| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > FY2003 White Paper on Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology >Part1 Chapter3 Section1.2 | ||
As seen in Chapter 2, under the new framework to guarantee quality and a more competitive environment, each higher education institution is to develop its own future vision. It is necessary to study the future concept of higher education, based on this kind of university autonomy, with a view to how higher education can appropriately fulfill its important role as the base that supports Japanese society. In light of this approach, higher education in Japan faces a number of large issues.
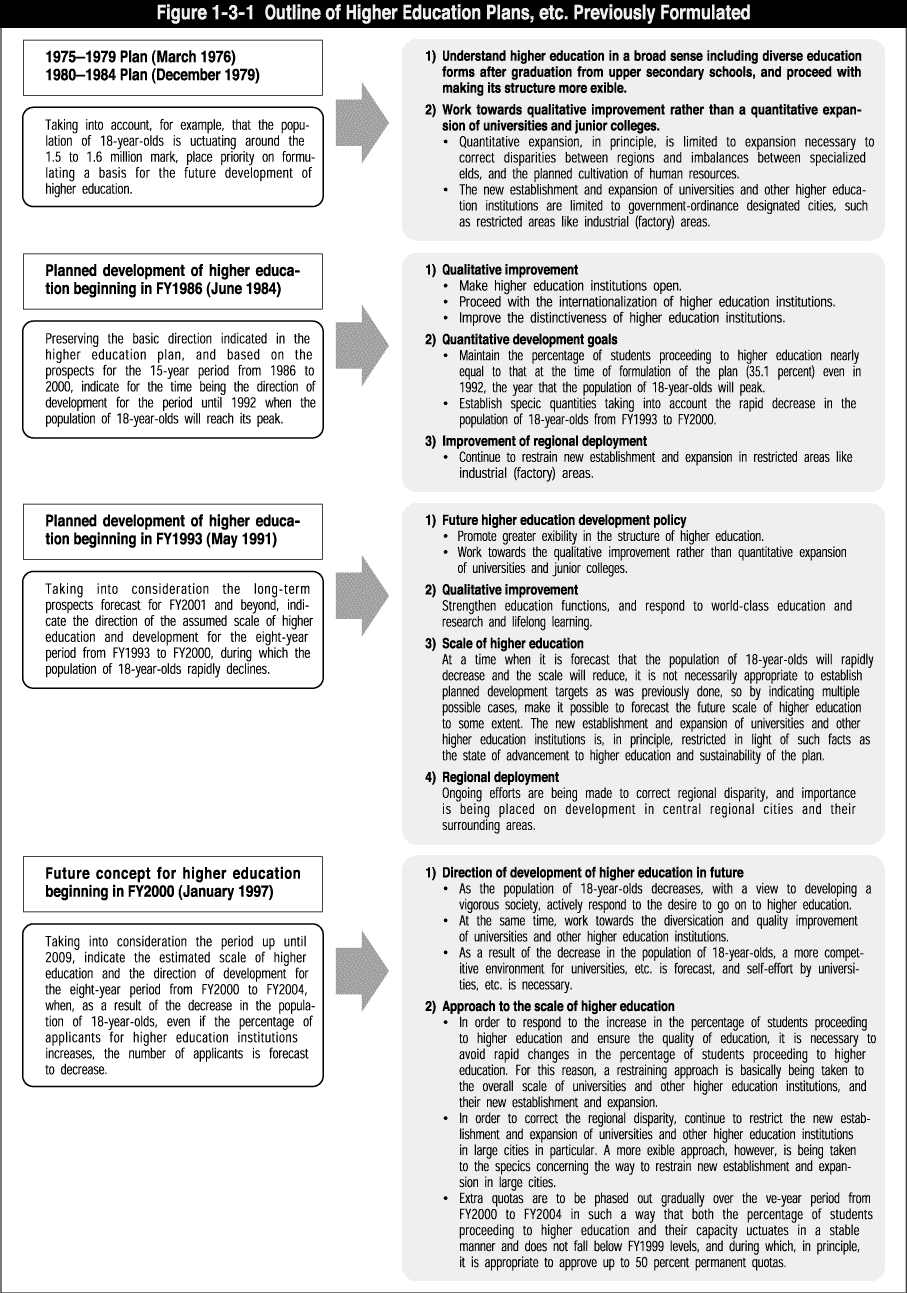
Firstly, taking the view that society as a whole benefits from higher education, it is necessary to strengthen cooperation with society greatly with respect to both education and research. When doing so, it is necessary to reconsider the respective positioning of universities, graduate schools, junior colleges, colleges of technology and professional training colleges, while taking into account wide-ranging educational opportunities after secondary education. It has been suggested that the essential social missions and development directions of each of these types of higher education institution have become unclear.
It is, therefore, important to work towards securing and improving the quality of education at each of these types of educational institution. It is necessary to cultivate "21st century citizens" to have a wide-ranging general education, select from a variety of information to explore future issues and then make independent judgments, and have a desire to contribute actively to society through intellectually productive activities. On the other hand, it is important to cultivate leaders to be at the forefront of world developments. In addition, as the birthrate falls and the population ages, guaranteeing "choice and access (use)" enabling the study of necessary subjects when required throughout one's life is an essential condition of realizing a "lifelong participation society." Furthermore, it is necessary to entrench as a highly trusted system a mechanism "guaranteeing quality" with a new evaluation system at its center, and at the same time to respond to international developments in higher education services and work towards international cooperation.
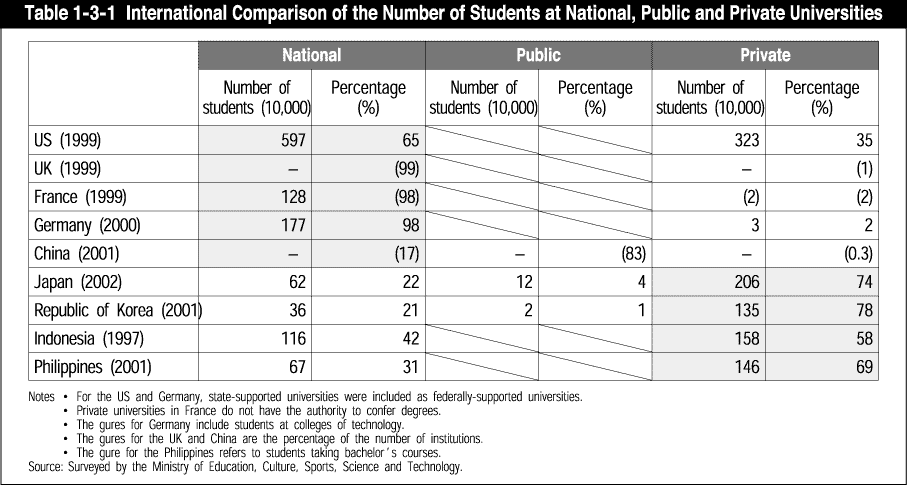
One major characteristic of higher education in Japan viewed internationally is that the percentage occupied by private education institutions is extremely high. In that sense, Japan is already well advanced along the path to privatization, although only with respect to higher education ( Table 1-3-1 ). In addition, looking at private universities, compared to US private universities, reliance on student fees has increased remarkably. As the population of 18-year-olds decreases, there are already some universities that have stopped recruiting students, so it is important to develop a variety of mechanisms and provide information to protect consumers.
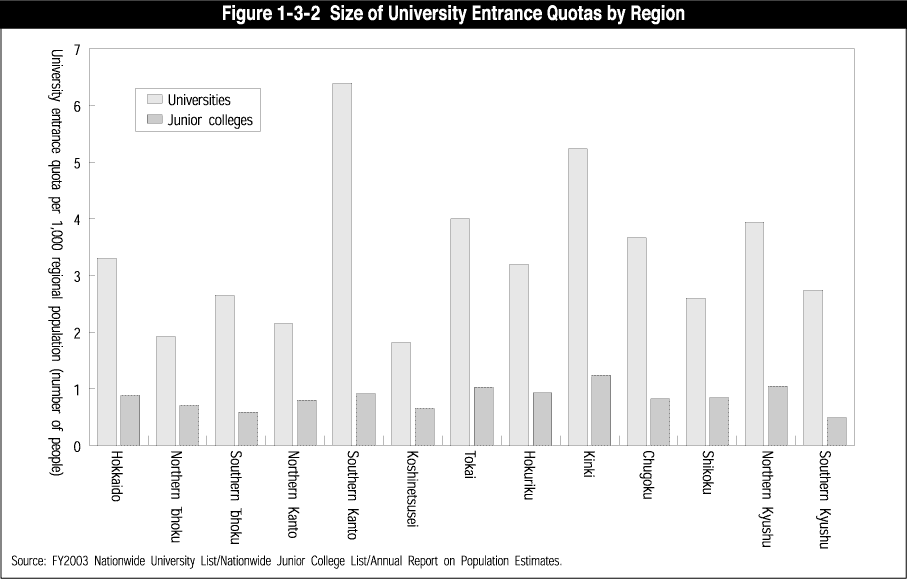
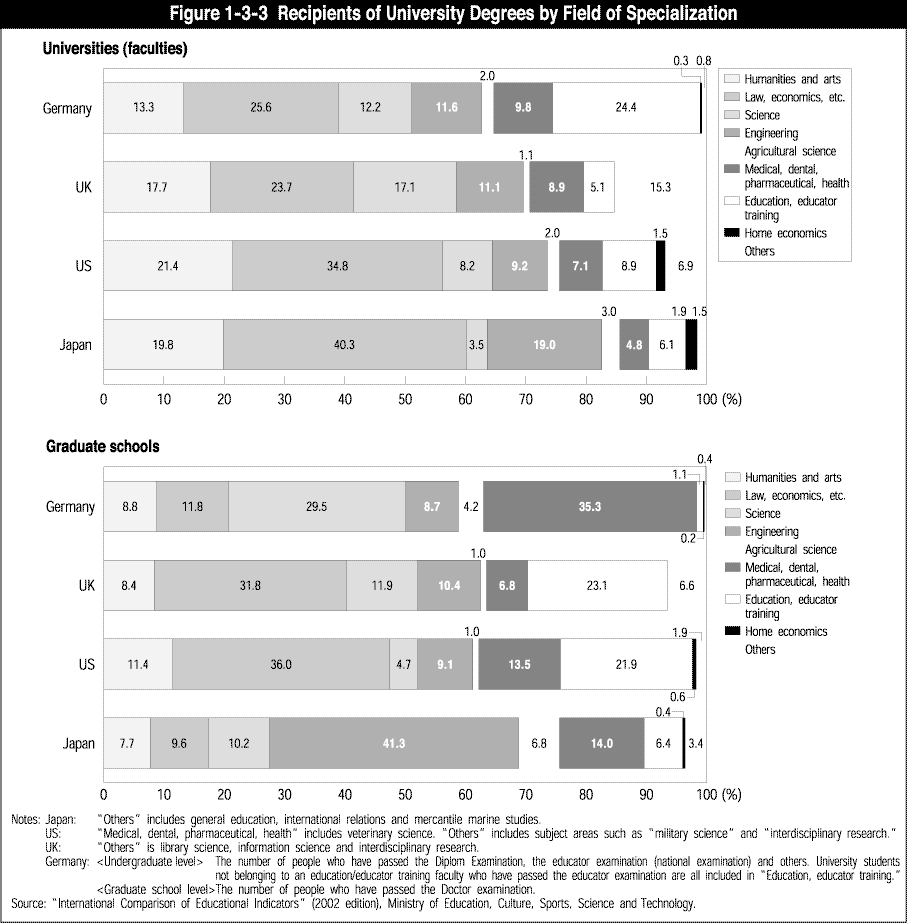
Another issue to be studied is the state of educational opportunities by region and by specialized field. In these studies, it is necessary to take into account such factors as the mobility of human resources and the expansion of distance learning, among others. Furthermore, it is necessary to take into account not only the educational aspects but also the role of knowledge and culture of local communities as a base ( Figures 1-3-2 and 1-3-3 ).
At the same time, it is necessary for society to put in place a structure to support the development of this kind of higher education. In addition to enhancing financial support, it is necessary for a social system to utilize effectively human resources that have received higher education and to put in place the results of research.
Currently, the Central Council for Education is organizing these many factors, which are interrelated in complex ways, and proceeding with deliberations concerning the future concept of higher education with a view to further developing higher education in future.
| Back To Top | MEXT HOME |