| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > Annual Report on the Promotion of Science and Technology 2000 > Part1 Chapter1 (1) | ||
![]() The world population, which was approximately 1 billion at
the beginning of the 19th century, increased to 1.6 billion people by the beginning
of the 20th century, and since the 1950s has increased explosively to reach 6
billion in 1999 ( Fig. 1 ).
The world population, which was approximately 1 billion at
the beginning of the 19th century, increased to 1.6 billion people by the beginning
of the 20th century, and since the 1950s has increased explosively to reach 6
billion in 1999 ( Fig. 1 ).
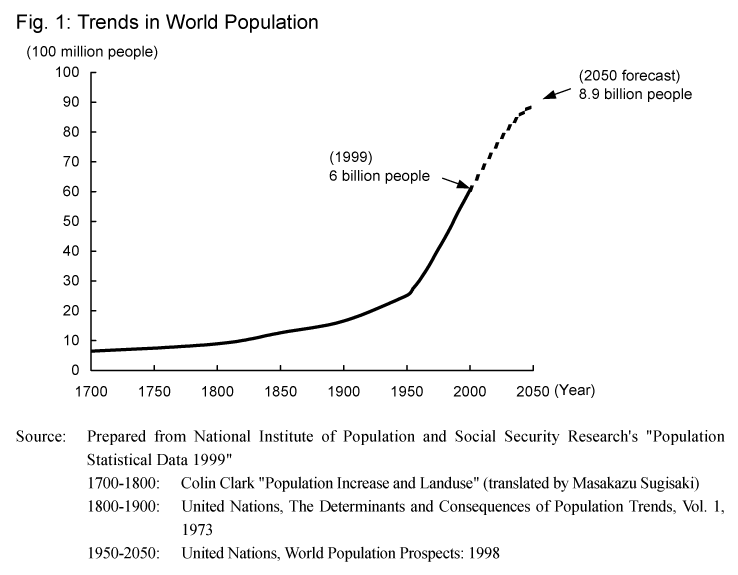
![]() Although the increase in world population is expected to slow
in the future, it is expected to reach 7.8 billion by 2025 and 8.9 billion by
2050.
Although the increase in world population is expected to slow
in the future, it is expected to reach 7.8 billion by 2025 and 8.9 billion by
2050.
![]() In Japan, the population, approximately 44 million at the
beginning of the 20th century, has increased to approximately 127 million in
1999, and is expected to reach approximately 128 million by 2007. But it is expected
to start decreasing to reach 100 million in 2050. In addition, by 2050 the peak
of the age structure is expected to be people in their 70s, and the aging of
society will deepen.
In Japan, the population, approximately 44 million at the
beginning of the 20th century, has increased to approximately 127 million in
1999, and is expected to reach approximately 128 million by 2007. But it is expected
to start decreasing to reach 100 million in 2050. In addition, by 2050 the peak
of the age structure is expected to be people in their 70s, and the aging of
society will deepen.
![]() The average life expectancy across the whole world has increased
over the past half-century from 45 to 63 for males, and from 48 to 68 for females.
The average life expectancy across the whole world has increased
over the past half-century from 45 to 63 for males, and from 48 to 68 for females.
![]() Japan in particular is the country with the longest life expectancy
in the world. For females this figure has risen from 43 years old in around 1920
to exceed 84 years old recently, and in 2050 this figure is forecast to reach
86.
Japan in particular is the country with the longest life expectancy
in the world. For females this figure has risen from 43 years old in around 1920
to exceed 84 years old recently, and in 2050 this figure is forecast to reach
86.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |