| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.2 3.2.2 3.2.2.5 | ||
For research and development in the energy sector,the Council for Science and Technology Policy acted on the Basic Plan to issue the"Strategy for Sector Promotion"(in September2001),which presents the areas of priority,research and development goals,and promotion policies for the next five years.The priority areas included:(1)research and development that brings innovative changes to the total energy system,in terms of supply,transport,conversion,and consumption(thorough,efficient efforts to achieve the3E's-energy security,environmental protection,and economic growth);(2)research and development necessary for upgrading the energy infrastructure(R&D for various elements related to the energy infrastructure;upgrading in terms of efficiency and the environment);(3)research and development for energy safety and security(R&D to ensure safety in every aspect of energy,in order to secure the people's trust);and(4)research for comprehensive social and economic evaluations and analyses of energy.Meanwhile,with prevention of global warming becoming a major issue of concern,Japan ratified the Kyoto Protocol(in June2002),and adopted a new"Guideline of Measures to Prevent Global Warming"(in March2002).In particular,with carbon dioxide emitted from energy sources accounting for90%of the greenhouse gases emitted in Japan,priority promotion of energy research and development that can contribute to control of greenhouse gas emissions is important.
| 3.2.2.5.1 Research,Development,and Utilization of Nuclear Energy |
Research,development,and utilization of nuclear energy in Japan have been carried out strictly for peaceful uses only,in accordance with the Atomic Energy Basic Law.In regard to basic and promotion policies,the Atomic Energy Commission adopted the"Long-Term Plan for Research,Development,and Utilization of Atomic Energy"(hereafter called the"Atomic Energy Long-Term Plan")in November2002,and is steadily moving ahead under this plan.
Today,nuclear power generation is major source of energy accounting for more than one-third of electric power supplies,and thus plays an important role in energy supply.Moreover,accelerators and other results of atomic energy science and technology continue to provide new knowledge in basic science sectors,and offer an essential research tool for the life science and materials science and technology sectors.In addition,use of radiation has spread to a wide range of sectors,including medicine,agriculture,manufacturing,and environmental protection.Thus,nuclear energy has greatly contributed to assuring stability in the nation's energy supplies and to improving the lives of the people.
Even so,the criticality accident that occurred at the J.C.O.uranium processing plant in September1999,as well as the revelations beginning in August2002of problems related to deceptive accounting of self-inspection operations at nuclear power plants,have heightened the people's concerns regarding the management of nuclear energy and their distrust of nuclear power experts.
The"Program for Reorganization and Stream-lining of Special Public Corporations,"adopted by the Cabinet in December2001,called for abolition of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,and for their merger through establishment of a new independent administrative institution for comprehensive implementation of atomic energy research and development.In response,the Atomic Energy Commission released in April2002the"Basic Thinking Toward the Abolition and Merger of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,and Conversion into an Independent Administrative Institution,"followed in December2002by the"Policy for Operations Priorities,and Administration,etc.,Toward the Abolition and Merger of the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute and Conversion into an Independent Administrative Institution,"in which the commission stated that the new entity will be expected to continue playing a central role in Japan's nuclear energy research and development.Furthermore,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology instituted the Preparation Council for Merging Two Public Atomic Power Corporations,which in August2002issued the"Basic Report Regarding the Merger of Two Public Atomic Power Corporations."Based on this report,studies are continuing regarding the major responsibilities,functions,and administrative operations of the new entity.
| 3.2.2.5.1.1 Ensuring Safety,and Emergency Preparedness |
Safety is the indispensable prerequisite for the research,development,and utilization of nuclear energy.Enforcement of stringent regulations and safety managements,and execution of safety research are essential to ensure safety.Moreover,in recognition of the impossibility to eliminate the occurrence of accidents to0%,there is also need to prepare countermeasures in the case of an accident to ensure that damage to the lives and health of local residents,etc.,is suppressed to an absolute minimum.
Because of these viewpoints,the government imposes stringent safety regulations on nuclear facilities at the design,construction,and operation stages for nuclear energy research,development,and this utilization in Japan,that is to a degree unseen in any other industrial sector.In addition to regulations,the government also has adopted various kinds of measures to ensure safety such as environmental radiation monitoring and emergency preparedness.
Furthermore,learning from the criticality accident that occurred at the J.C.O.uranium processing plant in September1999,inspections related to complete observance of security regulations are now being strictly performed in accordance with the Law for the Regulation of Nuclear Source Material,Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors 38) ,which was revised in1999.
Moreover,in response to revelations beginning in August2002of problems related to deceptive accounting of self-inspection operations at nuclear power plants,nuclear operators were asked to perform comprehensive inspections,and the suitability of their inspection result reports were checked.Furthermore,the Law for the Regulations of Nuclear Source Material,Nuclear Fuel Material,and Reactors,was revised again in FY2002 to incorporate regulations allowing collection of reports from maintenance and inspection operators at nuclear facilities,as part of efforts to further strengthen the safety regulations.
In the area of nuclear emergency preparedness,efforts to expand and strengthen nuclear disaster measures are now being promoted based on Special Law of Emergency Preparedness for Nuclear Disaster established in1999,including dispatch of the Senior Specialists for Nuclear Emergency Preparedness to nuclear accident sites,preparation of off-site centers and other disaster countermeasure sites,development of emergency plans and manuals,implementation of emergency drills,rearing and training of personnel.
For surveys of environmental radiation,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and other relevant ministries and agencies,prefectural governments,and atomic energy enterprises continue to conduct radiation surveys in areas surrounding nuclear energy facilities.In addition,surveys are conducted of Japan's environmental radioactive materials,as well as radiation surveys of nuclear-powered military vessels when they enter port.
Note38)The Law for the Regulation of Nuclear Source Material,Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors,was amended in1999to strengthen the safety regulations for transport control,as follows.
(1) Addition of the Facilities Periodical Inspection System for fuel fabricators
(2) Establishment of inspection system for strict compliance with safety regulations that business operators and employees must follow
(3) Institution of nuclear safety inspectors
(4) Clarification of the obligation of business operators to provide safety education to employees
(5) Establishment of system to accept proposals for improvement of safety assurance from employees
Enterprises engaged in handling radioactive materials reacted to the simultaneous multiple terrorist attacks that occurred in the United States in September2001by strengthening their controls of radioactive materials and reviewing their emergency communication procedures.
The Radiation Council examined exemptions of radiation sources and practices from regulatory control introduced in the Basic Safety Standards(BSS)issued by the International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA 39) )at its General Administrative Group,and adopted its report,"Exemptions from Regulation,"in October2002.Based on this report,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and other relevant government institutions are now studying specific legislative measures.
Also,in ensuring nuclear safety,it is important always to reflect the latest scientific and technological knowledge in safety regulations.To this end,the Nuclear Safety Commission is coordinating the"Five-Year Safety Research Program(FY2001 to FY2005)."
In FY2002,the safety research activities for FY2001 to FY2005 described below were implemented.In the area of safety research related to nuclear facilities,the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI)conducted evaluative and analytical research of light water reactors,regarding high burn-up of fuel,advanced aging,severe accidents,and other accidents and incidents,and also conduct research into criticality safety at nuclear fuel facilities.In addition,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute(JNC)conducted safety research on accident prevention and mitigation,accident evaluations,severe accidents,etc.,in fast breeder reactor(FBR),as well as safety research on the safety of criticality,shielding,and confinement,etc.,in nuclear fuel facilities.National research institutes also conducted various kinds of basic research.
For safety research related to environmental radiation,the National Institute of Radiological Sciences,working with JAERI,JNC,and other national research institutes,conducted research on the distribution and characteristics of radiation,as well as basic research into its effects.
Safety research for radioactive waste management included safety research conducted by JAERI and JNC concerning near surface disposal and geological disposal,as well as safety research into regulatory exemption(clearance)probate technology.
Note39)IAEA:International Atomic Energy Agency
| 3.2.2.5.1.2 Efforts by Nuclear Experts toward Assuring Trust,and Co-Existence with Communities |
In order to promote the smooth research,development,and utilization of nuclear energy,it is extremely important first to obtain the public reliance of the government and nuclear power operators.For this purpose,nuclear power operators must build up a record of safe operations,and to strive to obtain the people's understanding.Further-more,consistent active disclosure of information regarding nuclear power should be the norm,with the people's participation in the policymaking process encouraged.
For this purpose,information is actively disclosed,alongside efforts to enhance grassroots activities to obtain the better understanding of the people,such as dispatching lecturers and lending out simplified radiation detectors.
Furthermore,to promote co-existence between nuclear power research facilities and local candidate sites,the Power Source Grant program is being utilized to promote efforts in response to the needs of the local candidate sites.
| 3.2.2.5.1.3 Nuclear Power Generation and the Nuclear Fuel Cycle (1) Nuclear Power Generation |
With nuclear power generation being an important energy source for ensuring stable energy sup-plies in Japan,and also a superior energy source in terms of protection of the global environment,since it emits no carbon dioxide or nitrogen oxides in the course of power generation,its research,development,and utilization is being steadily promoted,predicated on assurance of safety and on peaceful utilization.
For the light-water reactors that are the main form of nuclear reactor currently in use in Japan,the government,electrical power companies,and manufacturers of atomic power equipment,etc.,cooperate to develop Japan's own technologies for enhancing the reliability of the light-water reactor,improving working efficiency,and reducing employee exposure to radiation.Nevertheless,in view of operations experiences to date,the parties involved are not satisfied with the current level of light-water reactor technology,and are striving to make the light-water reactor technology more economical while maintaining high levels of reliability and safety.
| (2) Research and Development of the Nuclear Fuel Cycle |
Japan,which must rely on imports for the vast majority of its energy resources,is steadily promoting efforts to establish the nuclear fuel cycle through effective utilization of the recovered plutonium,etc.,from the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel,in order to secure long-term energy supply stability in view of the future energy supply and demand in the world,and to reduce the load on the environment.It is important,therefore,to continue to promote research and development of the nuclear fuel cycle,and to steadily develop the Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant,the plutonium utilization program in light water reactors,and interim storage of spent nuclear fuel.
In promoting plutonium utilization,Japan strives to ensure the complete transparency of plutonium use by the full disclosure of information regarding plutonium inventories,not only from the viewpoint of rigorous management of nuclear materials,but also in clear observation of the principle of never holding plutonium in excess of amounts required to implement current programs,so as to avoid arousing international suspicions regarding proliferation of nuclear weapons.Specifically,Japan adopted international plutonium guidelines for improving the transparency of its plutonium use,and annually announces its plutonium management state through the International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA).
Concerning the enriched uranium used as fuel in nuclear power generation,Japan is promoting the development of domestic uranium enrichment projects to secure independence over the entire nuclear fuel cycle,endeavoring to maintain economy.
While some reprocessing of spent fuel from nuclear power plants is conducted at the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute's Tokai Re-processing Plant,most is consigned by contract to reprocessing by British Nuclear Fuel Limited(BNFL)and COGEMA,the French nuclear fuel company.
However,in view of the principle that reprocessing of spent fuel should be conducted domestically in Japan,construction is underway on a private-sector reprocessing facility(annual reprocessing capacity of800tons U)in Rokkasho-mura,Aomori Prefecture,and a series of tests are currently under-way,toward a projected completion date of July2005.
The aim is the firm establishment of reprocessing technology on a commercial scale through successful construction and operations of the facilities.
In this regard,the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has contracted with electrical power companies for re-processing of spent uranium fuel used in light water reactors,and has to date reprocessed a cumulative total of1,000tons.There are no plans to renew the contract when the period of the current contract is completed.
In addition,research and development of MOX fuel fabrication in Japan is now in progress at the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,and about169tons of MOX already produced by the end of June2002.
Since the interim storage of spent fuel makes it possible to adjust the amount of time required be-fore reprocessing,it is important as a method that grants flexibility to the general management of the nuclear fuel cycle.A legal framework related to interim storage was established in1999,and preparations are now in progress toward commencement of an interim storage system operated by the private sector by2010.
Domestic efforts had been underway on the advanced thermal reactor,because of its ability to flexibly and efficiently utilize plutonium,recovered uranium and other fuel.Operations at the prototype advanced thermal reactor"Fugen"were terminated in March2003,in accordance with a decision taken in1995by the Atomic Energy Commission.After summarization of research and development results,research and development on decommissioning technology will be conducted.As with the advanced thermal reactor,development of uranium enrichment technology and exploration of uranium overseas,both conducted by the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,have been terminated.Results regarding centrifugal uranium enrichment and exploration technology obtained during the research process are currently being transferred over to a private-sector enterprise.
| (3) Treatment and Disposal of Radioactive Wastes |
One of the most important issues from the viewpoint of executing coherent policies for the promotion of nuclear power utilization and of obtaining the people's understanding and trust is in the treatment and disposal of radioactive wastes,and decommissioning of nuclear facilities.Since radioactive wastes can vary in intensity of radioactivity,and in the type of radioactive substances contained,radioactive wastes are now classified not by the sources,but by the disposal methods,and specific measures are taken.
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,acting as the core institution working in close cooperation with the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute,the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology,and university-affiliated research institutions,is now engaged in research and development on the disposal of high-level radioactive wastes.In addition,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute is promoting the establishment of deep underground research laboratories as key facilities for promoting development in Mizunami City,Gifu Prefecture(crystalline rocks)and in Horonobe,Hokkaido Prefecture(sedimentary rocks).
In November1999,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute presented the Atomic Energy Commission with the"Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste(HLW)in Japan,"a summary of all research and development results up to that time.In October2000,the Atomic Energy Commission's Special Committee on Nuclear Back End Countermeasures concluded that the technical feasibility of the geological disposal concept had been shown,and the technical basis for implementation of geological disposal provided.In response to these efforts,the Law for Final Disposal of Specified Radioactive Waste was passed in May2000,followed in October of that year with the establishment of the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan.In December2002,the organization commenced looking for candidate disposal sites,targeting all municipalities in Japan.
Shallow land burial of low-level radioactive wastes generated by nuclear power plants has been carried out safely and smoothly at Japan Nuclear Fuel,Ltd's Low-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Center in Rokkashomura,Aomori Prefecture since December1992,with about151,000200-liter drums of waste already received by the center as of the end of March2003.
For the other low-level radioactive wastes,it is necessary to promote specific efforts toward realization of disposal.
Regarding radioisotope and research institute wastes,burial disposal is now being implemented in response to the Atomic Energy Commission's Special Committee on Nuclear Back End Counter-measures'summary report,prepared in May1998,on"Basic Ideas for Treatment and Disposal of Radioisotope and Research Institute Wastes."The Japan Atomic Energy Institute,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute,and the Japan Radio-isotope Association,the three main generators of this kind of waste,are at the center of studies into the formation of a waste disposal enterprise.In February2002,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology established the"Roundtable Discussion on Disposal Enterprises for Radioisotope and Research Institute Wastes,"to promote studies into the implementation of disposal enterprise implementation programs,toward the goal of early implementation of waste disposal operations.
Concerning the decommissioning of nuclear facilities,an on-site dismantling test of the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor(JPDR)was success-fully completed by the Japan Atomic Energy Re-search Institute in1996,while the first decommissioning of a commercial reactor in Japan was commenced in December2001.At present,the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute are engaged in surveys and technological research into the decommissioning of facilities related to the nuclear fuel cycle.
| 3.2.2.5.1.4 Research and Development of Fast Breeder Reactors and Related Nuclear Fuel Cycle Technology |
Fast breeder reactors and related nuclear fuel cycle technology(hereafter called"FBR cycle technology")can greatly boost the efficiency of uranium resource utilization.When this technology is put to practical use,it will become possible to continue using nuclear energy for several hundred years even if we only depend on the uranium resources known today to be technologically and economically utilizable.The use of FBR cycle technology could further reduce the environmental burden by minimizing the long-term residual radiation in high-level radioactive wastes.In terms of preparation for an uncertain future,and for assurance of an effective future energy option,development effort in this area is plainly important.
Since fast breeder reactors have an advantage of generating more nuclear fuel than they consume while generating electricity and greatly boosting the efficiency of uranium fuel utilization over light water reactors,their development has been steadily promoted through the cooperation between public and private sectors.The experimental fast reactor"Joyo"has been in operation since initial criticality in April1977.At present,the core upgrade program(MK-III),which increases the fast neutron flux and plant availability factor,is being conducted in order to improve its irradiation performance as a fast neutron irradiation reactor.
The prototype fast breeder reactor"Monju,"whose operations have been suspended since the sodium leak accident in December1995,uses technology based on MOX fuel and sodium cooling,the most advanced of the FBR cycle technologies,and it is the only fast breeder reactor plant with power generating facilities in Japan.In response to the sodium leak accident,the Science and Technology Agency(which now has been re-organized as the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology),the Nuclear Safety Commission,and others investigated and discussed the causes of the accident and determined measures for preventing its re-occurrence.Subsequently,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute has now documented the preventive measures based on these determinations.
For the direction of fast breeder reactor development,including"Monju",the"Long-Term Program for Research,Development and Utilization of Nuclear Energy"adopted by the Atomic Energy Commission in November2000emphasized that achievement of the objectives of demonstrating FBR reliability as a power generation plant and of establishing a sodium handling technology through FBR operations experience should be given top priority in future technology development,because they form the basis for comparison and evaluation with other options.The Long-term Program positioned"Monju"as the core of Japan's research and development activities in FBR cycle technology.
In addition,since July1999the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute has been collaborating with electric power companies in the framework of"Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems"to propose an appropriate model for FR cycle technology to be commercialized in the future and develop research and development plans toward its realization.The Study incorporates research and development of the candidate concepts of FR cycles to be commercialized in the future with advantages in terms of safety,economic competitiveness,reductions in the environmental bur-den,and nuclear nonproliferation.
Meanwhile,in regards to plant modification of"Monju"to reinforce countermeasures for sodium leakage,an application for the license of such plant modification was filed in May2001,and the license was granted by the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry in December2002.However,the Kanazawa branch of the Nagoya High Court issued a ruling to nullify the construction license of"Monju"in the administrative suit,which had been initiated by the local residents,in January2003.The government appealed the ruling to the Supreme Court that same month.
| 3.2.2.5.1.5 Promotion of Nuclear Science and Technology |
Nuclear science and technology uses the development and utilization of accelerators and high intense lasers to identify the ultimate components of matter and shed light on the laws of nature.The contribution of nuclear science and technology has two major aspects.The first is fundamental,theoretical research that supports science and technology development in the life sciences and materials-related scientific and technological sectors.The other is research and development that address the needs of the economy,society,and consumers by offering options for stable energy supplies in the future by means of nuclear fusion and innovative nuclear development.Promotion of nuclear science and technology requires the development of an environment conducive to creative research,and necessitates efficient and balanced development of the supporting fundamental,theoretical research.Accelerator science is constantly affected by international competition,and its technology-intensive character means that post-proposal and evaluation results should be reflected without delay in the next steps of research.The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI)and the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization(KEK)are jointly promoting High Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility Project that aims at construction of a proton accelerator with the highest beam power in the world and new development over a wide range of research fields,including life science,materials science,nuclear physics and particle physics.The project was evaluated in August2000by the Advisory Committee on Evaluation of High Intensity Proton Accelerator Project,which had been established under the Atomic Energy Com-mission(AEC)and the Science Council Accelerator Science Subcommittee.Based on the evaluation results,the construction on the High Intensity Proton Accelerator commenced in FY2001.In addition,RIKEN(The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research)is currently engaged in construction of the RI Beam Factory,an accelerator facility for generating beams of all types of radioactive isotopes(RI)from hydrogen to uranium at the highest intensities in the world.
Fusion research and development into nuclear fusion is important because it widens the range of future energy options and boosts the chances of their eventual realization.
In Japan,fusion research and development is based on the"The Third Phase Basic Program for Fusion Research and Development"and the"Long-Term Program for Nuclear Energy"adopted by the Atomic Energy Commission in1992,and is promoted through links and cooperation between JAERI,the National Institute for Fusion Science,and universities and colleges.In the future,prioritization efforts are to proceed based on"The Future of Nuclear Fusion Research in Japan"drawn up in January2003by the Science and Technology Council's Working Group on Nuclear Fusion Research.
JAERI is promoting R&D on tokamak-type reactor toward realization of practical reactor.In particular,the large tokamak device"JT-60"has achieved world-leading results,demonstrating the ability to maintain a steady nuclear fusion plasma in the core region to open the way toward efficient operation.The goal is for continuous tokamak operation through improvement of plasma confinement performance.Other activities include advanced experimental research on the medium-scale device"JFT-2M,"materials research,and safety-related tests.
The National Institute of Fusion Science,an inter-university research institute,has constructed a large helical device that is based on a unique idea originating in Japan.The facility is the largest helical device in the world,and its research into new plasma regions leads the world.
In addition,the Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University and other universities and in-dependent administrative institutions,etc.are engaged in basic research into various magnetic confinement and inertial confinement methods,and in research into essential technologies related to reactor engineering.
International cooperation on the bilateral and multilateral levels is also being actively promoted.
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor(ITER 40) )project aims for verification of the scientific and technological feasibility for nuclear fusion energy,and Japan plays a central and active role.The engineering design was completed in July2001.Later that year,in November2001,Japan,the EU,Russia,and Canada commenced inter-governmental negotiation preparatory for a joint implementation agreement regarding construction and operation of ITER,while in February2003the United States,China,and Korea in June2003joined the discussions.In Japan,the Council for Science and Technology Policy recommended that Rokkashomura,Aomori Prefecture,be proposed to the inter-governmental negotiations as a candidate site for ITER.The Cabinet approved the agreement on May31,2002,and the government is now negotiating the position.
Based on the assumption that ITER is actually sited in Japan,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology established the ITER Safety Regulations Review Working Group to perform specific expert studies into safety regulations for ITER,and the"Interim Report on ITER Safety Regulations,"was released in March2003.In response,the Ministry in the same month adopted the"Basic Policy of ITER Safety Regulations."Operations necessary for safety confirmation are now progressing in accordance with this basic policy,and the Ministry further studies the preparation of the legal framework.
Note40)ITER:International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor
The outlook for the21st century is for innovative new reactors with excellent economy and safety that are suited for thermal utilization and other diversified energy supplies and to the spread of nuclear reactor use,as well as for the advent of innovative nuclear fuel cycle systems that can alleviate the problem of how to dispose of spent fuel and radioactive wastes and also improve the nonproliferation situation.
Beginning in FY2002,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology has entertained various new ideas,using links between industry,academia,and government,to perform research and development into public canvassing methods for selection between proposals related to innovative nuclear power technologies.The Ministry of Economics,Trade,and Industry,as well,was also continuing research and development in FY2002 into public canvassing methods for selection between proposals related to innovative,creative,and practical nuclear power technologies,to ensure that there will be a variety of choices regarding future nuclear power generation and the nuclear fuel cycle.
JAERI has been conducting the rise to power test for the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor(HTTR),to establish a high-temperature gas-cooled reactor technology that explores the possibilities for diversification of energy supplies,such as high-temperature thermal supplies,and to promote re-search and development in hydrogen production and other heat utilization.Furthermore,JAERI,RIKEN,universities,and national research institutes,are broadly engaged in research and development in reactor and nuclear physics,and in fuels and materials,etc.
Basic research in nuclear science and technology nurtures the seeds that lead to diversification of nuclear power usage and future technological revolutions,and contributes to project research in the field of nuclear energy and to develop other scientific and technological sectors.
JAERI is making efforts to conduct fundamental research for renewed development of nuclear energy,with advanced basic research into the science in radiation fields being conducted at the Advanced Science Research Center.On the other hand,the Kansai Research Establishment,which is in the Kansai Science City,is engaged in development of the X-ray laser,as well as other advanced laser science.In addition,JAERI and RIKEN commenced operation of a large synchrotron radiation facility(SPring-8)in October1997,built in Harima Science Park City,for the purpose of promoting utilization and research by researchers from both Japan and abroad.Fundamental research and development into the four fundamental technology areas of substances and materials,biological and environmental effects,computation technologies,and disaster prevention and safety,is now being pursued at JAERI,RIKEN,and independent administrative institutions.
| 3.2.2.5.1.6 Promotion of Radiation Utilization |
One use for nuclear energy is the application of radiation in a wide range of sectors from basic research to utilization in medicine,engineering,agriculture,and other sectors;and promotion of research and development toward the widespread use of radiation is important.
As for the state of radiation utilization,the medical sciences already make wide use of diagnostic technology employing X-ray computerized tomography(CT)and X-ray or gamma ray radio-therapy for treatment of cancer,while research is being conducted on the use of protons and heavy ion beams,etc.,for the treatment of cancer.
In particular,the National Institute of Radio-logical Sciences(NIRS)is engaged in research on therapy using heavy ion beams,with high expectations for its clinical effectiveness against cancer.Clinical trials of the heavy ion therapy on actual patients commenced in June1994,and excellent results have been obtained for certain types of cancer.
In universities,as well,such as at the Tsukuba University's Proton Medical Research Center,re-search is progressing into the diagnosis,and treatment of cancer using proton beams.In the agricultural sector,radiation is used for improvement of crop varieties,for eradication of vermin without recourse to agricultural chemicals,and for prevention of budding in potatoes,etc.In the industrial sector,radiation is used for non-destructive testing of industrial products,for industrial measurements,and for quality improvements of rubber,plastics,and other polymer materials.In the research area,research is being conducted at JAERI's Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application and elsewhere in the creation of new functional materials useful for preserving resources or cleaning up the environment,in bio-technology,and in environmental protection technologies for elimination of toxic substances from smoke emissions.
| 3.2.2.5.1.7 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Policies and International Nuclear Energy Cooperation |
To smooth carry on with nuclear energy research,development,and utilization requires that Japan need to clearly explain to international society its stance underlying nuclear power policies,and to obtain their understanding and trust,in regard to concerns that the use of plutonium in Japan could result in international nuclear proliferation.In addition,in order to resolve international concerns related to nuclear energy,such as the issues of nuclear safety and disposal of radioactive wastes,it is important that Japan actively make use of its technology and experience in cooperation with international society,so as to obtain the understanding and trust of the international community.
| (1) Nuclear Non-Proliferation Policies |
In order to ensure smooth implementation of the peaceful use of nuclear energy,the maintenance of international nuclear non-proliferation regime,which along with safety assurances,is extremely important.Several numbers of international frame-works,i.e.the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons(NPT 41) ),the comprehensive safeguards by the International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA)based on the NPT,and the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty(CTBT 42) ),have been established.In addition to these frameworks,Japan reinforces the international nuclear non-proliferation regime with its technologies and skilled personnel in relation to the peaceful utilization of nuclear energy.
On the view of the Atomic Energy Basic Law,Japan promotes the development and utilization of nuclear energy under the strict restriction of peaceful purposes.For many years,Japan has implemented"safeguards"and"physical protection"to ensure the peaceful use of all nuclear materials,based on the Safeguards Agreement with the IAEA,the Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material,and the bilateral nuclear energy cooperation agreements with the United States and other countries.Japan has also promoted the necessary technology development for the implementation of the above.
In FY2002,Japan continued steady implementation of the IAEA Safeguard Agreement and of the Additional Protocol designed to strengthen the safeguard's effectiveness,and also engaged in studies with the IAEA toward a series of safeguards(Integrated safeguards)that achieve maximum effectiveness and efficiency.In addition,in preparation for the start of operations of the Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant,an important facility for safe-guards,the government commenced operations of the Rokkasho Safeguards Center and promoted development of the Rokkasho Safeguards Analytical Laboratory(on-site laboratory).The government has also joined with the IAEA to organize an international training course for the improvement of technologies for nuclear materials accounting.
In addition to responsibilities imposed under the NPT,it is important for Japan to ensure transparency by employing rational and consistent plans,while adhering strictly to the principle of non-possession of surplus plutonium.Therefore,in line with international plutonium guidelines designed to boost transparency of the nuclear fuel cycle program,Japan discloses through the IAEA the conditions of its plutonium management,and independently discloses more detailed data,to ensure that transparency is maintained at as high a level as possible.Furthermore,Japan actively promotes the development of technologies related to non-proliferation policy,and undertakes research and development activities with full consideration of nuclear Non-Proliferation in fields such as advanced recycling technologies.
Elsewhere,Japan in July1997swiftly ratified the CTBT banning all nuclear weapon test explosions and all other nuclear explosions,a historic step towards a world that is free of nuclear weapons,and is now engaged in development of an international monitoring system towards the treaty's eventual enforcement.
Note41)NPT:Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons
Note42)CTBT:Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty
| (2) International Nuclear Power Cooperation |
In the international nuclear cooperation,it is important to promote the international cooperation activities for common issues or R&Ds,such as these for research;development and utilization of nuclear non-proliferation as well as to respond positively to the expectations of developing nations.
For nuclear cooperation with Asian countries,exchanges of information,opinions,and technology are being promoted under the framework of the Forum for Nuclear Cooperation in Asia(FNCA)for the peaceful utilization of nuclear power,in such areas as research reactors and the medical utilization of radiation.
The third meeting of the FNCA was held in Seoul,Korea in October2002,at which the ministers in charge of each nation's nuclear power programs exchanged opinions on how to promote nuclear cooperation,utilization of radiation,and other topics.
Japan also participates in the Regional Cooperative Agreement for Research,Development&Training Related to Nuclear Science and Technology(RCA 43) ),a grouping since1978of IAEA member countries in the Asia-Pacific region,hosting study seminars and other events in the industrial,medical,and radiation protection fields,as well as making technology transfers through the dispatch of Japanese experts,providing equipment and materials,offering funding and personnel assistance,and contributing to the social and economic development of developing nations.
For the cooperation in nuclear energy with the countries of the former Soviet Union and of Central and Eastern Europe,Japan offers research co-operation for decommissioning of nuclear facilities,bilateral cooperation for quality improvement of plant operators through training projects,and provision of multilateral support through extra-budgetary contribution funding to the IAEA.In addition,regarding the management and disposal of Russia's surplus weapons-grade plutonium,Japan is determined to utilize its technologies for peaceful use of nuclear energy developed over many years in Japan to cooperate disposition program of Russia's surplus weapon-grade plutonium,as part of its contribution to nuclear disarmament and Non-Proliferation,in close cooperation with the principal countries of the United States and Russia,and with other involved countries.In particular,the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute(JNC)is engaged in research cooperation with Russia's Institute of Physical Energy Research and the Institutes,such as Research Institute for Atomic Reactors and Institute of Physics and Power Engineering.
Finally,for nuclear cooperation with Europe countries and United States,Japan exchanges experts and information regarding the peaceful use of nuclear energy,and the receipt and supply of nuclear materials and related services.Specifically,this includes research cooperation by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute(JAERI)and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute(JNC)with the U.S.Department of Energy(DOE)and French Atomic Energy Commission(CEA),and research cooperation between RIKEN and the U.S.-based Brookhaven National Laboratory,and also with Britain's Rutherford Appleton Laboratory.
Japan also participates in the Generation IV International Forum(GIF),related to the Gene-ration IV nuclear energy systems,a grouping of10countries that includes the United States and France,for studies related to the development of next-generation nuclear energy technology.
Note43)RCA:Regional Cooperative Agreement for Research,Development&Training Related to Nuclear Science and Technology
| 3.2.2.5.1.8 Infrastructure for Promotion of Nuclear Energy Use |
An important issue for the promotion of research,development,and utilization of nuclear energy while maintaining safety is the fostering and maintenance of superior personnel resources,and the maintenance and transmission of technology skills.As a result,the universities that handle the core function of human resource development need to be in contact with research and development institutions,private-sector enterprises,and other related institutions,while also maintaining an international perspective,in order to be able to foster diverse and capable human resources.In addition,government research institutions and private-sector enterprises need to create systems that will encourage mutual personnel and technology exchanges such as joint research activities and exchanges of personnel.It is important for Japan as a whole to strive to maintain,continue,and develop its personnel and technology capabilities.
Moreover,the development of R&D activities that challenge the broad possibilities of nuclear power,and also offer dreams and hope to young people,is important for fostering personnel willing to test nuclear power.The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,and the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry,are contributing to personnel development through implementation of links between industry,academia,and government,to perform research and development into public canvassing methods for selection between proposals related to innovative nuclear power technologies.
| 3.2.2.5.2 New Energy Research and Development |
While new energy can contribute to countermeasures for global warming,and to stable energy supplies,it also faces problems of economy,where low energy densities meet high electricity generating costs,and of stability,where output can be too easily swayed by the surrounding natural conditions.Research and development into fuel cells,photovoltaics,biomass energy,and other forms of new energy need to be aggressively promoted,so as to attempt resolution to these problems and to promote their introduction and broader dissemination.
| 3.2.2.5.2.1Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Energy Utilization |
Because fuel cells utilizing hydrogen for fuel are efficient and clean,much is expected of them as a key energy and environmental technology.While development of fuel cells for use in automobiles and as stationary generators is well-advanced,there still remain some performance and economy issues in the way of their commercialization and dissemination.For this reason,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry is promoting research and development of component technologies for elements of the fuel cell body,and research and development of the peripheral technologies related to hydrogen energy utilization,involving the manufacture,transport,and storage of hydrogen fuel,etc.The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology is promoting development of new components and materials for improved fuel cell performance.
| 3.2.2.5.2.2 Photovoltaic Power Generation |
Photovoltaic power generation has been spreading as the price has fallen.Nevertheless,development of technologies that can further lower costs is essential for the early appearance of a truly independent market.For this purpose,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry is promoting the development of technologies that achieve lower costs and higher levels of efficiency,as well as the development of recycling and reuse technologies.
| 3.2.2.5.2.3 Biomass Energy |
Biomass is a renewable energy source obtained through plant photosynthesis of solar energy,which fixes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into organisms.Once a serial biomass energy utilization system consisting of fixation,conversion,utilization,and recovery of energy can be established,there would be no possibility for the atmosphere's carbon dioxide levels to increase.To promote utilization of this biomass resource,the Cabinet adopted the"Biomass Nippon Strategy"in December2002.To commercialize and disseminate biomass energy,and create"Biomass Nippon,"the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry,the Ministry of Land,Infrastructure,and Transport,and the Ministry of the Environment,are promoting research and development into technologies for the efficient conversion of animal wastes,wood residues,organic sewage,food wastes,and other unusable biomass sources into universally acceptable fuel forms,such as methane and other gaseous fuels(gasification)or methanol and other liquid fuels(liquefaction),and into technologies for these fuels'efficient utilization.
| 3.2.2.5.3Clean Fossil Fuel Energy R&D |
Coal,oil,natural gas,and other fossil fuel energy sources are expected to provide the vast majority of energy supplies for the foreseeable future,and such issues as limited resources and global environmental problems will need to be addressed.For this reason,there is a need to promote research and development of cleaner,more efficient fossil fuel technologies so as to ensure stable energy supplies in response to forecasts of rising global energy demands,while also taking into consideration the effects on the global environment.
| 3.2.2.5.3.1Coal |
Coal offers excellent supply stability when compared with petroleum,etc.But since coal has one of the highest carbon dioxide emission volumes per unit of burned energy among the fossil fuel sources,development of innovative new technologies will be needed to reduce the carbon dioxide burden on the environment,so as to smooth the expanded utilization of coal while at the same time dealing with global environmental issues.
For this purpose,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry is promoting the development of high-efficiency power generation technologies and other clean coal technologies,such as the high-efficiency coal combustion technology or the Integrated coal Gasification Combined Cycle(IGCC 44) ).
Note44)IGCC:Integrated coal Gasification Combined Cycle
| 3.2.2.5.3.2Natural Gas,etc. |
Natural gas has lower carbon dioxide emission volumes per unit of burned energy than other fossil fuel sources,thus easing the burden on the environment.Promoting research and development of natural gas is therefore important to encourage its exploitation and utilization as a major energy source.
Consequently,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry is promoting research into technologies for the manufacture and utilization of liquid fuels(GTL,or Gas-to-Liquid 45) )or dimethyl ethyl(DME 46) ),obtained by converting natural gas into liquid fuels,which should lead to expansion of natural gas use.The ministry is also promoting research into development of new exploitation technologies for utilization of methane hydrates,believed to be available in relatively large quantities in the seas around Japan,as an energy source,as well as other technologies.
| 3.2.2.5.4Energy Conservation and Energy Efficiency R&D |
From the viewpoint of addressing global environmental issues and effectively utilizing limited energy resources,it is important to carry out re-search and development not only to improve efficiency in specific individual devices and in essential technologies but also to improve energy supply and utilization efficiency throughout all systems in society.This means the introduction and use of distributed systems and the utilization of unused energy.It is also necessary to promote research and development with a view to reducing all energy(life cycle energy)which is directly or indirectly consumed in the production,use,re-use,and disposal of products,and through the provision of services.To this end,the Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry,among others,is promoting the following research and development.
Promoting research and development into elemental technologies for improving the performance and economy of fuel cell and hydrogen utilization,of which much is expected as highly efficient and clean next-generation energy systems,toward their commercialization,and research and development into hydrogen fuel manufacture,transport,storage,and other hydrogen utilization technologies,as well as related technologies.
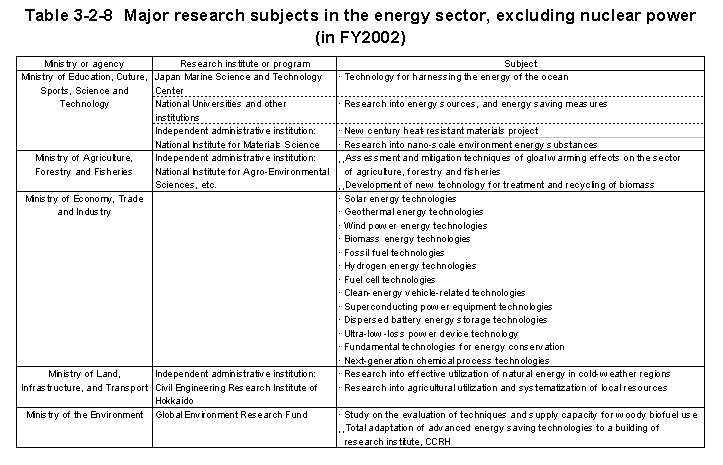
In addition,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology is promoting research and development of ultra-heat resistant materials,etc. Table3-2-8 shows a summary of the major research topics in the energy sector(excluding nuclear power)implemented during FY2002.
Note45)GTL:Gas to Liquid
Note46)DME:Dimethyl Ether
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |