| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > JAPANESE GOVERNMENT POLICIES IN EDUCATION,SCIENCE AND CULTURE1991 > PART |
||
Recently in Japan, along with various changes in society, there has been a rise in public interest in sports, and together with this an increase in the number of persons participating in sports activities. As a result, a diversification in both the types of sports available and in the reasons for participating in sports has occurred.
The following major issues can be considered as underlying societal changes in Japan.
First, urbanization and advances in science and technology have made life much more convenient. However, along with urbanization comes a decrease in available land for sports grounds. Also, accompanying the many recent conveniences of life such as the wide spread use of household appliances and developments in transportation, is a decrease in chances for daily exercise. As a result, a growing number of people are beginning to feel that they are physically out of shape.
Furthermore, along with rapid growth in the nation's economy, many aspects of our social life have become sophisticated and excessively complex giving rise to more and more stress in our daily lives. There is a growing trend now for people to take up sports activities as a means of relieving this stress.
Second, leisure time has increased. With the spread of the two day weekend and with the reduction in working hours, housework, etc., the amount of free time has increased encouraging the development of more sports activities among the public.
Third, the people's income level has risen. The rise in income and living standard has freed many people from excess economic strain making it possible for them to spend more time on sports and other life-enhancing activities.
Fourth, the nation is becoming an aging society. An increase in the average life expectancy and a great decline in the birth-rate have resulted in a rapid move towards an aging society. In fact, Japan's population structure is shifting towards an aging society at the fastest rate of any country in the world. In the future this aging trend is expected to continue bringing along with it, greater interest in health and fitness and a greater demand for sports activities.
Fifth, there has been a change in people's attitudes about what
is important in life. According to a survey by the Prime Minister's Office (May
1992), entitled "Survey on People's Life", since 1979 the number of citizens
who reported that they hope for a rich, well-balanced life more than simply a
rich material life has increased. The psychological aspect of sports is also
important to consider; snorts provide both mental satisfaction and pleasure.
In the coming years. the promotion of sports should p1ay a crucial role in Japan
as it becomes a society with more time for leisure and the enjoyment of life.
Concurrent with the aforementioned societal changes, attitudes
towards sports have also been changing. In 1991, a "Survey on Exercise and Sports," ("Sports
Survey") was commissioned by the Ministry and carried out by a private polling
organization. This "Sports Survey" was administered to a sample of the general
working population nineteen years of age or older with 2,468 questionnaires returned.
The following main points were revealed from the results of the survey:
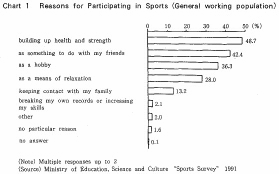
Approximately 70% of the sample engaged in some kind of sport during the one year period. Out of this number, 48.7% chose "building up health and strength" as a reason for participation. Other items chosen by a large number of the respondents included "as something to do with my friends," "keeping contact with my family," and "as a hobby or means of relaxation."
The "Sports Survey" examined the type of sports engaged in during the year of the survey and it was found that walking was the most popular, with 43.2% of respondents answering that they walked as a form of exercise. Walking was followed in popularity by bowling, golf, swimming and calisthenics in that order.
Respondents were also asked "In the future, which sports would you like to participate in?" These responses were ranked in order of popularity as follows: walking, golf, calisthenics, swimming, hiking, mountain climbing, skiing, tennis, angling, bowling and cycling. It can thus be predicted that convenient sports, outdoor activities and leisure sports will be increasing in popularity.
As to facilities for sports, it was shown that respondents made use of private facilities most (35.5%), followed by various facilities in their neighborhoods, such as prefectural and municipal facilities, public parks and grounds, vacant lots and streets, yards, inside the house or school sports facilities.
Furthermore, examining the partners which people choose for participating in sports with, it was found that most people were likely to engage in sports with their families; followed by colleagues from work, alone, with neighbors, and with persons from community clubs or circles.
As can be seen from the results of the survey, the types of
sports played are becoming more widely diversified according to individual interest
as are the places, facilities and sports partners.
Sport is not only a participatory activity it is also something to be viewed or listened to for enjoyment. Results of the "Sports Survey" showed that 28.4% of respondents "actually attend sports events" while 66.0% "don't actually attend but watch them on television or listen to them on the radio." Totaling these two figures shows that over 90% of the respondents indicated that they viewed or listened to sporting events.
Respondents were also asked about their favorite saectator sports.
Sumo was on top (48.2%), followed by professional baseball (40.9%), marathon
(l9.7%), high school or collene baseball (14.9%), volleyball (13%), and golf
(13%).
According to the results of a "Survey on Physical Fitness and Sports," conducted by the Prime Minister's Office in October 1991 (questionnaires were administered to adults 20 years old or older) the number of persons participating in a sport at least once a year has been increasing
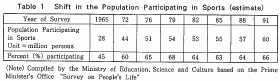
A closer look at this data shows that at the time of the survey, among those participating at least once a year, the percentage of persons engaging in sports three or more days a week was 18.2%, and one or two days a week was 24.2 %. It is estimated that 27.9% of the nationwide sample participated in sports one or more days per week.
The survey showed that approximately one fourth of the sample regularly engaged in sports one or more days a week. This would indicate that a large number of people are enjoying sports. At the same time, however, 62.8% of the respondents felt that they were "out of shape," and 75.6% said that, "in the future they would like to participate in sports." Thus it can be inferred from this survey that a great need for sports exists among the Japanese public.
The survey also showed that among the reasons for not participating in sports, almost half of the respondents (49.9%) answered that they were "too busy to take time off from work." It follows, that with the popularization of the two-day weekend and the increase in leisure time, the number of persons participating in sports is expected to increase.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |