| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part2 2.1 2.1.7 | ||
R&D expenditures break down into labor costs,materials,expenditures on tangible fixed assets(land and buildings,machinery,instruments,equipment and others)and lease fees(newly established in the FY2001 survey)and other expenses.
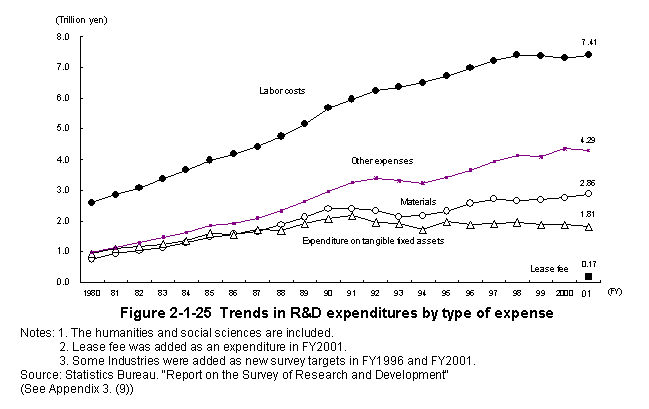
An examination of Japan's R&D expenditures by type of expense reveals that total labor cost increased for the first time in three years,registering a year-on-year increase of1.3%,to7.4078trillion yen.Materials expenditure has been increasing,with the total expenditures for materials increasing by3.7%in FY2001 over the previous fiscal year to2.8616trillion yen.The total expenditures for tangible fixed asset purchases decreased by4.2%to1.8067trillion yen over the previous fiscal year.The share of other expenses required for research,such as books and journals,utilities,travel,and telecommunications,etc.,decreased by1.1%over the previous fiscal year to4.2850trillion yen.Lease fee,introduced as a new survey category in FY2001,came to166.9billion yen (Figure2-1-25).
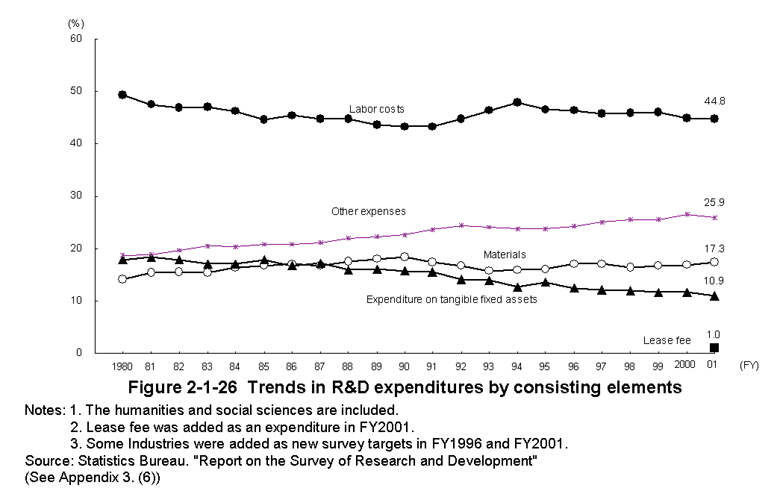
Moreover,the trends in the composition of expenditure reveal that while labor cost has long held the largest share of overall expenditure,that share has been declining in recent years.Tangible fixed asset purchase expenditure is declining.The shares of materials cost and other expenditures have remained almost the same (Figure2-1-26).
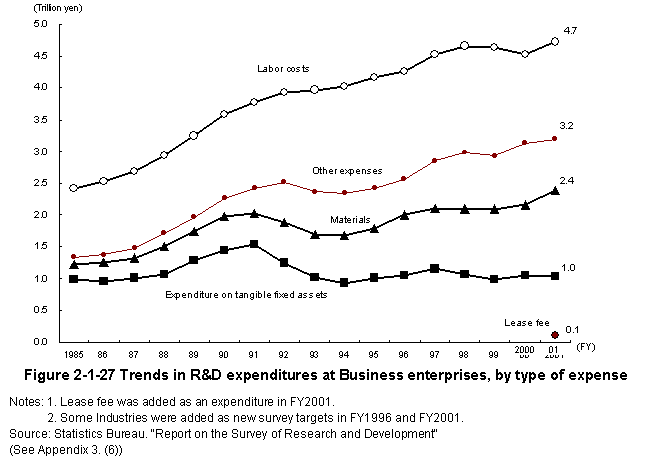
Company R&D expenditure by category rose with the exception of tangible fixed asset purchase expenditures and lease fees (Figure2-1-27).
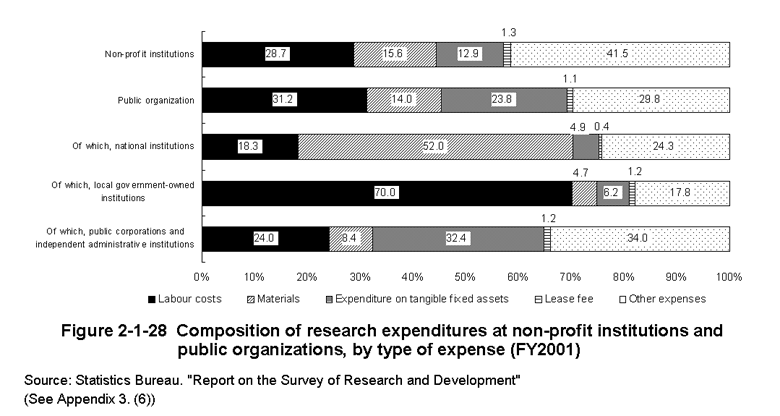
Non-profit institutions and public organizations had lower ratios than any other institutions on expenditures for labor cost,while their tangible fixed asset purchase expenditures showed higher ratios.When looking at expenditure by type of institution,local government-owned institutions were characterized by exceptionally high labor cost.On the other hand,public corporations and independent administrative institutions have higher ratios of expenditures for the purchase of tangible fixed as-sets because they include those requiring large-scale facilities and equipment for nuclear and space R&D (Figure2-1-28).
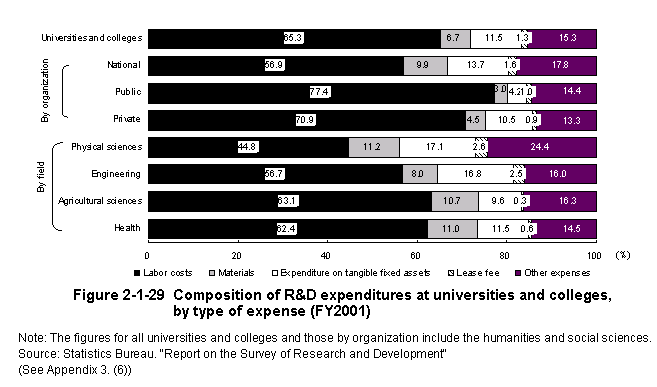
Universities and colleges had a higher share of labor cost than other institutions,accounting for about65%of expenditure,while raw material costs were the lowest in share.When looking at expenditure by the field of study within the natural sciences,all areas had lower than average shares of labor cost,while the physical sciences and engineering in particular tended to require larger than average shares of total costs for tangible fixed assets (Figure2-1-29).
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |