| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > JAPANESE GOVERMENT POLICICIES IN EDUCATION, SCIENCE AND CULTURE 1994 > PART II Chapter 3 Section 10 2 | ||
To meet the needs of contemporary schoolchildren and respond appropriately to the trend toward internationalization and the shift to an information-oriented society, in initial teacher training it is necessary to enhance teachers' expertise and practical teaching abilities and to deploy people with extensive scholastic knowledge in schools. Ongoing improvements are therefore being made to the initial teacher training and certification system, including amendment of the Educational Personnel Certification Law.
Since fiscal 1990 universities have been offering a number of new compulsory subjects designed to improve teachers' practical instruction skills. These include subjects on educational methods and technology, such as the use of information equipment and teaching materials, as well as subjects on student guidance and educational counseling. The first teachers trained under this new curriculum were employed in actual teaching positions in fiscal 1994. Universities need to apply their creativity and ingenuity to the further enhancement of the content and instruction methods of the new subjects in order to realize the aims set forth in the new Courses of Study and the broadened and simplified Standards for the Establishment of Universities.
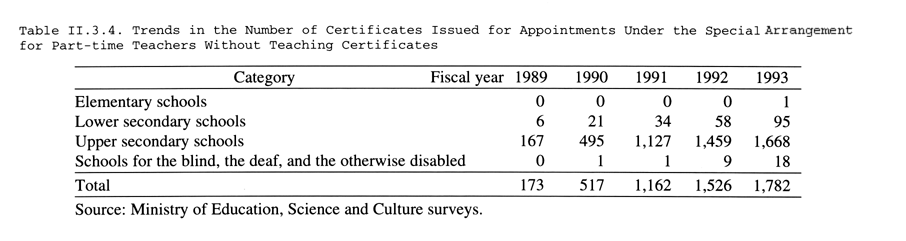
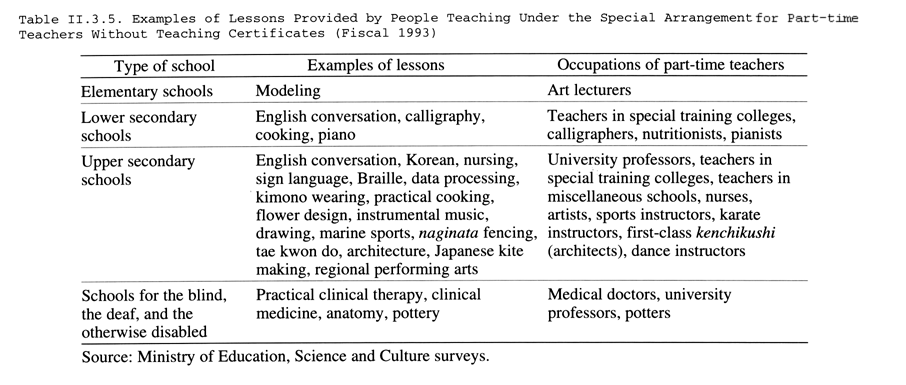
Other measures include the establishment of the Special Certificate System and the Special Arrangement for Part-time Teachers Without Teaching Certificates, which allow people outside of school with special knowledge and skills to be brought into the educational arena. People appointed under the Special Arrangement for Part-time Teachers Without Teaching Certificates are employed mainly in upper secondary schools and primarily in such areas as nursing, foreign language conversation, and physical education. In fiscal 1993 a total of 1,782 people taught under this system ( Tables II.3.4 , II.3.5 ). Teaching by people outside of school on the basis of their own experience allows educational content to be diversified and helps to foster individuality in education. There are also advantages in terms of career guidance, since students gain a better understanding of occupations and society. This approach is therefore expected to be used increasingly in the future. In fiscal 1994 the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture began providing subsidies to prefectures to cover part of the cost of deploying teachers to lower secondary schools under the Special Arrangement for Part-time Teachers Without Teaching Certificates.
A key priority from the viewpoint of improving teacher quality and ability is to ensure at the time of appointment that those recruited as teachers have the necessary qualities and abilities. The number of people taking teacher appointment examinations has tended to decline in recent years. Boards of education at the prefectural and designated-city levels are working to recruit suitable people as teachers through various improvements and innovations, including
In March 1994 the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture began conducting Research and Surveys on Teacher Appointment. The purpose is to improve teacher appointment methods and investigate measures to attract high-caliber examination candidates.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |