| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.3 3.3.1 3.3.1.1 | ||
| 3.3.1.1.1 Developing a Competitive Research and Development Environment |
The Second Science and Technology Basic Plan,adopted in March2001,sets forth the reform of Japan's science and technology system as a critical policy for creating and utilizing excellent output.The Basic Plan also clarifies the objective and role of competitive funding to form a competitive research and development environment,calls for implementation of appropriate evaluation and other system reforms,and sets a goal of doubling the use of competitive funding during the period that the Basic Plan is in force (Table3-3-1) .
In FY2002,the Council on Science and Technology Policy began to explore system reform.The Council presented its opinions in the"Interim Summary on Reform of the Competitive Funding System(opinion)"on June19,2002.Based on those opinions,in each system work has begun on improving the implementation structure by establishing program officers who will hold responsibility for servicing the competitive funding system from the science and technology side,and by making the use of funds more flexible so that research funds can be carried over to the following year.Data on researchers and funding is being inputted into a research and development database prepared by the CSTP.
Additionally,in each system,attempts were made to expand the overhead that is treated as necessary expenses-entailed with the implementation of research-for managing research institutions.Attempts were also made to expand employment by making it known to everyone that funds can be usedto hire doctoral students and post-doctoral students,and to introduce a scheme so that research on R&D topics that show promise of exceptional results and development can continue uninterrupted past the initial research and development period.
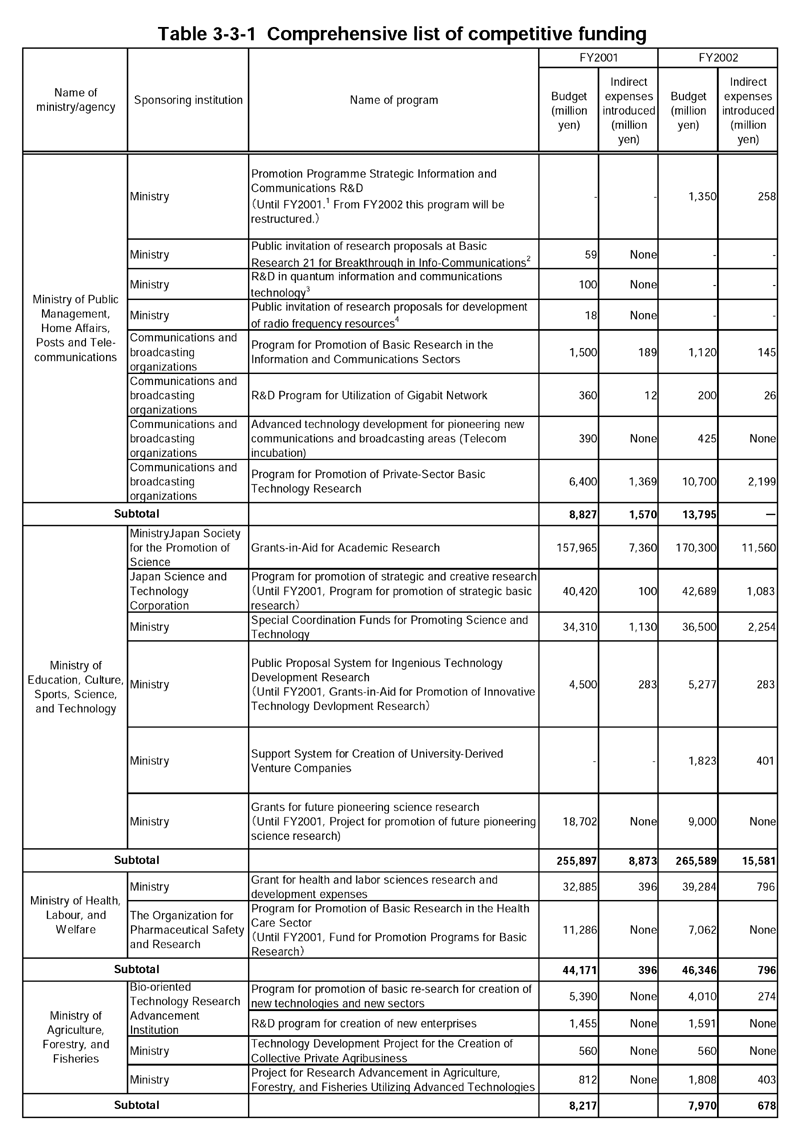
| 3.3.1.1.1.1 Competitive Funding of Ministries (1) Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications |
In FY2002 the Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications established the"Strategic Information and Communications R&D Promotion Programme"in an attempt to promote strategic R&D projects in the information and communications sector.The project aims to actively promote unique and innovative research and development that is in keeping with priority strategic targets in order to create world-leading intellectual assets,increase the level of researchers by creating competitive research environments,and improve research and development capabilities in information and communications technologies.
| (2) Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology |
To encourage creative and pioneering work conducted at universities,the Ministry is increasing the amount of Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research.This grant is awarded to the significant research that corresponds to the academic movement.The budget for the grant is170.3billion yen in FY2002,which has increased by7.8%from the previous fiscal year.About85,000new applications were received in FY2002 and about21,000of them were awarded.
The"Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology"(CREST)program,which was thus far implemented by the Japan Science and Tech-nology Corporation(JST),was reorganized into the"Creative Research for Evolutional Science and Technology Program,"newly established in FY2002.The new program promotes basic research that contributes to the creation of new technologies,for which the JST establishes research areas based on strategic targets defined by the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology on the basis of social and economic needs.Research themes for each area are publicly sought from all sorts of government,academic,and industry research institutions,such as national experimental research institutions and universities.In FY2002,research areas were established under six new strategic targets:(1)Investigation of sugar chain function for realizing effective development of innovative drugs for combating cancer and viral infection and establishment of technology for their application;(2)Establishment of basic technology for utilizing genome information to create tailor-made medical treatments without side effects,based on individual genetic information;(3)"Creation of functional materials/systems that utilize nanobio-technology to create a noninvasive medical treatment system;(4)Establishment of next generation integration simulation technology to create advanced treatment and precision product design based on phenomena at the atomic/molecular level in the medical treatment and information industry;(5)Creation of nanodevices/materials/systems for overcoming integration/function limits in data processing and communications;and(6)Creation of nanomaterials/systems for realizing environ-mental conservation and advanced energy recycling that minimize stress on the environment.Basic research was promoted to achieve these strategic targets.
The Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology,which offers comprehensive coordination of projects important to the promotion of science and technology,in line with policies laid down by the Council for Science and Technology Policy,received a budget of36.5billion yen in FY2002,an increase of6.4%over the previous fiscal year.
The Ministry revised the"Grant-in Aid for the Development of Innovative Technology"that was established in FY2000 as a part of the Millennium Project.As of FY2002,under the new"Open Competition for the Development of Innovative Technology"the public is invited to submit proposals for innovative and highly creative seeds of technology from the private sector,from which superior proposals are adopted and technology development subsidized in order to foster the proposals into even more innovative and practice-able forms,also utilizing the potential of universities.In FY2002,29proposals were adopted from among872applications.
In order to foster the creation of university-based start-ups,the"Project for Creation of University-based Start-ups"was established in FY2002 to subsidize technology development and the formulation of business start-up plans for university re-searchers who are expected to achieve successful results in developing new technologies when they set up venture.In the first year,34proposals were adopted from among143applications.
Furthermore,the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science implements Research for the Future Program to promote university-led science research with the potential to produce intellectual assets leading to the future development of Japan.
| (3)Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare |
The Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare provides funding to promote health and welfare science research,and strives to improve technology standards through scientific promotion of government measures related to health and medical care,welfare,environment health,occupational safety and health,and other aspects relevant to the citizens of Japan.
The FY2002 budget for the Grant for Health Sciences was40.7billion yen,promoting research in four main areas,including the administrative policy research area;the comprehensive project research area,which included"research into strategies for conquering cancer"based on the Second10-Year Cancer Strategy,and"research into human genome and regeneration science,"a part of the Millennium Project;the advanced health and welfare science area,which included"research on advanced medical technology,"which strives to promote research and development utilizing nano-technology,and"research on emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases,"which addresses provisions against infectious diseases;and the comprehensive research into maintenance of health and safety area,which included a"comprehensive research project in new drugs and other human science."
| (4)Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries |
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries made efforts to enhance and strengthen competitive funding with the establishment in FY2002 of the"project for research advancement in agriculture,forestry,and fisheries utilizing advanced technologies,"which aims to rapidly promote in-the-field experiments and research in the agriculture,forestry,and fisheries sector through collaboration between industry,government,and academia,and the"technology development project for the creation of collective private agribusiness,"which aims to revitalize agribusiness with the creation of new industries.Furthermore,measures for joint research aimed at strengthening basic research that promotes the advanced use of biological functions are implemented at the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Association(BRAIN).
| (5)Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry |
The Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry subsidizes the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization(NEDO),implemented the"Industrial Technology Research Grant Program"in FY2000 in and effort to develop human resources for industrial technology research and discover potential seeds of new industrial technologies that meet the needs of the industrial world and society by providing research funds to assist young researchers.
| (6)Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Transport |
The Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Trans-port invests in the Corporation for Advanced Transport&Technology(CATT),which implements the Program for Promotion of Basic Research in the Transport Sector.This program promotes creative and innovative basic research aimed at generating innovative new technologies with the potential for breakthrough technological innovation.
In addition,the Construction Technology Re-search and Development Subsidy Program was established in FY2001 to provide research and de-velopment Subsidies to researchers at universities,etc.,in order to promote cooperation with non-construction sectors,to promote innovations in construction technology in broad interdisciplinary areas,and to utilize the innovative results in public works projects.
| (7)Ministry of the Environment |
The Ministry of the Environment utilizes Global Environment Research Fund to promote research into global warming and other issues relevant to global environmental conservation,based on the Comprehensive Promotion Program for Global Environment Research,Monitoring and Technology that is drawn up at the Council of Ministers for Global Environmental conservation.
The Global Environment Research Fund pro-vides prioritized and strategic promotion for the development and diffusion of environmental technologies,while the Fund for Waste Disposal Science Research is used to promote restrictions on waste disposal and to encourage recovery and reuse,and develops research on all kinds of research into appropriate waste disposal measures.
| 3.3.1.1.2Improving the Mobility of Personnel through Popularization of the Fixed-term System |
In order to train researchers with broad perspectives who are rich in creativity and originality,and to be competitive and dynamic R&D environments,it's important that the mobility of researchers is improved and that researchers have experience at many kinds of research sites.
With an aim toward such improved mobility of researchers,employment of fixed-term researchers became possible at national experimental research institutes in accordance with"the Law Concerning the Special Measure for the Recruitment,Remuneration and Working Hours of Researchers with Fixed Terms in the Regular Service"enacted in1997.The performance to date is shown in Table3-3-2 .
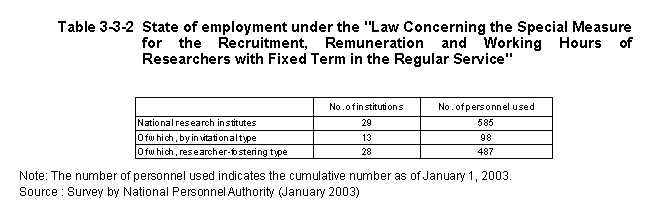
For universities and inter-university research institutes,"the Law Concerning the Term of Office for University Teachers,"enacted in1997,gives them the discretion to adopt the fixed-term system.The status of a fixed term system adopted on the basis of this law is shown in Table3-3-3 .
At the same time,in FY2001,the"Supporting young researchers with fixed-term appointments"program was established with the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology.The intent is to encourage broad implementation of the fixed-term system in the nation's research institutions,and to support young researchers on fixed-term contracts at universities or national experimental research institutions so that they may concentrate on independent research within the periods of their fixed terms.

The Second Science and Technology Basic Plan calls on the nation's research institutions"to prepare plans showing suitable policies for hiring re-searchers based on a fixed-term and public canvassing basis."The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology informed all relevant institutions in February2002of the"Basic Guidelines for Improvement of Researcher Mobility,"decided upon by the Council for Science and Technology Policy in December2001.The nation's research institutions are expected to try to improve researcher mobility actively by introducing the fixed-term system and implementing public canvassing.
| 3.3.1.1.3Increasing the Independence of Young Researchers |
It is critical to ensure the independence of young researchers in order to maximize the abilities demonstrated by distinguished young researchers.
| 3.3.1.1.3.1 Program to Support10,000Postdoctorals |
The"Program to Support10,000Postdoctrals,"set forth in the"First Science and Technology Basic Plan,"has been successful in its efforts-with the aim of fostering and securing young postdoctrals-to enhance support of young re-searchers so that they may proactively engage in research,and to establish and promote a system that propels creative basic research that actively employs young researchers.The"Second Science and Technology Basic Plan"regularly appraises the postdoctoral support program as"building an environment where postdoctorals can devote themselves to research,"and calls for"qualitative expansion of the postdoctoral program."
In FY2002,the national government made an overall effort to expand relevant measures and appropriated a budget for the support of a total of11,127postdoctorals. (Figure3-3-4) .
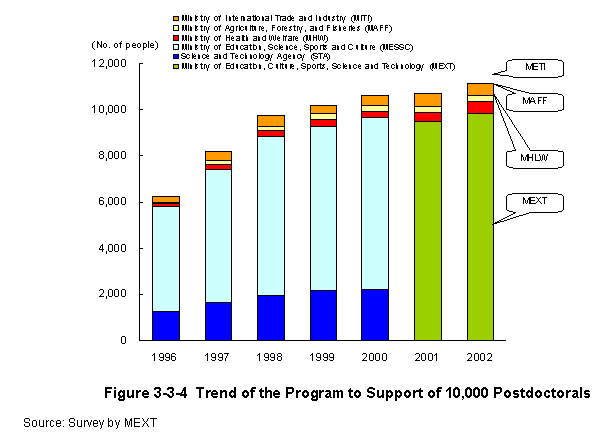
| (1)Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology(MEXT) |
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology appropriates the budget for9,800postdoctrals;90%of the total number supported by the government.Specifically,through the"Research Fellowships for Young Scientists"program run by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science,the Ministry is striving to enhance qualitative results by discovering particularly distinguished young researchers through the establishment of a fellowship(SPD)targeted at those who posses the ability to conduct research of the highest international standards.Various other sup-port programs are also being promoted,such as the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research(RIKEN)"Special Postdoctoral Researchers Program,"which provides a place where highly creative young researchers can proactively conduct research upon their own initiative at RIKEN's research facilities.
| (2)Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare(MHLW) |
The Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare has adopted measures to support and utilize541post-doctorals through its Health and Welfare Sciences Research Promotion Project.
| (3)Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries(MAFF) |
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries has adopted measures to utilize150young researchers as part of the Basic Research Promotion Project of the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Association(BRAIN),which is aimed at creating new technologies and research fields.In total,the Ministry adopted measures to utilize224postdoctorals.
| (4)Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry(METI) |
The Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry provided support and adopted measures to utilize a total of396postdoctorals through the industrial technology fellowship program run by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization(NEDO).
| 3.3.1.1.3.2 Active Promotion of the Utilization of Young Researchers in Creative Basic Research |
Many of the researchers around the world who come up with world-class research results have already conducted research in their30's that lays the groundwork for later achievements.In Japan,however,the normal method of promotion is through a rigid seniority system,and development of an environment for bringing out the abilities of young researchers lags far behind other countries.The relevant government ministries are currently in contact with each other for the creation and expansion of programs to promote basic research by actively utilizing young researchers.
| (1)Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications |
Under the"Program for Promoting Strategic Information and Communications Research and Development,"established in FY2002,the"re-search and development program for nurturing young advanced-IT researchers"was instituted with the aim of nurturing young researchers who are age35or younger.
| (2)Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology |
MEXT is working to expand competitive funding for young researchers by appropriating13.4billion yen of the Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research to young researchers aged37or younger who aim to conduct solo research founded on exceptionally original ideas for which future development can be expected.
| (3)Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fish-eries |
The Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Association(BRAIN)is working th-rough the Basic Research Promotion Project,which aims at the creation of new technologies and new sectors,to institute a young researcher support program that prepares the conditions for objective research by young researchers with flexible thinking and ambition.
| (4)Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry |
In FY2000,NEDO started"Industrial Technology Research Grant Program"for promoting basic and creative research and development by providing research fund to assist young researchers.
| 3.3.1.1.4 Reform of Japan's Evaluation Systems |
To promote science and technology,it is important to conduct appropriate evaluations,which stimulate researchers and encourage out-standing research and development activities.Effective evaluations will increase the efficiency and vitality of R&D activities,facilitate better R&D achievements,and nourish superior researchers.Evaluations also offer benefits to society and the economy,and also serve for accountability to the public.
The"Second Science and Technology Basic Plan"sets forth reforms of the evaluation system as one of its pillars for developing a science and technology system that will delivers excellent results.Based on the Second Basic Plan,the"National Guidelines on the Method of Evaluation for Governmental R&D"were decided upon by the Prime Minister in November2001to improve the evaluation program further.All ministries and agencies implement effective evaluations with de-tailed guidelines specifying evaluation methodologies under the revised General Guidelines.
In addition,the Cabinet Office in cooperation with related ministries and agencies developed a government R&D database system that brought together in a single,cross-ministerial system for data on researchers,funds,accomplishments,evaluators,and evaluation results for government-funded individual research and development topics.Along with restoring data,the system is being used for data analysis by the Cabinet Office and related ministries and agencies.
For other actions in this area,evaluations of in-dependent administrative institutions are now being implemented based on the Law concerning Rules for Independent Administrative Institutions(1999Law No.103).
In addition,under the Law for Evaluations of Policies Performed by Administrative Institutions(2001Law No.86),which commenced in April2002,it has been made mandatory to conduct appraisal evaluations for research and development topics that are expected to incur large costs,given their preceding experience in project evaluation.
| 3.3.1.1.5Flexible,Effective,and Efficient Program Management |
Flexible,effective,and efficient program operations and the efficient use of funding are necessary for in response to the characteristics of research and development.For this reason,at the national research institutes,efforts are being made to fully utilize organizational structures that allow mobile and flexible changes based on internal measures.These changes are aimed at responding to progress and changes in research and development,including the priority allocation of funding at the discretion of institute directors,etc.,in response to research performance,and the placement of re-searchers and establishment of research periods in line with research topics.
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science,and Technology uses the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology to position"urgent research"within"Promotion of Advanced Research,"to ensure a dynamic response to situations requiring urgent responses during the fiscal year.Urgent survey and research activities during FY2002 are as shown in Table3-3-5 .
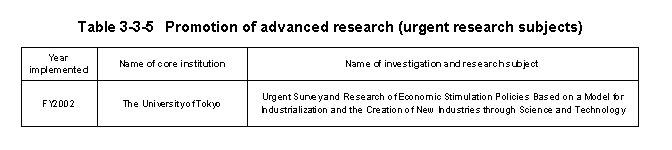
Furthermore,to address situations where teachers at national universities,etc.,are engaged in re-search commissioned from corporations or other outside bodies,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology moved in FY1998 to merge the three expense categories into a single new accounting item(research expenses for partnership between universities and industry,etc.)in order to encourage a flexible response to changes in expense items that occur as research progresses or as research plans change.
Regarding announcement of research results at research meetings,Article30of the Patent Law stipulates that"announcement of documents at research meetings that are hosted by scientific groups specially designated by the head of the Patent Agency"is an exception to the rule that newness of a patent idea is lost.Now the Patent Agency has extended the application of this exception to research activities conducted at universities and colleges.
| 3.3.1.1.6Utilizing Personnel and Developing Diversified Career Paths |
To reinvigorate research activity and to improve the ability to propose policies for research and development,it is critical that the research organization and the governmental agency that promotes research and development tackle actively about appointment of diversified personnel.
The employment of outside personnel at research institutes is progressing with the increase in independent administrative institutions that are welcoming university professors as institute directors,in order to reinvigorate their organizations and deepen the links between academia and industry.
More and more universities are using open hiring systems for employing teachers to boost personnel mobility and to secure superior personnel.To ensure the availability of superior personnel with diverse careers and experience,universities are also actively promoting the recruitment of members of the workforce at large or people from overseas,and are actively employing non-university personnel,such as researchers from national research institutes or from private sector corporations.
Furthermore,in its first recommendation in July2002,the Council for Science and Technology's Committee on Human Resources suggested the following measures to reform the graduate school organization in order to develop world-class re-searchers:
1.To gather together researchers with varied backgrounds and to prepare research environments in which they can mutually stimulate and influence each other,with the aim of heightening the research capabilities of re-search institutions;
2.To perform self reviews,asking questions about the body of researchers,such as whether that body has become overly homogenous,and to reduce the ratio of alumni faculty,with the aim of ensuring diversity and to revitalize the graduate school organization itself;and
3.To encourage postdoctorals to accumulate diverse experience at different research institutions,to promote their research activities overseas,and to increase the employment of postdoctoral faculty at the level of assistant.
It is important that graduate schools take into account the above recommendations and strive to secure diverse personnel.
With respect to the utilization of research personnel at government administrative organizations,bodies such as the Council for Science and Technology Policy,Cabinet Office are entrusted with the task of ensuring that researchers take part in the planning and drafting of government policies.
In this regard,it is also important to open up various career paths to researchers by promoting science and technology personnel's participation in activities besides research and by developing environments were female researchers can make use of their abilities that are not being fully exhibited due to institutional barriers.
| 3.3.1.1.7Achieving a Creative Research and Development System |
To create excellent results and to realize a research and development system capable of pioneering a new era,the heads of research institutions of a certain size need to use superior concepts and leadership to promote organizational reform at their R&D institutions,and to create Centers of Excellence(COEs)with international appeal.
Toward this end,the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology were used in FY2001 to support the start of the"Fostering Strategic Research Centers"program.The program's goal is to foster and support R&D institutions that make efforts at management reform,by incorporating novel methods into organizational operations in order to utilize the R&D skills and results of these institutions,so as to transform existing R&D organizations into world-class R&D centers.
In FY2002,two institutions were selected for fostering under the program,as shown in Table3-3-6 .
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |