| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > EDUCATIONAL STANDARDS IN JAPAN 1971 > CHAPTER |
||
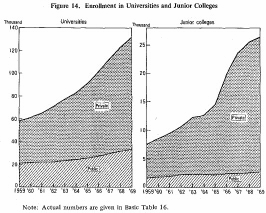
Enrollment in universities and junior colleges has increased rapidly in recent years, reaching 1,580,000 in 1969 (l, 320,000 in universities and 260,000 in junior colleges).
The increase was especially large in private universities and junior colleges. The proportion of students enrolled in private universities and junior colleges increased from 66% in 1959 (430,000) to 78% in 1969 (1,230,000). Seventy-five percent of the university students (990,000) and 90% of the junior college students (240,000) were enrolled in private institutions in 1969.
Note: Actual numbers are given Basic Table 16. Basic Table 16
Such an increase in enrollment was made possible by the establishment of new institutions, faculties and departments. The establishment of new faculties and departments within existing universities and junior colleges contributed greatly to the increase in enrollment. In 1969 there were 852 universities and junior colleges (379 universities and 473 junior colleges), 1.7 times as many as in 1959, while enrollment rose 2.4 times (2.3 times for universities and 3.5times for junior colleges). This shows that the size of institutions of higher education has tended to become large. There were only ten universities with an enrollment of more than 10,000 in 1959. By 1969, however, this number had increased to 32.This tendency has raised various problems.
In other major countries, the recent increase in enrollment has 11150 resulted in the expansion of the size of universities, and various administrative and managerial measures have been taken to meet this situation. Table 9 presents some large universities in various major countries.

New York State University and California State College, which enroll more than 100,COO students, are examples of affiliating universities which have consolidated various types of higher educational institutions within the states under the supervision of state regents so that higher education in these two states may be expanded according to a central plan. The University of London also falls into this category. On the other hand according to the Fundamental Law of Higher Education enacted in [968, the University of Paris in France is to be divided into thirteen independent universities to counter the tendency for the university to be come large scale due to enrollment increases.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |