| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > JAPANESE GOVERNMENT POLICES IN EDUCATION, SCIENCE, SPORTS AND CULTURE 1997 > Scientific Research Chapter 2 Section 3 1 | ||
Scientific research, which is dedicated to the pursuit of truth, should transcend national boundaries. Researchers focusing on the same goals must be able to improve the quality of their research through information exchanges, joint research, and reciprocal criticism of their results, whether in Japan or elsewhere. This type of international exchange is vital to the advancement of scientific research.
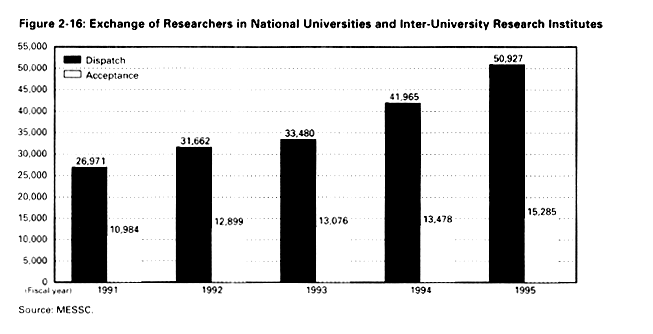
The past few years have brought a notable increase in international scientific exchange in Japanese universities and inter-university research institutes. According to surveys conducted by MESSC, the number of Japanese researchers sent overseas doubled in the four years up to FY1995, and the number of foreign researchers accepted in Japan increased approximately 1.5 times ( Figure 2-16 ). The following factors appear to be propelling this growth, which is expected to accelerate in the years ahead.
In some fields, the increasing sophistication of research is reflected in the growing size and complexity of research facilities. In the field of particle physics, for example. experiments designed to discover more elemental particles require accelerators that are more powerful and hence bigger. The increasing size and sophistication of research equipment used in various fields means that it is becoming more and more difficult, both technically and economically, for individual countries to build and operate such facilities entirely by themselves. International cooperation is therefore vital in advanced fields that require massive investments of human and material resources.
More and more fields require a global approach based on international cooperation, including fields like climatology, geology, and oceanography that have implications for global environmental problems and natural disasters. Japan must participate actively in these areas.
Exposure to different ideas and research methods helps to broaden the scope of one's own research and enrich one's ideas. Interaction with researchers from other countries is especially valuable, since it helps to raise the overall standard of research in Japan, while information provided by Japanese researchers contributes to the advancement of science globally.
In order to make an international contribution commensurate with its status in the world, Japan needs to participate actively in global joint research projects, to provide leadership in specialized fields in which Japanese researchers excel, and to accept more young researchers from Asia.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |