- 現在位置
- トップ > 白書・統計・出版物 > 白書 > JAPAN'S MODERN EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM > e. The Establishment of Kindergartens
e. The Establishment of Kindergartens
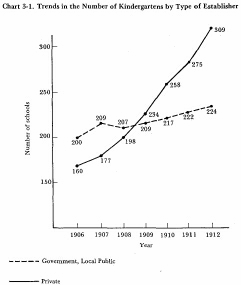
In 1886 there were only 38 kindergartens, but the number steadily increased and by 1906 there were 360. Thereafter, the increase in private kindergartens was particularly striking (Refer to Chart 3-1.); public resources were used largely for improving compulsory education with little left for kindergartens. In response to the development of kindergartens, in June, 1899, Regulations concerning Kindergarten Education and Facilities were issued, which came into force in September of that year. These Regulations indicated that kindergartens could be used for the education of children at least three years of age and up to the elementary school entering age. The maximum school time was set at five hours each day, and the maximum number of children per kindergarten teacher was set at forty. A kindergarten could receive up to one hundred children, and was expected to include play, singing, conversation, and manual skills in its curriculum. These Regulations were replaced by corresponding provisions of Regulations for the Enforcement of the 1900 Elementary School Order in September, 1900, when the latter Regulations came into force.
Chart 3-1. Trends in the Number of Kindergartens by type of Establisher
お問合せ先
(C)COPYRIGHT Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
-- 登録:平成21年以前 --