| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > WHITE PAPER ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY2003 > Part3 3.2 3.2.2 3.2.2.1 | ||
| 3.2.2.1.1Promotion of Life Sciences |
The life sciences aim at elucidating the complex and elaborate mechanisms of biological phenomena produced by living things,and its results contribute greatly to the improvement of the people's lives and to development of the national economy,through dramatic advances in medicine,resolutions of food supply and environmental problems,and other areas.
| 3.2.2.1.1.1 Basic Policies for the Promotion of Life Sciences Research |
In Japan,the life sciences are being promoted more aggressively than in past years.The"Second Science and Technology Basic Plan"(hereafter called the"Basic Plan")adopted by the Cabinet in March2001positioned the life sciences as one of the four priority sectors,and called for prioritized,strategic efforts in this sector.
In response to the Basic Plan,the Council for Science and Technology Policy adopted the"Pro-motion Strategy by Sector"in September2001for the life sciences sector,clarifying fields of priority,research and development goals,and promoting policies for the next five years.For technologies to be researched for"protecting the people's health,"the promotion strategy listed as priority areas:(1)technologies that utilize genome-related technologies for the prevention and treatment of disease,in order to achieve a vital,long-lived society;(2)elucidation of life-protecting mechanisms in relation to infectious diseases and environmental factors and technologies for the prevention and treatment of disease;and(3)promotion of basic technologies for mental health and for the brain,and technologies for the prevention and treatment of disease.In the area of"development of technologies for competitiveness and sustainable growth,"it listed:(4)technologies for materials production and environmental treatment that utilize the functions of living things;and(5)food science technologies that contribute to better food supply security and to improved diet.In the area of"joint basic science"it listed:(6)development of technologies for emerging and interdisciplinary areas,and advanced analytical technologies;and(7)construction of systems for the promotion of research into the efficient return to society of the fruits of advanced research.
In the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Science and Technology Council drew up the"Policy for Promotion of Research and Development in the Life Sciences"in June2002.This promotion policy,developed in response to the priority areas delineated in the Basic Plan,extracts specific research and development topics that the ministry should promote in the future,as well as presenting strategies for the nation in the long term,including the importance of strengthening foundations and building suitable environments for life sciences research and development,and specific ideas for the general promotion of research and development in Japan.
| 3.2.2.1.1.2Efforts Toward Industrialization,Etc. |
To strengthen efforts toward commercialization of the life sciences,in January1999the heads of five ministries and agencies(the Director General of the Science and Technology Agency,the Minister of Education,the Minister of Health and Welfare,the Minister of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries,and the Minister of International Trade and Industry(as they were then constituted))drew up the"Basic Policy for the Creation of Biotechnology Industries,"which proposed promotion of research and development of biotechnology and commercialization of such programs.The five ministries and agencies followed up the Basic Policy in July of that same year with adoption of the"Basic Strategy for the Creation of Bio-technology Indus-tries."
In FY2000,the"Millennium Project"was instituted to promote revolutionary advances in medicine for the elderly,and to promote environments that offer prosperous and healthy eating habits and secure living,with achievement of the following goals set for FY2004.
Regarding implementation of this project,an evaluation and support council consisting of third-party experts was established to provide annual evaluations of the state of the project,including an interim evaluation for FY2002,the project's middle year.Furthermore,the Prime Minister's Office established the BT(Biotechnology)Strategy Council in July2002.This strategy council issued the"Strategies for Development of Biotechnology"in December2002,detailing three strategies focused on2010,including:(1)revamping research and development;(2)enhancing the process of industrialization;and(3)ensuring public under-standing,and specific action plans for achieving those strategies.The Council of Science and Technology Policy also examined the strategic policies from the viewpoint of science experts,and in December2002drew up its own report,"On Promotion of BT Research and Development,"the contents of which were reflected in the strategy outline.
| 3.2.2.1.1.3 Strategic Fields in Life Sciences (1)Genome-Related Research |
In June2000,the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium,a joint team of researchers from Japan,Europe,North America,and China pursuing the project of sequencing the human genome containing all human genetic information,announced that they had completed sequencing about90%of the entire base sequence of the human genome.In February2001,the consortium announced the results of the draft sequencing.
At this time,a project involving detailed sequencing of DNA base pairs on human chromosomes21and22,led by Japan,was also completed,and the results,which included discoveries of genes related to specific diseases,were highly praised in the scientific community.Also,in December2000,the Committee on Policy Matters of the Council for Science and Technology hosted a roundtable discussion on the promotion of post-genome strategies,and summarized its conclusions in"On Promotion of a Post-Genome Strategy"(hereafter called the"Post-Genome Strategy"),including the need for quick action on post-genome research,and discussion of some basic strategies.
The Consortium set a goal to complete the de-tailed sequencing of all three billion base pairs of the human genome by April2003,and preparations are in progress in Japan for issuance of the final report announcing the completion of the sequencing project,as well as for symposiums honoring Japan's participating researchers.
The Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,having just shouldered part of the international effort toward completion of a detailed sequencing of the human genome,has now turned to post-genome strategies involving the steady promotion of research in such fields as the analysis of protein structures and functions related to genome-based drug discoveries,etc.,and the development of revolutionary medical technologies that make use of individual genome information.In addition,as part of the"Millennium Project,"the ministry is working through the"Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research and the Research for the Future Program"to promote the priority of basic research in this sector at universities and colleges.In FY2002,the Institute of Physical and Chemical Re-search(RIKEN)published sequences and functional annotation of full-length cDNA 2) for60,770mouse clones,which play medically important roles as model animals for human conditions.
Since FY2000,The Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare is involved in the Millennium Project,using elucidation of genes related to senility,cancer,diabetes,high blood pressure,asthma,and other ailments of the elderly,to promote R&D toward establishment of methods for the prevention and treatment of disease and development of revolutionary new drugs.Moreover,as part of research for the promotion of incipient advanced medical technologies,especially those that build on the rapid advances in genomic sciences seen in recent years,research and development commenced in FY2002 into basic technologies(toxico-genomics)that allow rapid and effective prediction of the safety(toxicity,side effects,etc.)of compounds that are candidates for medical products.
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries,in research mainly by the National Institute on Agrobiological Resources,targeted the rice plant and animals to isolate genes useful for improving agricultural production,such as a gene that confers resistance to rice blight,developed a DNA utilization technology,and implemented the MAFF gene bank project for systematic collection,accumulation,and distribution of the DNA utilization results.In particular,the Rice Genome Project is important for laying the foundations for research into major grains and other crops,and Japan led the world in establishing the project back in FY1991.The second stage of the"Rice Genome Project,"launched in FY1998,has consisted of reading the entire base sequence for the rice genome and elucidating the functions of useful genes.Already well underway to worldwide acclaim,the"Rice Genome Project"has now been repositioned to be part of the"Millennium Project."
Japan has assumed a leading role in sequencing the rice genome.Although the project's international consortium consists of10countries and regions,Japan alone has accounted for about60%of the total sequence.With the completion of a precise sequence for the most important parts of the genome under Japan's supervision,Prime Minister Koizumi announced to the world on December18,2002that the sequence analysis on the important parts was complete.In addition,the"Project for Development of a Complete Rice Plant cDNA Library"launched in FY1999 had collected information for about30,000different rice genes by FY2002.
Furthermore,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry engaged in genome function research and technology development at the National Institute of Industrial Research,performed DNA analysis,etc.,of industrially useful microorganisms at the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation,and worked through the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization to utilize private-sector vitality to pursue technology development for analysis of genetic information.In FY2001,analysis of the complete human cDNA structure led to identification of about30,000new human genes,and analysis of those genes is now in progress.
At the Ministry of the Environment,the independent National Institute for Environmental Research is researching the utilization of genome technology in research for preservation of biological diversity,and also the health effects of toxic chemical sub-stances.a)Promotion of Protein Structural and Functional Analyses
Analysis of protein structure and molecular function is one of the most important fields in post-genome research because the research results can link directly to applications in medicine or to uses in industry.
Toward the goal of developing genome-based drugs in Japan,in FY2002,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology made available two facilities-the world's largest NMR(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance)facility and SPring-8(the Large-Scale Synchrotron Radiation Facility)-to promote the"National Project on Protein Structural and Functional Analysis.""This project brings together researchers from industry,academia,and government to elucidate the structures and functions of more than one-third(about3,000)of the approximately10,000basic protein folds known to exist,and to patent the results.
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries has been promoting research into the comprezhensive elucidation of rice proteins as one aspect of its research into the rice genome,while its genome analysis center is engaged in researching the expression of proteins from genes and prediction of their functions by comparing their three-dimensional structures with those of already known proteins.
The Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry has brought researchers from industry,academia,and government to its newly established Japan Biological Information Research Center,to engage in"analysis of the three-dimensional structures in biological molecules,"specifically,R&D into the structural analysis of membrane proteins believed to play particularly important roles in the body,and in"analysis of protein functions"for analysis of newly discovered human genes using results obtained from analysis of the total human cDNA structure.
The Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare is promoting research and development as part of its Medical Frontier Strategy into elucidation of the functions and interactions of proteins affiliated with disease,in order to improve prevention and treatment performance for cancer and heart attacks,the two main causes of death for work-prone Japanese,as well as for such illnesses as strokes,senility,and bone fractures,that are a major source of demand for nursing assistance.b)Promotion of Bio-Informatics
Recent research into the genome sciences has made available vast volumes of genome-related in-formation,necessitating the appearance of the new field of bio-informatics,an integration of the life sciences and IT(information technology)sectors,as a way to utilize this information.
In the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Institute for Bio-informatics Research and Development(BIRD)at the Japan Science and Technology Corporation is actively engaged in the upgrading,standardization,and expansion of databases required for the development of bio-informatics,as well as in the development of genome analysis tools with the cooperation of researchers in both the biology and information technology sectors.The ministry is also promoting development of the DNA Data Bank of Japan(DDBJ),one of the three largest of its kind in the world,under the operation of the National Institute of Genetics and other genome-related data-bases,and is using the Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research for priority promotion of basic research in this sector at universities and colleges as part of"Millennium Project."Furthermore,in FY2002 the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology was utilized to implement programs related to personnel development in the bioinformatics field,with funding targeted at universities and national research institutes,etc.
At the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries,research into"development of the rice genome simulator"is going forward as part of research into the rice genome.The simulator is being developed as a virtual testing system that will collect base sequence data obtained from the rice genome research and data from analyzing useful gene functions,and add in related information from conventional rice breeding and culturing research data,etc.,to enable computer-based simulations of improvements to rice and other crop varieties.
In FY2000,the Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry commenced building a comprehensive database complete with independently-obtained data and advanced search and analysis tools,to enable utilization in research and industrialization of the vast amounts of biotechnology-related data and achievements obtained from the Millennium Project.In addition,the ministry commenced the"Project for Analysis of the Gene Diversity Model"in FY2000(based on the supplementary budget)to implement development of software that will make it possible to conduct efficient searches for genes related to disease,based on micro-satellites,SNPs 3) ,and other polymorphic gene information.c)Promotion of Gene Polymorphic Research
Various ministries are engaged in the promotion of research and development for elucidation of genes related to specific diseases,toward the goal of more effective medicine suited to specific individuals.At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,for example,the SNPs Research Center at RIKEN is engaged in the search for genes related to specific diseases as part of"Millennium Project"activities,while the Institute of Medical Science,the University of Tokyo,and the Japan Science and Technology Corporation are cooperating in the search for Single Nucleotite Polymorphism(SNPs,individual differentces in genetic information)in healthy people.By March2003,the joint group had published SNPs data for200,000locations,via the JSNP database 4) .In the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry,the SNPs data is being jointly examined by the Institute of Medical Science and the Bio-Industrialization Consortium(JBiC),in the form of analysis of gene polymorph frequencies(allele frequency analysis).Currently,data about SNPs locations is being issued from both the JBiC bio-data base system and the JSNP database.The speed and precision of these SNPs analyses conducted in Japan is as advanced as anywhere in the world,and SNPs data in gene regions,in particular,is attracting attention as an essential element in the achievement of tailor-made medicine in the future.Furthermore,the ministry is seeking prioritized promotion of basic research in this area at universities and colleges using the Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research.
The Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare is promoting searches for gene polymorphs for disease-related genes and drug-reactive genes related to senility,cancer,diabetes,high blood pressure,asthma,and other ailments,all as part of the Millennium Project.
In FY2002,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries commenced development of SNPs markers in agricultural crops for the purpose of developing effective crop breeding and nurturing systems that make use of gene polymorphs.
Note2)cDNA:Abbreviation for"complementary DNA(or complementary deoxyribonucleic acid)."The term denotes DNA synthesized by using reverse transcriptase in a template for messenger RNA(m-RNA).cDNA consists only of the gene regions of the DNA,so that a complete cDNA encompasses all information about a single gene.
Note3)SNPs:Abbreviation for Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms.It refers both to the expression of base sequences on the genome that vary according to race or individual(such as the difference between a healthy individual and a sick person),and to the corresponding area on the genome.
Note4)JSNP database:A database set up for the Millennium Project,jointly promoted by the Human Genome Analysis Center at the University of Tokyo's Institute of Medical Science,and the Japan Science and Technology Corporation,for SNPs scattered throughout the human genome's gene regions.(http://snp.ims.u-tokyo.ac.jp)
| (2)Promotion of Brain Sciences Research |
Brain science is a frontier with huge potential,and aggressive promotion of research and development is expected to lead to results that improve the quality of life,as well as to improved medical science and to the creation of new technologies and industries.In this regard,the Council for Science and Technology's Life Sciences Division Committee of Brain Science issued a"Long-Term Strategy for Research and Development on the Brain"in May1997,a long-term plan for promotion of brain sciences research in Japan.The resulting efforts have greatly strengthened Japan's brain sciences research,which have been divided broadly into the three fields of"understanding the brain,""protecting the brain,"and"creating the brain,"through research and development that makes maximum use of the many universities and national research institutions that extend beyond the bounds of individual ministries and agencies.
At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the three fields of brain science research are being promoted at the Brain Science Institute at RIKEN,and through utilization of competitive research funds by the Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology and by the Japan Science and Technology Corporation.In addition,as part of the"Millennium Project,"Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research are being used to promote prioritization of research in this field at universities and colleges.
Activities in other ministries and agencies include the Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare's efforts to promote research on the elucidation of mental and nervous system disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease,and on the development of methods of treatment,while the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries is engaged in research on brain and nervous system functions in animals,and the Ministry of Public Management,Home Affairs,Posts and Telecommunications is engaged in research into the elucidation and application of info-communication functions in living organisms.
Furthermore,the"Human Frontier Science Pro-gram"(HSFP),which was first proposed by Japan at the Venice Summit of advanced nations in June1987,operates based on the principles of"internationality,""interdisciplinarity,"and"encouragement of young scientists,"to provide subsidies within an international framework for research that contributes to the elucidation of brain functions and other complex mechanisms of living organisms.
| (3)Promotion of Development,Differentiation,and Regeneration Science Research |
Research into the generation,differentiation,and regenerative fields entails the elucidation and application of the basic mechanisms that give rise to advanced biological phenomena,such as the coding for creation of individuals and the integral processes for biological functioning as individuals.In particular,rapid advances in stem cell and embryonic stem(ES)cell research in recent years is opening the way for broader applications such as the development of cell transplant technologies(bone marrow,skin,etc.)that do not cause graft rejections,and other regenerative medical techniques.
At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Center for Develop-mental Biology was established at the RIKEN as a part of the Millennium Project for elucidation of the basic mechanisms for the generation,differentiation,and regeneration of living things,and to contribute to advanced regenerative medicine.The center is engaged in its own research and the ministry is also utilizing such competitive funding projects as the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology and the Research for the Future Program to promote generation,differentiation,and regeneration research at universities and colleges.
Furthermore,to contribute to the realization of regenerative medicine,the Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare is using the Grant for Health Sciences as a part of the Millennium Project to promote research into the elucidation of mechanisms for the occurrence of five major diseases afflicting the elderly,including strokes,bedsores,and broken bones.In addition,national research institutions(such as the National Cancer Center and the National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry)are at the center of research into efforts to prevent graft rejections following organ transplants and to utilize the self-repair mechanisms of human cells to prevent other side effects.
In FY2002,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry began promoting development of equipment in support of practical applications of regenerative medicine,with development of technology and supporting equipment for artificial control and cultivation at the genetic level of human stem cell proliferation and differentiation processes by the Foundation for the Promotion of Advanced Medicine.
| (4) Promotion of Plant Science Research |
Advances in genome science have also led to progress in the analysis of plant genome structures and functions.Control of plant functions based on these results is expected to lead to the development of plants that can contribute to improvements in eating habits,etc.
Rice genome research is important for laying the foundations for research into the major cereals and other crops.The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries is currently promoting the Second Phase of the"Rice Genome Project,"which involves the reading of all DNA base sequences for the rice genome,and the elucidation and patenting of the functions of useful genes,which are efforts that have attracted worldwide acclaim.
Japan took a leading role in the international consortium of10countries and regions to promote reading out the entire genome base sequence for rice.When a group of foreign private-sector corporations announced that they had completed a summary reading of the rice genome base sequence,however,Japan in August2001called for completing the project nearly two years earlier than originally planned,and operations were accelerated.
As a result,a precise sequence for the most important parts of the genome was successfully completed,so that Prime Minister Koizumi was able to announce to the world on December18,2002that the sequence analysis was complete.The data sequenced by the international consortium was made available on the Web,and is now being examined by researchers around the world as the optimum information resource(Golden Reference)for crop genome research.
The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries commenced post-genome sequence research even as the base sequence readings were continuing.By the end of FY2002,research centering on the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences had isolated more than40useful rice genes and elucidated their functions,using gene maps and mutant panel methods,etc.(with plans to have isolated and elucidated functions for more than100genes by the end of FY2004).
In the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Plant Science Center at RIKEN is engaged,as part of the"Millennium Project,"in research into the relationship of advanced functions and genes in plants at the molecular,cell,individual,and group levels.In addition,the"Research for the Future Program"by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science(JSPS)promotes plant gene research,as well as a broad range of other basic research at universities and colleges.
| (5)Development of the Bioresources |
The field of bioresources is not limited to the mere preservation of genetic resources,but also plays an important role in exploring new areas of research.The national interest is served in the development,collection,storage,and supply of bioresources.
In FY2002,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology instituted the"National Bioresource Project"for the purpose of establishing a system facilitating the systematic collection,storage,and supply of bioresources that are of particular strategic importance to the nation,such as test animals and plants(such as mouse clones),various kinds of stem cells,and genetic material from various life forms.
At the Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare,the National Institute of Health Sciences(responsible for cells)and the National Institute of Infectious Diseases(genes)joined to establish a Master Bank(in FY2001,these two institutions began setting up the Pharmaceuticals Basic Technology Research Facility toward an eventual merger)for the collection and preservation of human and animal-derived cultured cells and genes needed for use in research in medical and pharmaceutical fields.The supply of cultured cells and genes is made through the Japan Health Sciences Foundation to researchers and other personnel.The foundation has also commenced distribution of human tissue with careful consideration for the bio-ethics issue.It also collects,stores,and supplies medicinal plants,and breeds and supplies kanikui-zaru monkeys and other animals used for medical testing.
In the Agriculture,Forestry,and Fisheries Ministry,the Gene Bank Project collects,classifies,and identifies all plants,animals,microorganisms,trees,marine life,and other bioresources utilized in the agricultural,forestry,and fisheries industries.The project also conducts evaluations of characteristics,and propagates and preserves specimens.It provides bioresources and information about those resources to the national research institutes,the independent administrative institutions,the private sector,and universities,etc.In addition,the ministry maintains a DNA Bank for collection,storage,and supply of DNA obtained through genome research and other gene-level research results,and of DNA information.
In addition,the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry established the NITE Biological Resource Center at the National Institute of Technology and Evaluation,to serve as Japan's core bioresource organization for microorganisms,etc.The Center engages in search,isolation,collection,and identification of biological genetic resources,as well as storage.It also collects and sorts information related to bioresources(information regarding systematic identification in microbiology,base sequence information,and information about genes,etc.),and offers supplies of the actual bioresources.As one part of these activities,the Center is acting in accordance with the Convention on Biological Diversity to ensure access to biological genetic resources in Southeast Asia.
The Ministry of Environment instituted the"Environmental Sample Time Capsule Project"in FY2002 for the purpose of preserving the cells of wildlife threatened with extinction.In addition,the independent National Institute for Environmental Research is engaged in the collection,preservation,and supply of algae,and in building an algae database.
| (6)Promotion of Food Science and Technology |
Building a stable and sustainable production and distribution system for agricultural,forestry,and fisheries products,and promoting the development of functional foods that can contribute to improving the people's health,are essential if Japan is to be able to maintain food security and to guarantee an abundant food supply.
For this purpose,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries continues to promote the development of new horticultural crop breeding and production technologies to improve rates of food self-sufficiency ratio in wheat,soybeans,and feed crops,as well as the development of cloning and other animal husbandry-related technologies.Moreover,in response to the recent sharp rise in imports of raw vegetables,the ministry in FY2002 accelerated development of technologies for culturing and differentiating new types of vegetables rich in nutrition and functional constituents,and research into the elucidation of bio-regulatory functions through combinations of foodstuffs capable of contributing to the development of new functional foods.In addition,the ministry is supporting the development of technologies for the use of bio-markers(simple biological indices)in the scientific evaluation of food efficacy,and the development of production technologies for food that is efficacious at maintaining health.
In order to improve food safety and security,research into BSE(bovine spongiform encephalopathy),which is based on research achievements into sheep-prone diseases,at the National Institute of Animal Health at the National Agricultural Research Organization and several universities and colleges is being further strengthened through implementation of joint research with the United Kingdom.
The Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare has conducted basic research into the application of biotechnology for development of highly functional foods that can maintain and improve health,and has continued its surveys and research into the safety of food using gene recombination,etc.
| (7) Promotion of Cancer-Related Research |
Cancer accounts for about30%of total deaths in Japan.Under the"Second Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy against Cancer"(ratified at the Cabinet Conference for Cancer-Related Measures in June1993),researchers in Japan are promoting elucidation of the essential elements of cancer,and of new prevention,diagnostic,and treatment methods that utilize these research results.
At the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the National Institute of Radiological Sciences is acting under this10-year strategy to perform clinical trials of a heavy ion medical accelerator that is expected to become a revolutionary new treatment method for particularly difficult-to-treat cancers.In addition,as part of the"Millennium Project,"Grants-in-Aid for Academic Research promote priority research at universities and colleges.The Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare,meanwhile,is engaged in development of a helical CT that will be useful in the early detection of lung cancer,and in development of safe cancer treatment methods using endoscopes that reduce the burden on the patient.In August2001,the two above-mentioned ministries established the"Expert's Committee on the State of Future Cancer Research,"which then proceeded to conduct a general survey on cancer research to date.In March2003,the committee issued a report entitled"On the Future of Cancer Research."It now plans,based on the report,to engage in studies into the direction of medium and long-term cancer research policies following the conclusion of the"Second Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy against Cancer."
| (8) Promotion of Research on Immunologic and Allergic Diseases |
In the area of promotion of research into the immune system,allergy-related,and infectious diseases,there is a need to promote comprehensive research that goes beyond existing approaches by boosting cooperation with immunologists to create radical new treatment methods for hay fever,said to afflict30%of the population in Japan,atopic dermatitis,rheumatoid arthritis,and other immunologic and allergic diseases,and to eradicate infectious diseases.
In this situation,at the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the Re-search Center for Allergy and Immunology in FY2001 at RIKEN is engaged in research into basic and comprehensive elucidation of immune systems toward the development of effective counters to immunologic diseases.In addition,Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research is being used for prioritized promotion of basic research in this sector at universities and colleges.
In addition,the Ministry of Health,Labour,and Welfare established a clinical research center at the National Sagamihara Hospital aiming at elucidation of rheumatism,bronchial asthma,hay fever,atopic dermatitis,and other immunologic and allergic diseases,and the development of treatment methods.The center's research is currently concentrated on the clinical side.
| (9) Promotion of Other Research and Development |
Because living things are generally efficient at energy conversion,consuming little energy for reactions at normal temperatures and pressures,the Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry has launched the"Program for Creation of Recycling-Type Industrial Systems Using Bio-Functions"to develop the basic technologies required for effective utilization of bio-functions based on genome information,and for their expanded use in industrial systems.
In the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,the supplementary bud-gets have been utilized to promote stronger research foundations for the development of facilities and equipment at universities and colleges regarding research into sugar chains,which are believed to play important roles in a vast array of biological functions.The Ministry of Economy,Trade,and Industry is promoting research and development into automatic devices for synthesizing sugar chains and into analysis of functions for general acquisition of genes related to sugar chain synthesis.
Utilizing and strengthening the excellent re-search capabilities of certain regions can be effective for promoting research and development in the life sciences sector.In this regard,the government's Urban Renewal Office decided in August2001,in"Urban Renewal Project No.2,"on the"formation of an international center for life sciences in the Osaka region."This action was followed in July2002,in"Urban Renewal Project No.4,"with the"formation of an international center for genome sciences in the Tokyo region."In line with these decisions,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology has expanded related facilities and equipment at universities and colleges,and promoted translational research that bridges the gaps between basic research and applied research through cooperation between industry,academia,and government to form life science research sites and to build systems that link the research sites with each other.In addition,the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare is promoting the development of core research institutions in the Osaka region for infrastructure technology towards the development of revolutionary new pharmaceutical products,etc.
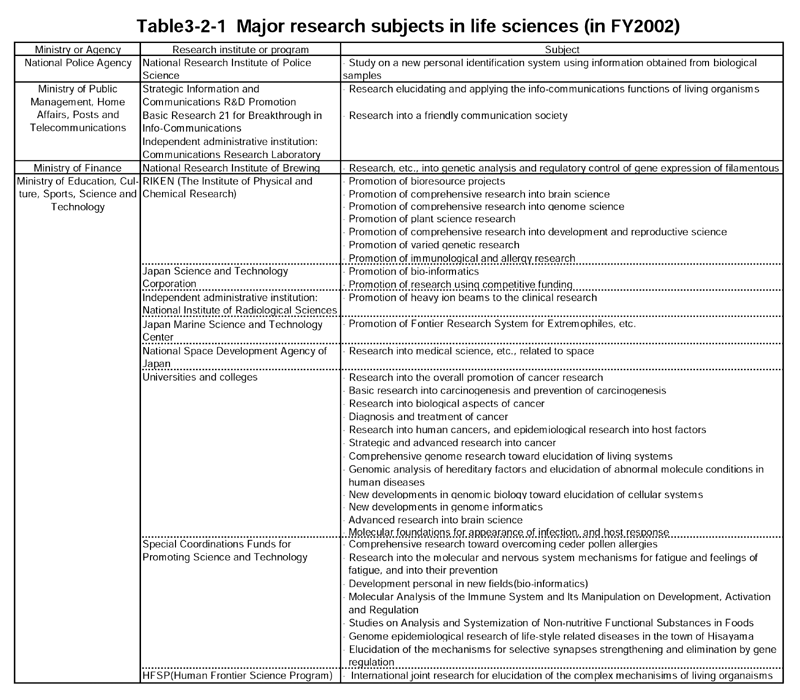
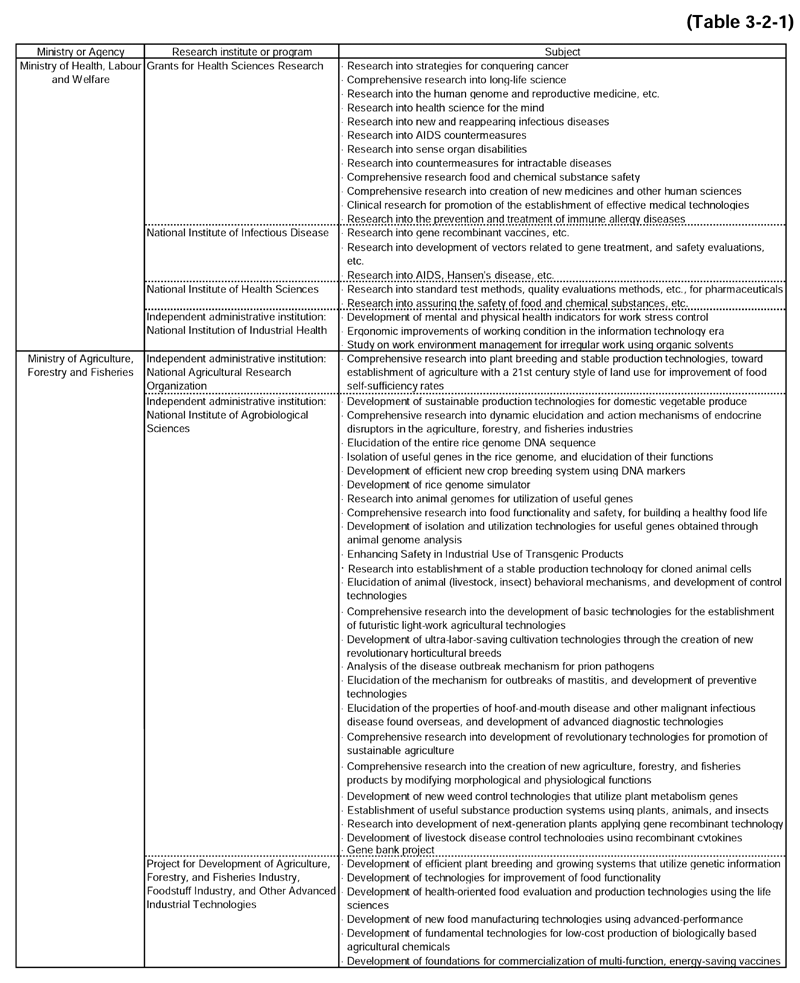
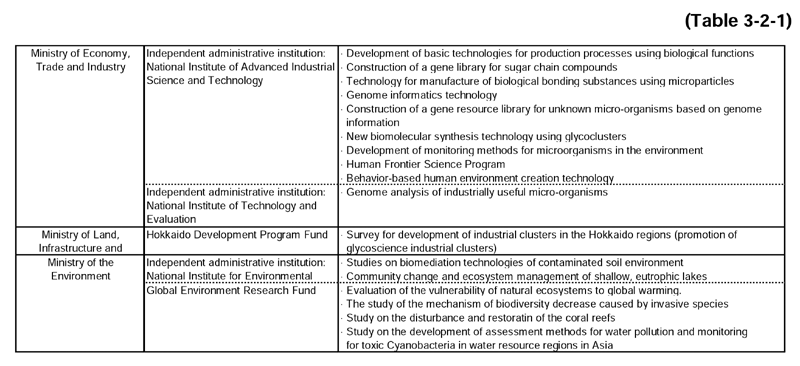
The major life science research projects implemented in FY2002 are shown in Table3-2-1 ,by ministry or agency.
| 3.2.2.1.2 Efforts for Bioethics and Bio-safety |
| 3.2.2.1.2.1 Efforts for Bioethical Issues |
Rapid developments in the life sciences in recent years have given rise to expectations of revolutionary achievements in the fields of medicine and elsewhere.On the other hand,because the possibility of new bioethical issues that might violate human rights and dignity has arisen,the Expert Panel on Bioethics,established under the Council for Science and Technology Policy(CSTP),is now engaged in surveys and examinations of basic policies and specific important issues concerning bioethics,while the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,alongside other government entities,is preparing the relevant laws,regulations,and guidelines,and studying their appropriateness.
Regarding human cloning technology,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology has taken measures prohibiting the production of human clone individuals and regulating the handling of cloned embryos,based on the Law Concerning Regulation Relating to Human Cloning Techniques and Other Similar Techniques(Year2000,Law No.146)and the accompanying"Guidelines for Handling of a Specified Embryo 5) (FY2001 Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,Notification No.173)"that were drawn up based on that law.
The Expert Panel on Bioethics under the CSTP is continuing studies and investigations on"how to handle the human fertilized embryo as the beginning of a human life,"based on Paragraph2of the Law Regulating Cloning Technology.
At the United Nations,studies are proceeding into adoption of an international treaty prohibiting the generation of human clone individuals,and Japan has from the start been an active participant in these discussions.A working group for drawing up such a treaty was established in September2002.While Japan supported a proposalmade by France and Germany limiting the treaty to prohibition of the generation of human clone individuals,which appeared to be a consensus opinion among the world's nations,there were states holding the opinion that human clone embryo research should also be prohibited,and it was decided to continue studies into the issue.
Note5)A Specified Embryo:Refers to nine types of embryos,including a human split embryo,a human embryonic clone embryo,a human somatic clone embryo,a human-human chimeric embryo,a human-animal amphimictic,a human-animal hybrid embryo,a human-animal chimeric embryo,an animal-human hybrid embryo,or an animal-human chimeric embryo.
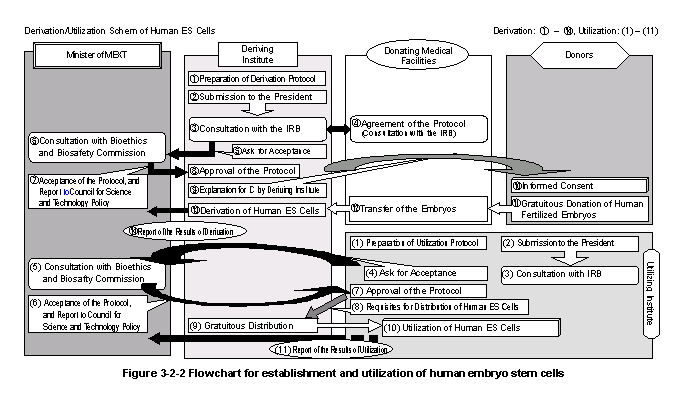
In the area of human embryonic stem(ES)cell 6) research,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology has proceeded under the"Guidelines for Derivation and Utilization of Human Embryonic Stem Cells(FY2001 Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,Notification No.155)"to review the compliance of specific derivation and utilization plans with the guidelines (Fig.3-2-2) .In April2002,the minister confirmed the Japan's first cases of compliance with the guidelines for a derivation and utilization plans.
Epidemiological research 7) ,meanwhile,involves the collection and utilization of information on vast numbers of individuals,and retention of that information for relatively long periods of time.Because of the need to protect the rights of people targeted in such research,and for suitable control over the information,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology and the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare jointly adopted the"Ethical Guidelines for Epidemiological Research(FY2002 Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,and Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare,Notification No.2)."
| 3.2.2.1.2.2Efforts to Ensure Safety in the Life Sciences |
Recombinant DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid)technology contributes to human welfare in a broad range of ways,from basic biological research to the elucidation of the causes of disease and the mass production of pharmaceuticals.One of its characteristics,however,is its application of new properties to living organisms.For this reason,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology is moving to ensure the safety of recombinant DNA experiments under its"Guidelines for Recombinant DNA Experiments(FY2002 Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,Notification No.5)."The guidelines now also include a framework for"recombinant DNA experiments for educational purposes"with the intent of teaching introductory level recombinant DNA experimentation in high schools,and mark the start of efforts to develop the"super-science high school"concept.
Regarding commercial applications,the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries,and the Ministry of Economy,Trade and Industry have each drawn up safety guidelines for commercial utilization of organisms obtained through gene recombinant technology.In addition,because it is important to obtain public acceptance before commercialization of gene recombination technology can occur,the Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries has published pamphlets and hosted study groups,and also was host to the"Conference on the People's Thoughts Regarding Recombinant Gene Agricultural Crops"so as to better respond to the people's demands and proposals regarding the safety of recombinant genes.The ministry is now conducting surveys and research based on the people's proposals.
Regarding the Cartagena Protocol on Bio-safety 8) ,an international framework designed to prevent adverse effects on biological diversity due to the utilization of genetically modified organisms,the relevant ministries are currently involved in studying what laws will need to be implemented in Japan to ensure early ratification of the protocol.
Note6)Human embryonic stem(ES)cells:These primordial cells have attracted high expectations for medical applications because of their capa-bility of differentiating into all parts of the human body.At the same time,however,sacrificing human emblyos would raise ethical concerns.
Note7) Epidemiological Research:Scientific research that clarifies causes of a disease by investigating the frequency and geographical distribution of disease incidence and other factors related to human health.
Note8)The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety:Adopted in January2000under the Convention on Biological Diversity.The protocol is intended to ensure adequate protections regarding the movement across national borders of genetically modified organisms that could have adverse effects on biological diversity,and sets standards for their safe use.The protocol was scheduled to go into effect on the90th day after being ratified by50nations.(A total of44nations and the EU had ratified the protocol as of March4,2003.)
For clinical research aiming at the establishment of gene therapy 9) ,the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,and the Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare review the compatibility of research implementation plans,and ensure that scientific propriety and ethics are maintained,based on their joint"Guidelines for Clinical Research for Gene Therapy(FY2002 Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology,and Ministry of Health,Labour and Welfare,Notification No.1)."
Note9)Gene therapy:A treatment method that involves insertion of genes,or cells containing genes,into the bodies of patients for the purpose of treatment of disease.It is not an established method of treatment at present,but is practiced as one aspect of clinical research.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |