| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.2 3.2.2 3.2.2.8 | ||
Frontier science is positioned in the Basic Plan as fundamental to the nation's existence,and an area in which it is essential for Japan to be involved.The Promotion Strategies by Sector adopted in September2001stipulate the following areas and items as meriting priority.
1. Assurance of safety
2. Technology innovations aimed at pioneering the world market
3. International contributions to human intellectual creation,and assurance of international position
| 3.2.2.8.1Space Development |
Space development is extremely important be-cause it uses the acquisition of commonly applicable knowledge regarding the origin of the universe and various phenomena about the Earth to"accumulate intellectual properties common to all humankind,"and also because expanded use of space contributes to"expansion of socio-economic infrastructure"through communications and broad-casting,weather forecasting,and global environment and disaster monitoring,and to"developing advanced technologies"that might result in the creation of new technologies in various fields and of new industries with high added value.
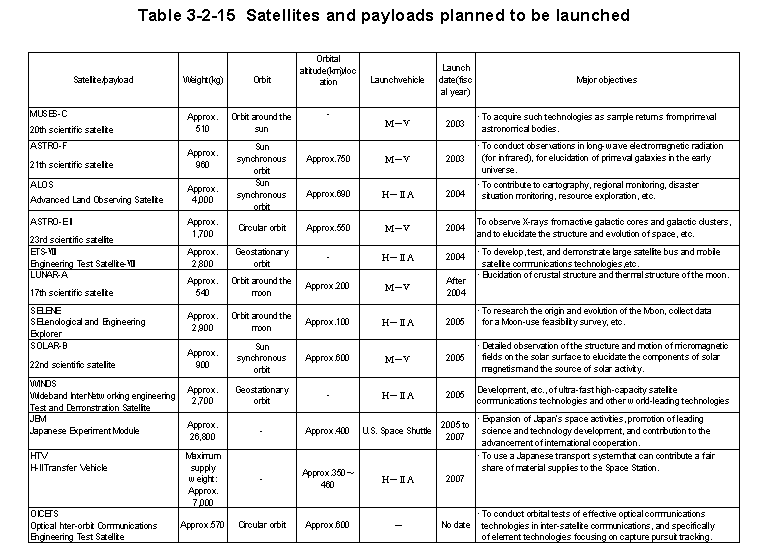
Since the successful launch of Japan's first satellite,"Ohsumi,"in1970,Japan has successfully launched94satellites as of end-December2002,ranking third in the number of satellites launched behind the United States and the former Soviet Union. Table3-2-15 shows the major satellites planned for future launch by Japan and their objective For an overall view of Japan's space development and utilization efforts,the Council for Science and Technology Policy in June2002issued"On the Basis for Future Efforts Related to Space Development and Utilization,"which summarizeed Japan's goals for the development and utilization of space,as well as issues,strategies,industrialization,basic and fundamental research and development over the long term,and the program for future studies.The various ministries and agencies are proceeding with space development and utilization based on this report.
In August2001,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology determined to merge into a single organization the three core space development organizations in Japan,the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science,the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan,and the National Space Development Agency of Japan,to establish a system for promotion of more efficient and effective research and development.The Preparatory Committee for the Integration of Three Aerospace Organizations,established to discuss the specifics on accomplishing the merger,released its final report in March2002.The"Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Law,"detailing the name,objective,and range of responsibilities for the new entity following the merger of the three space development organizations,passed the Diet in December2002,and preparations are now in progress toward the October2003launch of the new independent administrative entity,the Japan Aero-space Exploration Agency.
With an eye to the Basic Policy as it relates to Japan's development and utilization of space over-all,the Space Activities Commission has been engaged in discussing the basic plans that form the basis of administrative operations at the National Space Development Agency of Japan,and has per-formed safety investigations for rocket launches and investigations into accidents and other problems.The commission also assisted in studies toward the merger of the three space developmentagencies with its June2002report,"Goals and Direction of Japan's Space Development and Utilization."In March2003,the commission commenced discussion of long-term plans related to space activities,to serve as mid-range goals for the newly established Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
| 3.2.2.8.1.1Earth Observation and Earth Science |
In addition to the projects mentioned in Section3.2.2.3Environment,the"Himawari5"geostationary
meteorological satellite launched in March1995is currently in operation.Also,the
Multi-functional Transport Satellite(MTSAT)new series No.1(replacement)will be
launched by an H-![]() A rocket in summer2003.
A rocket in summer2003.
| 3.2.2.8.1.2Space Science and Lunar Exploration |
The Institute of Space and Astronautical Science forms the core of Japan's efforts in the field of space science,launching scientific satellites with the participation of researchers from universities and colleges nationwide.Scientific Satellite No.18PLANET-B"Nozomi"was launched in July1998,which is intended to conduct research on the structure and behavior of the Martian atmosphere,and its interactions with the solar wind."Nozomi"is currently on a trajectory toward Mars towards entry into orbit around Mars in early2004.
Other projects in development include Scientific Satellite No.17LUNAR-A
designed for elucidation of the lunar internal structure and thermal structure,Scientific
Satellite No.20MUSES-C for performing engineering test for a mission planned
to take samples from an asteroid,and return them to Earth,Scientific Satellite
No.21ASTRO-F for observations in long-wave electromagnetic waves(far infrared)for
elucidation of primeval galaxies in the early universe,and Scientific Satellite
No.22SOLAR-B for detailed observations of the structure and behavior of magnetic
fields on the solar surface to elucidate the origins and causes of solar activity,and
Scientific Satellite No.23ASTRO-E![]() for observation of X-rays emitted from active
galactic cores and galactic clusters,and elucidation of the structure and evolution
of the universe.
for observation of X-rays emitted from active
galactic cores and galactic clusters,and elucidation of the structure and evolution
of the universe.
In addition,the National Space Development Agency of Japan and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science are jointly promoting development of the Moon orbiter SELENE,toward the objective of gathering data over the entire surface of the Moon in order to elucidate the origin and evolution of the Moon,and clarifying the feasibility of using the Moon for future space activities.The two organizations are also promoting the collection of data suitable for research into lunar soft-landing technologies as ISAS/NASDA joint program.
| 3.2.2.8.1.3Communications,Broadcasting,and Positioning |
The National Space Development Agency of Japan is cooperating with the Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications to promote research and development into the Wideband Inter Networking engineering test and Demonstration Satellite(WINDS),to establish a satellite communications technology for ultra-high speed Internet and large-capacity data communications,and to carry out new joint government and private-sector utilization tests of these technologies,for the purpose of promoting the IT revolution in Japan.Joint government and private-sector research commenced in FY2003 into a quasi-zenithal satellite communications system that will ensure that at least one satellite is always visible at the zenith in the skies over Japan,in order to achieve100%coverage of the nation for high-quality communications,broadcasting,and posi-tioning services without being affected by narrow mountain valleys or tall buildings.
| 3.2.2.8.1.4Promotion of Space Environment Utilization |
The space environment offers unique characteristics for research,such as microgravity and high vacuum,that are difficult to obtain on Earth.Utilization of space environment is expected to promote research,experiments,and observation across a broad range of fields and will contribute to the development of society and the improvement of living conditions.
The National Space Development Agency of Japan is proceeding with development of the Japanese Experiment Module(JEM)"Kibo"for the International Space Station,including a multi user experiment facility in the Pressurized Module and an Exposed Facility payload.It is also promoting research activities that effectively utilize the space environment.Public announcement of ground-based research projects offering opportunities to researchers in a broad array of fields as preparation for utilization of the space environment began in1997,and a total of63research themes were selected in FY2002.Moreover,pilot projects for applied research were started in1999to encourage private-sector utilization of the space environment,and preparations are proceeding to make use of the Space Shuttle or other launch vehicles for timely implementation of research themes that have already been selected.Furthermore,Japan also participates in international research announcement for the mutual use of experimental facilities among partners of the International Space Station program,and studies are in progress for specific implementation of research themes already selected as candidates for experimentation.
Recent utilization of the space environment has included the use of a high-definition camera in the Russian Service Module of the International Space Station and other facilities for medical experiments and public broadcasting tests,environmental durability tests for materials to be used in space,and a protein crystal formation program run jointly by the government and the private sector.On the ill-fated Space Shuttle Columbia flight of January2003,Japan had a protein crystal formation experiment and a biological science experiment,but the accident during reentry prevented retrieval of the test materials.
Pilot projects for space business have also been started,as part of an active effort to promote the diversified use of the International Space Station in areas other than scientific research.Meanwhile,an ISS education event was held in September2002for the third time,giving Japanese primary and middle school students an opportunity to communicate with astronauts on the International Space Station.
The Utilization Work Group meeting of the Space Activities Commission conducted surveys and reviews of space environment utilization on the International Space Station and of satellite-based Earth observation,and also surveyed and discussed policies for promoting space utilization in new fields,as well as cooperation with space development institutions and with other countries,summarizing its conclusions in June2002in"Basic Direction and Current Policies for Promotion of Japan's Space Utilization."In March2003,the"Special Committee for Utilization of the Inter-national Space Station"was established under the auspices of the Committee on Space Environment Utilization.The Special Committee looks at issues related to utilization plans for the International Space Station,and to systems for its operation and utilization.
The Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry developed a next-generation
Unmanned Space Experiment Recovery System(USERS 53) ).The
USERS satellite carrying a space experimentation module was launched by H-![]() A
Launch Vehicle No.3on September10,2002.After lift-off,experiments involving development
of a large-scale superconducting materials crystal in a micro-gravity space environment
were successfully con-ducted,and the part of the space capsule carrying the experimental
results was planned to be returned and retrieved from above the sea-in May2003.
A
Launch Vehicle No.3on September10,2002.After lift-off,experiments involving development
of a large-scale superconducting materials crystal in a micro-gravity space environment
were successfully con-ducted,and the part of the space capsule carrying the experimental
results was planned to be returned and retrieved from above the sea-in May2003.
Note53)USERS:Unmanned Space Experiment Recovery System
In addition,to encourage the broad use of Japan's well-developed industrial technology in comercial satellite production processes,and to rationalize their design,procurement,and manufacture,etc.,the Space Environment Reliability Verification Integrated System(SERVIS 54) )will be developed.SERVIS is a satellite that prepares guidelines for transfer of industrial technologies to space-related devices and databases of industrial components that could be used for space-related devices.SERVIS is planned to be launched during FY2003.
| 3.2.2.8.1.5Fundamental Satellite Technology (1)Engineering
Test Satellite |
Engineering Test Satellite ![]() (ETS-
(ETS-![]() )is being developed
for the purpose of developing large-scale geostationary satellite bus technologies,large-scale
deployable antenna technologies,mobile multimedia satellite broadcast system
technologies,and basic technologies related to satellite positioning systems
utilizing high-accuracy clock standards,and for their in-orbit experiments and
demonstrations,in cooperation between NASDA and the Ministry of Public Management,Home
Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications.
)is being developed
for the purpose of developing large-scale geostationary satellite bus technologies,large-scale
deployable antenna technologies,mobile multimedia satellite broadcast system
technologies,and basic technologies related to satellite positioning systems
utilizing high-accuracy clock standards,and for their in-orbit experiments and
demonstrations,in cooperation between NASDA and the Ministry of Public Management,Home
Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications.
| (2)Mission Demonstration Test Satellite(MDS 56) ) |
NASDA's Mission Demonstration test Satellite-1(MDS-1)"Tsubasa,"launched
by H-![]() A Launch Vehicle No.2in February2002,was intended to verify the function
of commercial parts in orbit,to verify the technology for shrinking the size
of components,etc.,and to measure radiation and other space environment data.During
the one-year mission,data from all mission instruments was successfully collected."Tsubasa"entered
its post-mission stage of utilization in February2003.
A Launch Vehicle No.2in February2002,was intended to verify the function
of commercial parts in orbit,to verify the technology for shrinking the size
of components,etc.,and to measure radiation and other space environment data.During
the one-year mission,data from all mission instruments was successfully collected."Tsubasa"entered
its post-mission stage of utilization in February2003.
Note54)SERVIS:Space Environment Reliability Verification Integrated System
Note55)ETS:Engineering Test Satellite
Note56)MDS:Mission Demonstration Test Satellite
| 3.2.2.8.1.6 Space Infrastructure (1) M- |
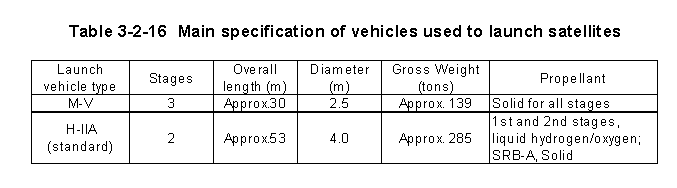
For the launch of scientific payloads,the Institute of Space
and Astronautical Science first developed the L(Lambda)series rockets and the
M-3S2 and other M(Mu)series rockets,both of which used solid propellant for all
stages,before moving on to development of the M-![]() rocket.The M-
rocket.The M-![]() rocket is capable
of launching approximately1.8tons of payload into low orbit(Table3-2-16),and
launches No.1and No.3were a success.Launch No.4in February2000,however,was a
failure due to a problem in the first-stage motor.Countermeasures for the problem
were taken on the basis of the results of an investigation conducted by the Space
Activities Commission's Technology Evaluation Division into the accident's
causes.Launch No.5was scheduled for May2003.
rocket is capable
of launching approximately1.8tons of payload into low orbit(Table3-2-16),and
launches No.1and No.3were a success.Launch No.4in February2000,however,was a
failure due to a problem in the first-stage motor.Countermeasures for the problem
were taken on the basis of the results of an investigation conducted by the Space
Activities Commission's Technology Evaluation Division into the accident's
causes.Launch No.5was scheduled for May2003.
| (2) H- |
For launching of satellites into geostationary orbit,etc.,NASDA
developed the N series rocket and then the H series of launch vehicles,including
the H-![]() Launch Vehicle,before moving on to the H-
Launch Vehicle,before moving on to the H-![]() A Launch Vehicle.The H-
A Launch Vehicle.The H-![]() A
is a two-stage rocket that uses liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen-fueled engines
for both the first and second stages (Table3-2-16) ,and
is capable of lifting as much as two tons of payload into geostationary orbit.H-
A
is a two-stage rocket that uses liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen-fueled engines
for both the first and second stages (Table3-2-16) ,and
is capable of lifting as much as two tons of payload into geostationary orbit.H-![]() A
Launch Vehicle No.1was launched in August2001,with four successful launches completed
by December2002,marking several firm steps toward improved reliability for the
nation as Japan's main launch vehicle.Moreover the H-
A
Launch Vehicle No.1was launched in August2001,with four successful launches completed
by December2002,marking several firm steps toward improved reliability for the
nation as Japan's main launch vehicle.Moreover the H-![]() A standard type is
to be transferred to the private sector in FY2005,to ensure international competitiveness
through unification of manufacturing responsibility for improvement of product
quality.A basic contract for transfer was signed in February2003between NASDA
and the private-sector entity,Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
A standard type is
to be transferred to the private sector in FY2005,to ensure international competitiveness
through unification of manufacturing responsibility for improvement of product
quality.A basic contract for transfer was signed in February2003between NASDA
and the private-sector entity,Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
| (3) H- |
As one aspect in laying the technological ground-work for a
reusable space transportation system,NASDA and the National Aerospace Laboratory
are promoting the development of H-![]() Orbiting Plane-Experimental(HOPE-X)to confirm
the major technologies for unmanned,winged space planes,and to accumulate the
technologies required for research into future reusable space transportation
vehicles.Currently,research and development is being concentrated on the essential
technologies for reusable space transportation systems and on the High Speed
Flight Demonstration,based on the recognition of the need for adequate study
of the ideal form of future methods of reusable space transportation systems,and
on a careful study of development results achieved to date.In October and November2002,the
High Speed Flight Demonstration(Phase I)was conducted at Christmas Island in
the Republic of Kiribati,verifying the flight path tracking capabilities.
Orbiting Plane-Experimental(HOPE-X)to confirm
the major technologies for unmanned,winged space planes,and to accumulate the
technologies required for research into future reusable space transportation
vehicles.Currently,research and development is being concentrated on the essential
technologies for reusable space transportation systems and on the High Speed
Flight Demonstration,based on the recognition of the need for adequate study
of the ideal form of future methods of reusable space transportation systems,and
on a careful study of development results achieved to date.In October and November2002,the
High Speed Flight Demonstration(Phase I)was conducted at Christmas Island in
the Republic of Kiribati,verifying the flight path tracking capabilities.
| (4) Optical Inter-orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite(OICETS 58) ) |
NASDA was forced to put off the launch date for the Optical Inter-orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite(OICETS),which was to conduct orbital experiments on the elemental technologies needed for optical communications technologies in inter-satellite communication systems,because of problems with the launching of the European Space Agency's 59) geostationary satellite,ARTEMIS 60) ,which was to be a part of the joint project.Investigation of counter-measures revealed a possible solution that will allow ARTEMIS to reach the requisite orbit and perform the experiments,with the result that preparations are now in progress toward a new launch date in FY2005.
Note57)HOPE-X:H-![]() Orbiting Plane-Experimental
Orbiting Plane-Experimental
Note58)OICETS:Optical Inter-Orbit Communications Engineering Test Satellite
Note59)ESA:EUROPEAN Space Agency
Note60)ARTEMIS:Advanced Relay and Technology Mission
| (5) Data Relay Test Satellite(DRTS 61) ) |
For the objective of performing data relay experiments between
earth observing satellites and the Japan Experiment Module(JEM)on the International
Space Station in order to promote development of data relay functions for the
Communications and Broadcasting Engineering Test Satellite(COMETS)and to accumulate
experience in more advanced inter-satellite communications technology,NASDA launched
the Data Relay Test Satellite(DRTS)"Kodama"on September10,2002on top
of H-![]() A Launch Vehicle No.3.In February2003,DRTS success-fully relayed imaging
data in real-time from the Advanced Earth Observing Satellite(ADEOS-
A Launch Vehicle No.3.In February2003,DRTS success-fully relayed imaging
data in real-time from the Advanced Earth Observing Satellite(ADEOS-![]() )"Midori
)"Midori
![]() ,"and further data relay demonstration tests are planned.
,"and further data relay demonstration tests are planned.
| 3.2.2.8.1.7 Fundamental and Advanced Research on Satellite and Launch Vehicle Technology |
The National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan and research institutes of related ministries and agencies are conducting fundamental research on launch vehicle and satellite technology.The laboratories and research institutes are also working in a number of advanced research areas,including an unmanned winged reusable space vehicle and a space-plane.
| 3.2.2.8.1.8 Promotion of International Cooperation in Space |
With the increasing importance of observations from space by Earth observation satellites as global problems such as earth environmental problems and disasters have become more serious in recent years,and with the increasing internationalization of space activities as the society and the economy have become more globalized,the need for international cooperation in space activities is now greater than ever before.Consequently,Japan is promoting cooperation with many countries,includeing the United States,European countries,Russia,Canada,and countries of the Asia-Pacific region in various fields.
In the area of multilateral cooperation,Japan is actively engaged in the promotion of such cooperation through the activities in the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space(COPUOS 62) )which discusses the inter-national order on exploration and utilization of space,and on the promotion of international co-operation,the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum(APRSAF 63) ),a place for exchanging opinions about the international cooperation in space development in the Asia-Pacific region,and the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites(CEOS),where technical coordination and information exchange in earth observation satellite systems is undertaken.
Japan is participating in the International Space Station(ISS 64) )program,the largest international cooperation project in space development,by providing its own Experiment Module(JEM)"Kibo."It is in close cooperation with all participating nations in the construction and utilization of ISS.
In the area of bilateral cooperation,cooperative space activities between Japan and the United States of America are proceeding smoothly under the Agreement between the Government of Japan and the Government of the United States of America concerning Cross-Waiver of Liability for Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Space for Peaceful Purposes.
For cooperation with Europe,the27th Japan-ESA annual meeting was held in October2002under the close cooperative relationship.In addition,the10th Japan-Canada Space Panel was held in December2002based on the Agreement between the Government of Japan and the Government of Canada on Cooperation in science and technology.Moreover,cooperation with Russia is proceeding based on the Agreement between the Government of the Russia Federation and the Government of Japan on Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space for Peaceful Purposes,for study of cooperative projects.
Note61)DRTS:Data Relay Test Satellite
Note62)COPUOS:Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space
Note63)APRSAF:Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum
Note64)ISS:International Space Station
| 3.2.2.8.2Ocean Development |
The development and use of the ocean,which contains an abundance of resources,including bio-logical and mineral resources,as well as vast space,is an important issue for a country as physically small and confined by sea as Japan.Furthermore,because the ocean plays an important role in global environmental changes and the movements of oceanic crusts are believed to be a major source of earthquakes and volcanic activity,elucidation of their mechanisms is urgent.In light of these conditions,the United Nations Educational,Scientific,and Cultural Organization(UNESCO)and the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission(IOC 65) )called for the implementation in the early1990s of the Global Ocean Observing System(GOOS 66) ),which aims to build a system for the conduct of comprehensive observations and research of ocean phenomena on a worldwide scale.The GOOS project is now being promoted in co-operation with the World Meteorological Organization(WMO 67) ).
This plan was also incorporated into the Agenda21that was adopted by the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development(UNCED;also called the Earth Summit).Based on these international efforts,it is crucial for Japan to promote ocean research related to global environment issues,and to promote other research and development of ocean sciences and technologies.
Furthermore,in order to shed some light on ocean phenomena occurring on a global scale,the relevant ministries and agencies have joined with universities,etc.,to actively participate in international ocean research programs such as GOOS.Also,Japan has taken a leading role in cooperation with China,South Korea,and Russia to promote the North East Asian Regional Global Ocean Observing System(NEAR-GOOS 68) )as a regional pilot project for GOOS.
Japan's ocean development adheres closely to the report of the Council for Science and Technology Subdivision on Ocean Development,and research and development is being promoted with the co-operation of relevant ministries and agencies according to their various situations.In"Basic Concepts and Promotion Measures for Ocean Development from the Long-Term Viewpoint(report),"the subdivision's responded in August2002to an inquiry by the Minister of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,by noting that"it is important to carefully balance knowing,protecting,and using the ocean for the policies for future ocean development when presenting strategic policies and promotion policies toward realization of sustainable utilization."Moreover,the"Inter-Ministerial Liaison Committee for Survey of the Continental Shelf"was established in June2002to promote surveys for the establishment of the outer limits of Japanese continental shelf that can be of assistance to Japan's ocean development.The liaison committee recognizes the importance to the government as a whole of firmly implementing these surveys,and that maximizing the use of scientific knowledge is important for the performance of appropriate surveys and analyses.
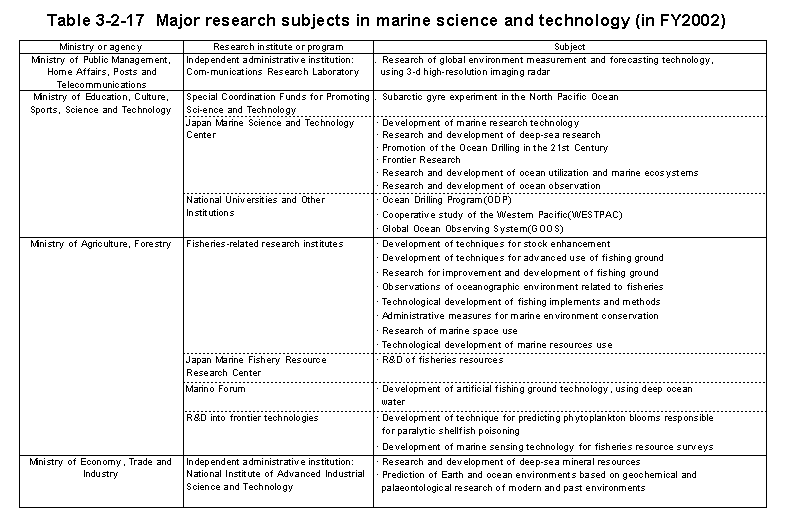
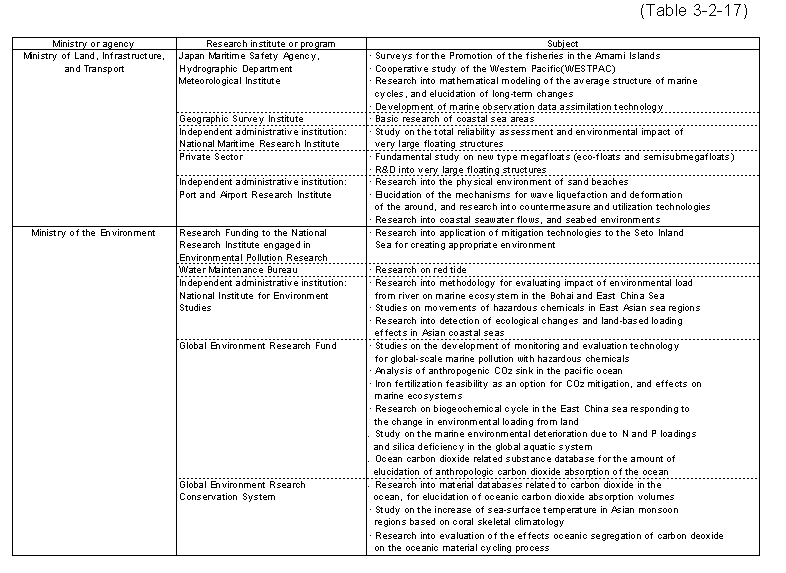
At the Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications,the Communications Research Laboratory is conducting research into high-resolution three-dimensional microwave radar and shortwave ocean radar to facilitate the establishment of methods for measurement of marine oil pollution,currents,and waves,etc.,and prediction of changes in the global environment.
At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science,and Technology,Research Institutions including the Japan Marine Science and Technology Center(JAMSTEC)are promoting advanced and basic research and development into ocean sciences and technologies.These Institutions cooperate with related ministries and agencies,and universities,etc.,to promote comprehensive projects.
In particular,JAMSTEC used the oceanographic research vessel"MIRAI"to conduct intensive observations in support of elucidation of the effects of the El Nino phenomenon and other weather phenomena on interactions between the atmosphere and ocean,and on climate change.In addition,the10,000m-class unmanned deep sea ROV"KAIKO"and the deep sea research vessel"KAIREI"were at the center of ocean surveys for research into the dynamics of ocean plates and into various forms of crustal movements occurring under the seafloor.For the Ocean Drilling in the21st Century Project,construction of a deep sea drilling vessel continues to progress since its commencement in1999.
Furthermore,the Frontier Research System for Extremophiles promoted research for elucidation of the physiological adaptivity of deep-sea micro-organisms existing in extreme environments.
In addition,the University of Tokyo Ocean Research Institute is at the center of continuing ocean-related scientific research,including basic research related to GOOS for the purpose of building a comprehensive observation system for the elucidation and forecast of changes in the ocean environment,and for its preservation,participation in joint surveys of the Western Pacific region,and research into ocean flux,which can contribute to elucidation of physical cycles in the ocean.In addition,national universities are engaged in research into marine biosystems and conducting observations of changes in the atmosphere and oceans.
At the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries,fisheries-related research institutes conducted research into the rationalization of production methods and sustainable utilization of re-sources,through introduction of new technologies and understanding of the characteristics of marine resources,the promotion of fish farming and breeding industries,the preservation of fishing bank environments,and the diverse and advanced utilization of marine products.
At the Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry,the Metal Mining Agency of Japan,the Japan National Oil Corporation,and the National Institute for Advanced Industrial Science and Technology are at the center of continuing efforts at development of ocean floor mineral resources and prediction of environmental effects,and of geo-logical surveys of the seabed.
The Ministry of Land,Infrastructure,and Transport promoted research and development into next-generation coasting vessels(the Super Eco-Ship)and expanded the Nationwide Ocean Wave Information Network for Ports and Harbors(NOWPHAS 69) )in cooperation with the Port and Airport Research Institute.
The Maritime Safety Agency is engaged in research into upgrading water channel measurement and marine condition monitoring technologies,and into the development of seabed monitoring technologies and upgrading of the accuracy of current flow forecasting.The Meteorological Agency is continuing investigations and research toward expansion of observation and forecast information for marine phenomena and climate change,including marine weather observations and elucidation of the El Nino phenomenon.
Moreover,the National Maritime Research Institute is carrying out research into safety and environmental protection in the field of marine technology.In relation to the NEAR-GOOS project,the Meteorological Agency and the Maritime Safety Agency operate a system for promoting exchange of oceanic data for sea regions bordering on Japan,in order to better promote oceanographic research.
In addition,the Geographical Survey Institute conducts basic research of coastal sea areas for the purpose of providing the basic information needed for formulation of comprehensive development,utilization,and protection plans for coastal sea areas.
At the Ministry of the Environment,the Global Environment Research Fund is being used to conduct research into the elucidation of the effects of pollution from the Changjiang River on marine ecosystem in the East China Sea,and on global-scale ocean pollution due to toxic substances. Table3-2-17 summarizes the main research subjects undertaken in the ocean sciences and technology sector by the various ministries and agencies in2002.
Note65)IOC:Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission
Note66)GOOS:Global Ocean Observing System
Note67)WMO:World Meteorological Organization
Note68)NEAR-GOOS:North East Asian Regional-Global Ocean Observing System
Note69)NOWPHAS:Nationwide Ocean Wave information network for Ports and Harbours
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |