| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > Annual Report on the Promotion of Science and Technology 2002 > Part1 Chapter3 Section3 2 | ||
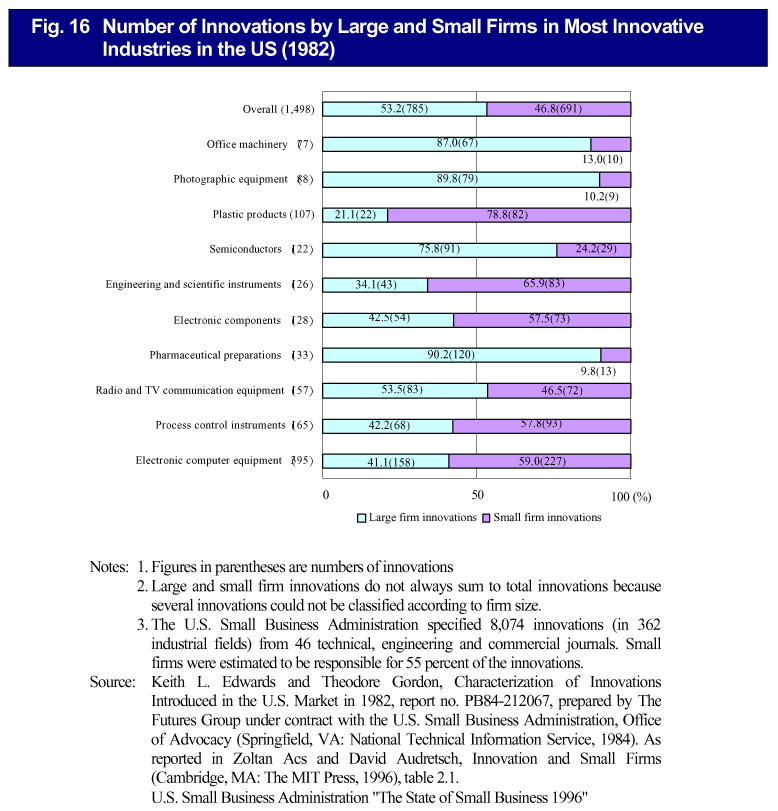
Recently venture companies have been the focus of attention as the key player in innovation. In the US, close to half of all innovations are created outside major companies ( Fig. 16 ). The environment of innovation activities in major corporations and venture companies differs in terms of the culture and size of the company, but both feature the soil to create innovations, and it is impossible to make generalizations as to which is more advantageous.
For Japan to promote entrepreneurs, more than anything else the existence of entrepreneurs themselves is vital, and initiatives to effectively develop and produce entrepreneurs are important. For this to be achieved, the provision of a support environment goes without saying, and it is necessary to foster a climate which chants the praises of entrepreneurs.
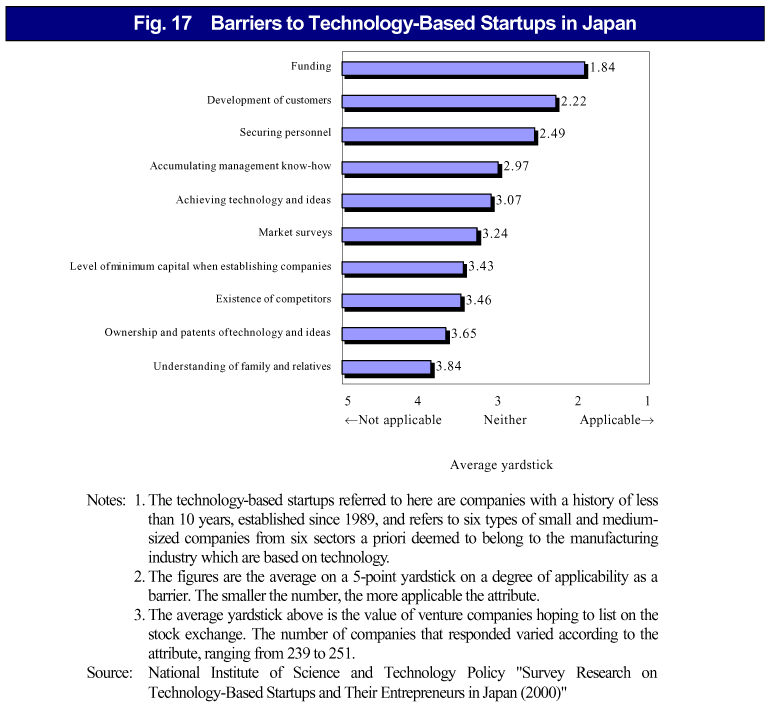
For venture start-ups, initiatives are called for to provide external support for the necessary resources (support personnel, equipment funds, development funds and sales funds, etc.) ( Fig. 17 ). Therefore, in addition to promoting the function of external resources such as venture capital and official support, it is necessary to put in place a support environment through appropriate legislation, establishing preferential tax measures, and adopting a comprehensive and effective approach.
Furthermore, in Japan, it is extremely important to alleviate the uncertainty and the incumbent risk in the success of venture startups by taking a national approach to developing and securing expert personnel and support personnel.
| (Development of Entrepreneurial Human Resources) |
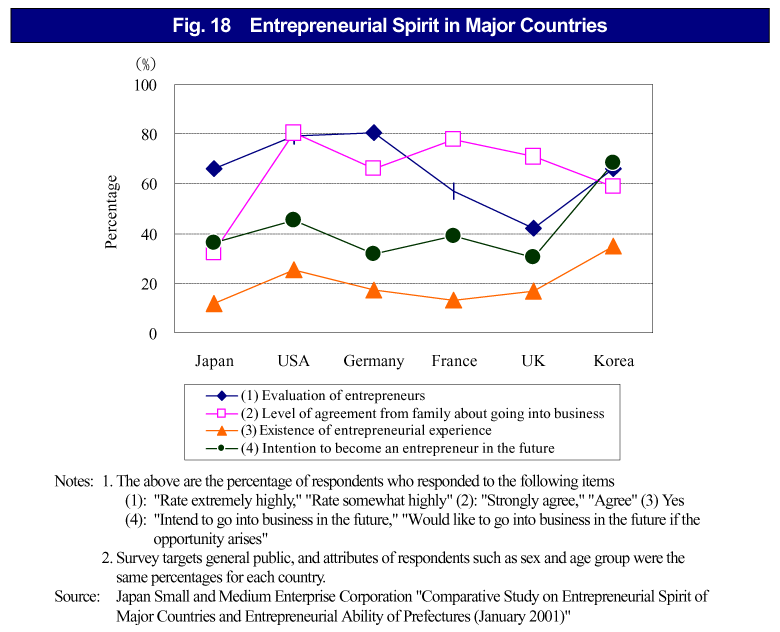
With regard to entrepreneurial consciousness, Japan is not inferior to other countries in terms of entrepreneurial intent, and entrepreneurs are regarded positively. However, as a major difference from other countries, Japan has a much lower percentage of cases where family members are in agreement with going into business ( Fig. 18 ). Generally in Japan the lifetime employment system has been established for many years, which is thought to suggest that a stability-oriented environment and climate has been developed.
In the future, in order to foster creativity and originality in young people, it is important to actively tackle understanding and work study about entrepreneurs.
| (Securing Support Personnel) |
A key issue facing research and development ventures is the securing of support personnel to build business strategies. For people that apply themselves to management, it is desirable that they are personnel with a wealth of practical experience, but the employment resources of venture companies are generally limited, and there is a strong inclination among support personnel to be employed by major companies, which makes it difficult to secure appropriate human resources.
In addition, in incubators, a variety of intangible support services such as business, technology and finance are being provided to entrepreneurs and venture companies with new technology and/or know-how. It is important to enhance the intangible aspects of incubators as organizations that support the gap in human resources lacking in venture companies and entrepreneurs.
| (Support by VC) |
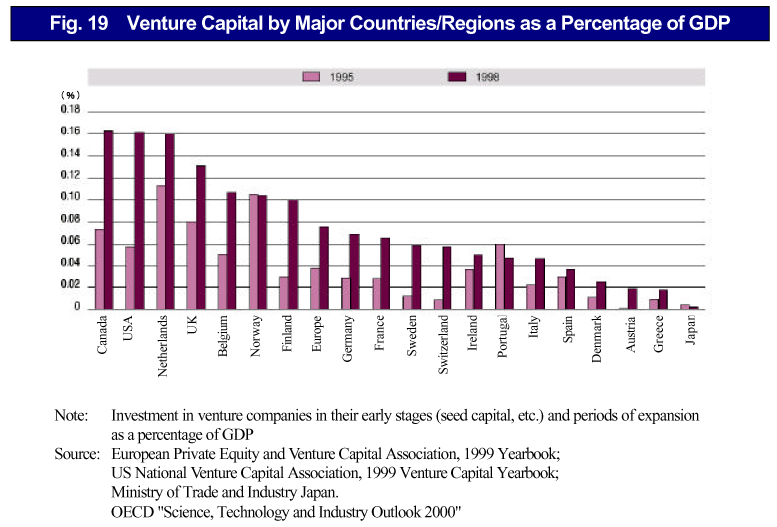
Indirect financing in the form of bank finances account for a relatively high percentage of the source of financing for Japan's venture companies, and Japan's amount of investment from VC is at the lowest rank compared to other major countries, so there is a lack of such investment in Japan ( Fig. 19 ).
VC are also expected to provide comprehensive support in the form of management guidance, technical evaluation and support for listing on the stock exchange. In Japan there is a need for increased "hands-on" investment like that which takes place in the US, where external employees of the company being invested in participate directly in management, providing a variety of support to improve corporate value.
| (Support by Angels) |
In Japan, the investment and loan organizations in the stages
of growth of venture companies are said to be non-continuous. In the US, with
regard to the introduction of external capital at startup, the existence of individual
investors called angel investors in the US play an important role, so in Japan
too it is necessary to promote systems to evoke individual investment and to
promote the understanding of investment.
| (University Ventures) |
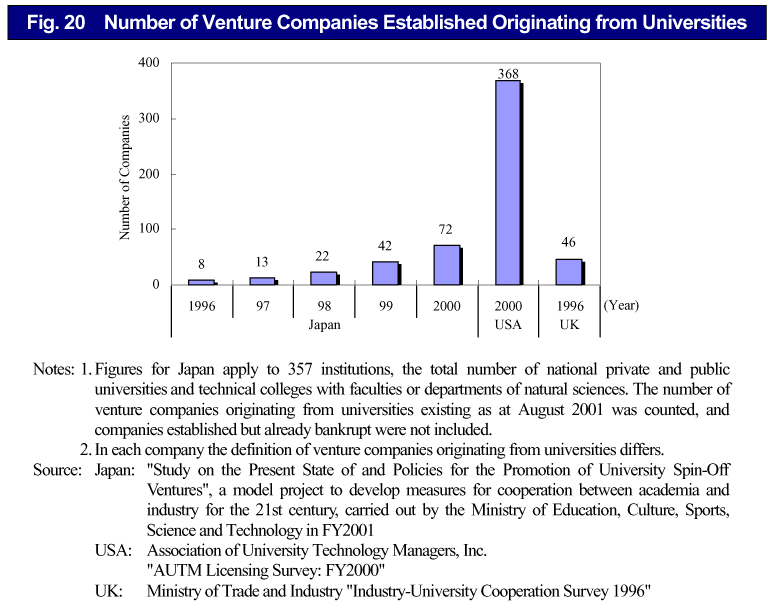
It is expected that the research achievements of universities will create new industries and contribute to solving social problems by presenting breakthroughs and new concepts. Although relatively low when compared with other major countries, the number of ventures established originating from Japanese universities is increasing as the years go by ( Fig. 20 ). In universities, it is important to heighten the awareness and understanding of entrepreneurship among researchers, and to promote venture companies originating from universities. In addition to support companies by enhancing startup funds and by putting in place venture development systems such as campus incubators, it is necessary to work towards creating an environment for the creation of venture companies originating from universities, by such means as developing and securing human resources to link the needs of economy and society with the seeds provided by universities.
| (Intra-Venture) |
Intra-ventures entail starting a new business within an existing company, with the company fulfilling the role of incubator, thereby allowing the venture to receive support such as utilizing corporate resources and receiving funding at startup. This makes them an effective support system in reducing risk and the lack of resources experienced by entrepreneurs.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |