| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > JAPANESE GOVERNMENT POLICIES IN EDUCATION, SCIENCE AND CULTURE 1993 > CHAPTER 3 �3 2 (1) | ||
Important Intangible Cultural Properties are designated in two fields of art; one field being traditional performing arts that include music, dance, drama and so on, and the other being craft techniques such as pottery, textiles, lacquerwork and metalwork. Criteria for designating Important Intangible Cultural Properties are; 1)those that are of an extremely high artistic value. 2)those which occupy a very important position in the history of performing arts and craft techniques and 3) those which have a high artistic value or which hold an important position in the history of performing arts or craft techniques and which feature distinct characteristics of localities or schools of art. Expansion of the fields of designation to include fields other than those of the presently designated fields of performing arts and craft techniques is a topic for future discussion.
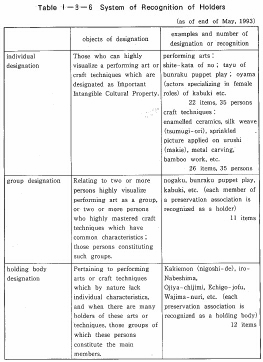
When designating an Important Intangible Cultural Property. in order to give concrete expression to the skill, recognition is given to the individual possessing the skill. There are three classifications for those possessing such skills: "Individual Designation", "Group Designation" and "Holding Body Designation", as is shown in Table I-3-6.
Certain favorable protective measures accompany designation as an Important Intangible Cultural Property, such as the training of successors, public presentation and the making of accurate records. In designating an Important Intangible Cultural Property, due consideration is given to maintaining a balance between the designated areas in each of the two fields. Priority is also given to those fields that are at risk of extinction due to a decline in the number of successors.
A total of 199 individuals have been recognized in the "Individual Designation" category since this designation system began in 1955. These holders are popularly referred to as "Living National Treasures". This system of designation and recognition has taken root in society, and has been responsible for notable achievements in the protection of Important Intangible Cultural Properties by arousing public interest in this area.
There are, of course, other Intangible Cultural Properties which are not designated as Important Intangible Cultural Properties, which are nevertheless in need of recording and public presentation because of the importance of being aware of changes that may take place in Japanese performing arts and craft techniques. These are selected as "Intangible Cultural Properties Which Should be Recorded and Preserved". The national government itself makes records concerning these cultural properties, or subsidizes local governments to keep records and make them available to the public.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |