| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > JAPANESE GOVERMENT POLICICIES IN EDUCATION, SCIENCE AND CULTURE 1994 > PART II Chapter 5 Section 2 1 | ||
The Ministry of Education, Science and Culture provides school corporations with subsidies through the Japan Private School Promotion Foundation. The purpose of these subsidies, which cover essential current expenditures for education and research (including salaries of teaching staff and other employees and facility expenses for education and research), is to maintain and improve educational and research conditions in private universities, junior colleges, and colleges of technology and to reduce the financial burden on students and parents.
Subsidies are divided into general subsidies and special subsidies and are calculated according to certain criteria. Allocations of general subsidies are based on the number of teachers, other personnel, and students and are weighted according to various factors, such as
Special subsidies are paid in addition to general subsidies to schools that have implemented original educational and research activities that closely reflect society's needs, such as the expansion of graduate schools, the advancement of education and research, the development of international exchange in education and research, and the promotion of lifelong learning.
In recent years special subsidies have been expanded, and increased emphasis has been placed on the weighting of general subsidy allocations. These changes reflect the need to prioritize subsidies and ensure efficient utilization through policy guidance designed to encourage active management efforts to maintain and improve educational and research conditions and to expand original education and research activities.
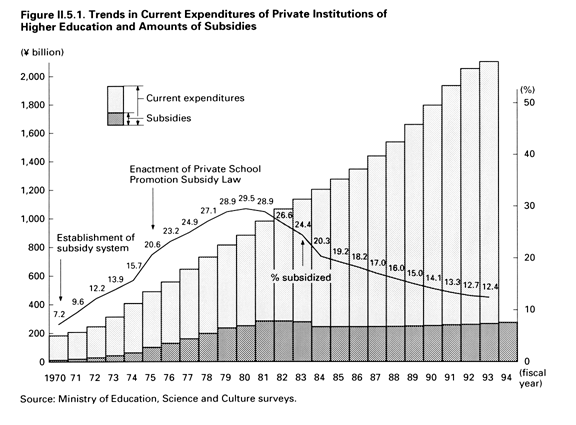
Despite the central government's extremely difficult fiscal situation, provision in the fiscal 1994 budget for this purpose was increased by 7.8 billion yen to 273.35 billion yen( Figure II.5.1,Table II.5.1 ). This figure included 47.5 billion yen for special subsidies. Budgeting in this area reflects the need to promote the advancement, individualization, and revitalization of education and research through active university reform efforts, as recommended in the reports of the University Council and other reports.
Subsidies are provided for expenditures on large-scale research equipment for private universities and graduate schools and for expenditures on large-scale educational equipment for private universities, junior colleges, colleges of technology, and special training colleges (postsecondary courses). The purpose of these subsidies is to promote scientific research and information processing education and other fields of education in private institutions of higher education and thus to help revitalize higher education.
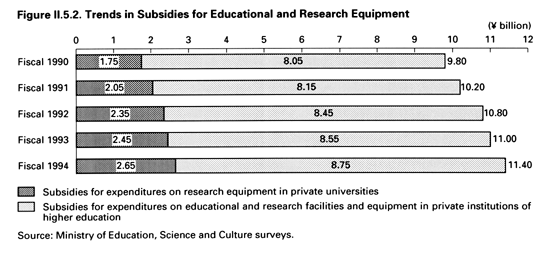
Subsidies for expenditures on educational and research facilities and equipment in private institutions of higher education were introduced in response to various recommendations, including the recommendation of the Ad Hoc Commission on Administrative Reform that priority be given to the subsidization of appropriate educational and research projects. The system has been enhanced progressively over the years, and in fiscal 1994 a total of 8.75 billion yen was allocated for this purpose. As in earlier years, priority targets for subsidies included advanced equipment for use in original postgraduate research and for use in information processing education that closely reflects social needs.
Subsidies for expenditures on research equipment in private universities have traditionally been provided to cover essential expenditures to improve research equipment and information processing equipment, which are defined as machinery and equipment needed for basic research.
The aim is to promote scientific research in private universities. In fiscal 1994 a total of 2,653.36 million yen was allocated for subsidies in this area ( Figure II.5.2 )
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |