| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > Annual Report on the Promotion of Science and Technology 1999 > Part1 Chapter1 Section1 1 | ||
![]() The Japanese economy now faces extremely severe situation,
in response to which the government is taking general economic measures and other
measures to stimulate demand immediately.
The Japanese economy now faces extremely severe situation,
in response to which the government is taking general economic measures and other
measures to stimulate demand immediately.
![]() The supply-side potential GDP growth rate, which determines
the economy's medium to long-term growth trend, is exhibiting a downward tendency.
Although raising productivity is an important prerequisite for raising the potential
GDP growth rate, Japan's rate of productivity growth has been slowing down in
recent years. Such were the circumstances that prompted the drafting of the Strategy
for Revitalizing Industry and the convening of the Conference for Industrial
Competitiveness.
The supply-side potential GDP growth rate, which determines
the economy's medium to long-term growth trend, is exhibiting a downward tendency.
Although raising productivity is an important prerequisite for raising the potential
GDP growth rate, Japan's rate of productivity growth has been slowing down in
recent years. Such were the circumstances that prompted the drafting of the Strategy
for Revitalizing Industry and the convening of the Conference for Industrial
Competitiveness.
![]() Forty percent of Japan's private enterprises express concerns
over declining competitiveness in their business outlook.
Forty percent of Japan's private enterprises express concerns
over declining competitiveness in their business outlook.
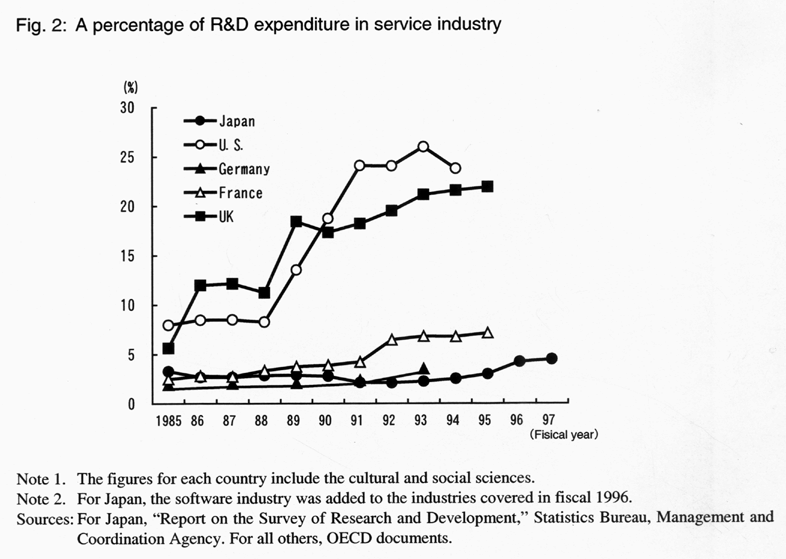
![]() In each principal nation, the service industry accounts for
an increasing percentage of overall industry. In Japan, however, R&D expenditures
for the service industry have been limited to only a small percentage of total
R&D expenditures, giving rise to concerns about the competitiveness of the
service industry ( Fig.
2 ).
In each principal nation, the service industry accounts for
an increasing percentage of overall industry. In Japan, however, R&D expenditures
for the service industry have been limited to only a small percentage of total
R&D expenditures, giving rise to concerns about the competitiveness of the
service industry ( Fig.
2 ).
![]() Japan's postwar economic recovery was due in large part that
the manufacturing industry produced internationally competitive low cost and
high-quality products by using scientific and technological power. Today, Japan
must again make maximum use of the power of science and technology to create
new, internationally competitive products and services and to found new industries.
Japan's postwar economic recovery was due in large part that
the manufacturing industry produced internationally competitive low cost and
high-quality products by using scientific and technological power. Today, Japan
must again make maximum use of the power of science and technology to create
new, internationally competitive products and services and to found new industries.
![]() The outcome of research executed at the National and quasi
National Institutes, is useful for the private sector as seeds of new products,
services, and industries. The further promotion of the transfer of it is important.
It is also important to improve the research environment in ways that promote
the creation of new products, services, and industries.
The outcome of research executed at the National and quasi
National Institutes, is useful for the private sector as seeds of new products,
services, and industries. The further promotion of the transfer of it is important.
It is also important to improve the research environment in ways that promote
the creation of new products, services, and industries.
![]() It is hoped that regional industries will also develop new
products and services using their peculiar resources of production. It is more
important to promote regional science and technology through such measures as
expanding R&D activity at laboratories, universities and other institutions
founded by the local government, and promoting the use of findings the obtained
through their R&D.
It is hoped that regional industries will also develop new
products and services using their peculiar resources of production. It is more
important to promote regional science and technology through such measures as
expanding R&D activity at laboratories, universities and other institutions
founded by the local government, and promoting the use of findings the obtained
through their R&D.
![]() It is being afraid Japan's service industry may become less
competitive, and so must become more sophisticated through application software
development and the creation of new financial products using simulation analysis
based on mathematical theory, for instance.
It is being afraid Japan's service industry may become less
competitive, and so must become more sophisticated through application software
development and the creation of new financial products using simulation analysis
based on mathematical theory, for instance.
![]() In view of the trend toward the international standardization
spurred by economic globalization, Japan must actively and strategically participate
in the determination of the international standards that affect the international
competitiveness and profitability of Japanese industry.
In view of the trend toward the international standardization
spurred by economic globalization, Japan must actively and strategically participate
in the determination of the international standards that affect the international
competitiveness and profitability of Japanese industry.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |