(PALSAR 31) )to be mounted on ALOS.It is also engaged in development of the ground-based processing and analysis technologies required for the observation data obtained from the satellite sensors.
The Meteorological Agency is promoting development of the Multi-functional Transport Satellite(MTSAT 32) ),as a successor to the currently operational Geostationary Meteorological Satellite Himawari No.5.
Under the Ministry of the Environment,valuable observation data
obtained from the Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer(ILAS 33) )and
the Retroreflector In Space(RIS 34) )ozone
monitoring sensors,which were both mounted on the ADEOS-![]() "Midori"that
ceased operation in June1997,are currently being used for assessing the global
environment,and causes of environ-mental change.
"Midori"that
ceased operation in June1997,are currently being used for assessing the global
environment,and causes of environ-mental change.
In addition,various tests are being performed toward normal
operation of the next-generation ozone monitoring sensor,the Improved Limb Atmospheric
Spectrometer-![]() (ILAS-
(ILAS-![]() 35) )to be
mounted on the ADEOS-
35) )to be
mounted on the ADEOS-![]() "Midori
"Midori ![]() ",and research has been undertaken
on sensors to be used mainly for monitoring greenhouse gases and the ozone layer
destructive substances.
",and research has been undertaken
on sensors to be used mainly for monitoring greenhouse gases and the ozone layer
destructive substances.
Furthermore,the Ministry of the Environment has set out to develop a method that uses remote sensing information for the understanding of regional water-retention capabilities.
For the establishment of Earth environmental observation and processing techniques using satellites,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology is promoting research into Earth environment remote-sensing technology,in cooperation with related organizations:the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries is conducting research and development of remote-sensing technology to assess land use,planting areas,and growing conditions,while the Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Transportation is promoting the monitoring of the national land environment based on the satellite remote-sensing technology.
As use of the data collected from satellites is important,NASDA's Earth Observation Research Center is cooperating closely with related organizations to promote research that utilizes Earth observation data,and development of an Earth observation information network.
Note23)JEM:Japanese Experiment Module
Note24)PR:Precipitation Radar
Note25)TRMM:Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission
Note26)AMSR-E:Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-E
Note27)ADEOS-![]() :Advance Earth Observing Satellite-
:Advance Earth Observing Satellite-![]()
Note28)ALOS:Advance Land Observing Satellite
Note29)GOSAT:Greenhouse gas Observing Satellite
Note30)ASTER:Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflectance radiometer
Note31)PALSAR:Phased array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar
Note32)MTSAT:
Note33)ILAS:Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer
Note34)RIS:Retroreflector In Space
Note35)ILAS-![]() :Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer
:Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer ![]()
| (2)Ocean Observation Technology |
The oceans are strongly related to many global-scale phenomena on earth and they are very important to make clear the roles of oceans for environmental changes,and elucidation of the roles that they play is an important issue.To advance knowledge in this area,the Japan Marine Science and Technology Center is promoting several areas of R&D for ocean observation technology,including research and development of the TRITON buoy at mid and high latitudes,and JAMSTEC-Compact Arctic Drifter(J-CAD).Also,the oceanographic research vessel"MIRAI"was used to conduct research monitoring the western Pacific Ocean and the Arctic Ocean.
The Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications promoted the development of extended-range marine radar to be put into Ishigaki Island and Yonaguni island,to perform long-term observation of the Kuroshio Current flowing northward through the East China Sea continuously.In addition,research is being conducted into development of high-resolution three-dimensional microwave visual radar and of shortwave marine data,which contribute to the establishment of methods for monitoring marine oil pollution,currents,and waves and for forecasting changes in the global environment.
To observe the global ocean in real time,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and the Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Transport have begun developing for establishing an advanced ocean observing system(Japan ARGO 36) )since FY2000.This project is planned to deploy an array of profiling floats to measure temperatures and salinity profiles of the upper2,000m in the ocean in cooperation with the global ocean observation system,Argo,which aims to establish a global3,000float array.
In addition,the Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry is promoting research on the mechanism for CO2 circulation in the Pacific Ocean.
The Ministry of the Environment is promoting research into utilization of satellite remote sensing technology,a special method for monitoring the ocean environment,as a part of the Northwest Pacific Regional Ocean Action Program(NOW-PAP)promoted by the United Nations Environment Program(UNEP)in the Sea of Japan and the Yellow Sea.
Note36)ARGO:Signify the capital letters of an abbreviation of Array for Real-Time Geostrophic Oceanography(ARGO),it is today generally taken to mean the Greek ship"Argo,"which was the ship belonging to the Greek mythic hero Jason.The name has a nuances of corporation with the satellite.
| (3) Research and Development of Stratospheric Platforms |
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and the Ministry of Public Management have started a collaboration to pursue research and development into stratospheric plat-forms,which are stationary units positioned in the stratosphere,and equipped with observation sensors and radio transmitters,etc.,for use in Earth monitoring,telecommunications,and broadcasting,etc.
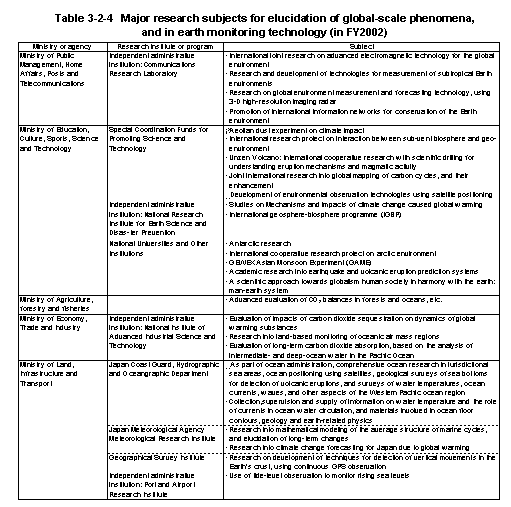
Major research subjects promoted in relevant ministries and agencies in the area of Earth science and technology are as shown in Table3-2-4 .

| 3.2.2.3.2Research into Building a Recycling Society |
In order to secure sustainable growth of the economy and society in Japan's future,R&D is needed for the introduction of production systems that reduce to a minimum the input of resources and the emission of wastes,etc.,and to create a recycling-based society that effectively utilizes resources and restricts the generation of wastes,etc.,through the use of nature's own recycling functions and the other functions of biological resources.
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology established the"Roundtable Discussion for Science and Technology Toward Realization of the Sustainable Economic Society"to study how science and technology should be applied to this sector.Based on the report of the study,the ministry launched a new research and development project for economic revitalization in FY2002,"a project to design sustainable management and recycling system of biomass,general and industrial wastes"to promote detoxification disposal or recycling of wastes generated by cities and regions,and also to pursue research and development into technologies for disseminating and encouraging commercialization of recycling,and design of economic and social systems.
The Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry is actively engaged in research and development for the full-scale promotion of recycling technologies in a wide range of areas,including:1)developmentof technologies for the recycling of containers and packaging,such as liquefaction of waste plastics,and for the expansion of recycling capabilities such as advanced technologies for recycling metal scrap;2)development of technologies related to thermal recycling(use of energy from waste incineration),such as expanded use of high-efficiency waste power generation and of wastes converted to solid fuel(RDF);3)development of technologies for the use of ash from incinerated wastes of urban areas as cement materials;and4)technology for the proper disposal and recycling of discarded consumer electronics and automobiles.
To promote environmental conservation measures and the effective use of organic resources,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries is promoting the development of innovative treatment and recycling technologies for farm animal wastes,including a method for clean-up of polluted water that utilizes methane fermentation vats,and technologies that use fermentation to convert food wastes into fertilizer and animal feed.The ministry is also supporting development of technologies that discourage the generation of food wastes and promote recycling,as well as technologies for introduction and commercialization of biodegradable substances that do not require separation into food containers,etc.
The Ministry of Land,Infrastructure,and Trans-port is promoting the development of technology for recycling of branches pruned during the maintenance and management of plants,the development of new geo-materials made from various wastes and research into applications of these to port and harbor facilities,the development of methods for strategic stock management of housing and social infrastructure capital,the development of technologies for restricting and recycling of wastes generated during construction projects,the formation of systems that promote utilization of recycled resources,and research into recovery of biomass from sewer sludge,etc.
The Ministry of the Environment is working toward formation of a recycling-based society through research and development of processing technologies for detoxification of dioxins and other toxic chemical substances generated in the course of waste processing,of technologies for safe recycling of plastics,etc.,and technologies for proper management of final disposal sites.Elsewhere,the ministry is engaged in research into elucidation of the mechanisms of generation of micropollutants at waste disposal and recycling facilities,and into control of their emissions,to reduce the attendant environmental risks.The ministry is also conducting research to clarify the long-term behavior of micropollutants buried in reclamation layers,and into the long-term control of risks attendant with micropollutants.
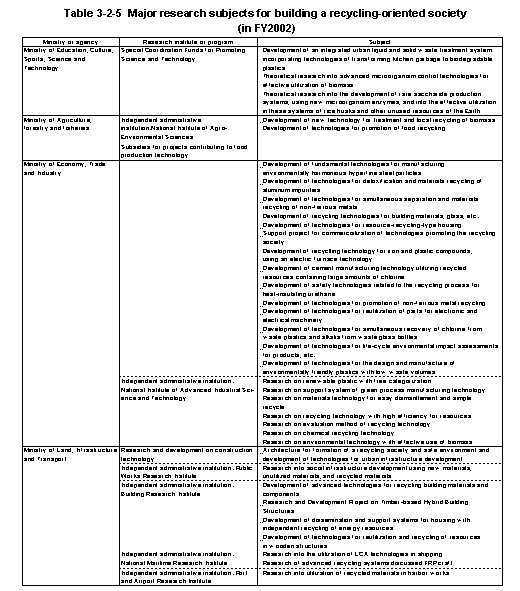
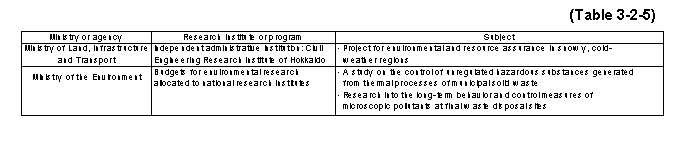
The major research topics currently being promoted by the relevant ministries and agencies are as shown in Table3-2-5 .
| 3.2.2.3.3Research Related to Building a Society that Co-Exists with Nature,Research Related to Comprehensive Management of Chemical Substances,and Research Related to Other Sectors |
| 3.2.2.3.3.1Research and Development Related to Biological Diversity |
With the extinction of wildlife species of wild animals proceeding at a speed never seen before,the"Convention on Biological Diversity"was adopted for the purpose of conserving the diversity of living things on Earth and their habitats,and conducting sustainable use of biological resources.Japan has responded with active measures,including adoption of measures for conservation of bio-logical diversity and assurance of sustainable use.Based on the Convention,the National Strategy of Japan on Biological Diversity,a systematic summary of Japan's basic policies and other measures from the viewpoint of conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in Japan,was updated on March27,2002by the Council of Ministers for Global Environment Conservation.The strategy calls for promotion of basic surveys for the purpose of scientific and objective data collection and facilitation regarding the current state of the natural environment and how it is evolving over time,expansion of ecological and taxonomic knowledge of living things,and basic research for the purpose of elucidating the structure and maintenance mechanisms of ecosystems.
Furthermore,there is a need to conduct comprehensive research to elucidate the natural order whereby a diversity of organisms,ranging from the higher animals,including man,to the smallest microorganisms can coexist while also undergoing change in the environment.The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries is promoting research into development of technologies for the promotion of sustainable agriculture that reduce the burden on the environment,for analyses of the mechanisms that enable plants to resist environ-mental stress,and technologies that encourage human coexistence with wild animals and birds while reducing their damage to agriculture and forestry.
The ministry is also promoting the development of technologies for elucidation of the mechanism for the water and materials cycle in drainage basins covering from mountain forests to coastal districts,for elucidation of the functions in agricultural,forestry,and fisheries ecological systems,as well as for maintenance and improvement of agricultural,forestry,and fisheries ecological systems.The ministry is also supporting development of methods for comprehensive management of drainage basin environments,including the cities located there.
| 3.2.2.3.3.2Research and Development Related to Antipollution Measures |
In the area of pollution prevention,the government adopts"Items Requiring Particular Priority in Tests and Research for Pollution Prevention"(prepared annually by the Ministry of the Environment)and promotes their priority in research and development.In recent years,research interests have turned particularly to finding countermeasures to environmental risks posed by chemical substances such asdioxins and endocrine disrupters.The relevant ministries and agencies are currently actively engaged in surveys and R&D toward the development of methods for testing and measuring these substances.
| 3.2.2.3.3.3Other |
The Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications is promoting research into an international information network technology for protection of the global environment,to facilitate the effective distribution of global environmental data.In addition,the Ministry of the Environment is using the Global Environment Research Fund to promote research into global warming forecasting,effects,and countermeasures.The Ministry of the Environment is using the Global Environment Research Fund etc.,to promote research into forecasting and alleviating the effects of global warming.The ministry also drew up the"Basic Plan for Environmental Research and Technology"in July1999to articulate specific policies for the comprehensive and planned promotion of environ-mental research and the development of environmental technologies.For the promotion of environmental research and environmental technology development,the Basic Plan called for more strategic planning,proposals,and promotion of environmental research programs overall,and for comprehensive studies and evaluations of the scientific knowledge required for specific environmental problems.
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries is promoting research into assessment methods based on environmental accounting systems in order to enable comprehensive evaluation of agriculture's diverse functions and of the burden on the environment,and is also engaged in monitoring greenhouse gases in the agriculture,forestry,and fisheries sectors,in the development of technologies for evaluation and prediction of global warming effects on agriculture,forestry,and fisheries,and in development of technologies in the forestry sector for absorbing and fixing greenhouse gases.The Ministry of Land,Infrastructure,and Transport is promoting the development of drainage basin restoration and recovery technologies that take the entire drainage basin into account for comprehensive hydrologic cycle management,as well as development of land and infrastructure technologies offering co-existence with nature.
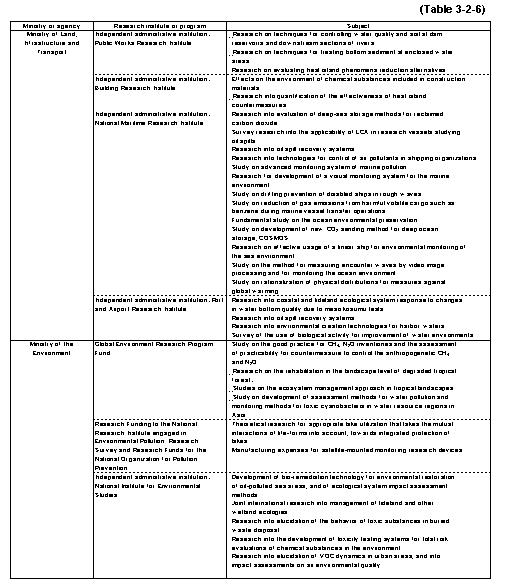
The major research topics currently being promoted by the relevant ministries and agencies are as shown in Table3-2-6 .

| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |