Joseph Schumpeter, an Austrian economist, defined the term "innovation" for the first time. In his book "Theory of Economic Development," he stated that internal factors such as innovation play a main role in economic development, rather than external factors such as population growth and change of climate. He also stated that innovation is to produce new things or produce existing things by new methods and that production is to combine things or powers. As examples of innovation, he pointed out (1) development of new products by creative activity, (2) introduction of new production methods, (3) cultivation of new markets, (4) acquirement of new (source of supply for) resources, and (5) organizational reforms. In addition, he stated that destruction of existing value and creation of new value (creative destruction) by so-called entrepreneurs are the source of economic growth.
The 3rd Science and Technology Basic Plan describes the importance of ensuring sustainable prosperity of the Japanese economy and the life of Japanese people by using the potential of science and technology, through the realization of our country's innovation in wide-ranging fields of economy and society, to achieve superiority in full-fledged industrial competitiveness and contribution towards the solutions to a wide range of social problems including security and health. It further defines innovation as "the reform to merge scientific discovery and technological invention with insight, and develop it to create new social value and/or economic value."
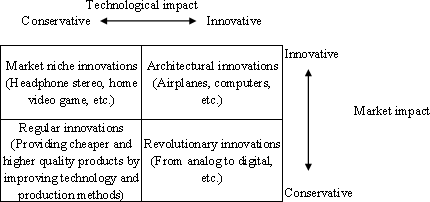
- Types of innovation by market or technological impact
It is said
that there are the following four types of innovations depending on the degree
of impact from the viewpoints of technology and the market:
(1) Architectural innovation: disrupts existing technology
and production systems and creates completely new markets (Example: Invention
of airplanes and computers)
(2) Revolutionary innovation: disrupts existing
technology and production systems, yet is applied to existing markets (Example:
Technological innovation of audio from analog to digital, Transfer of automobiles
from manual to automatic)
(3) Market niche innovation: cultivates new
markets within existing technology and production systems (Example: Headphone
stereo, home video game)
(4) Regular innovation: provides cheaper and
higher quality products or services by improving technology and production methods
Source:
Created by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science
and Technology using information from Professor Seiichiro Yonekura of Hitotsubashi
University
- Models of innovation concerning the creation of economic value
Stephen
J. Kline has recently shown that technological innovation does not follow a
linear flow (linear model) of "research" - "development"
- "design" - "production" - "sales," but is explained
by a chain-link model, as shown below, where each function is linked and interacts,
and feedback is generated.
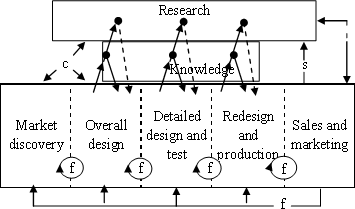
f:Feedback
I:New equipment stimulates science, and science generates
new equipment
C:Idea germination
S:Company's support for long-term research
Source:
Created by the Center for Research and Development Strategy
based on the chain-link model of Stephen J. Kline
Contacts
Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau
(Research and Coordination Division, Science and Technology Policy Bureau)