| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > EDUCATIONAL STANDARDS IN JAPAN 1975 > CHAPTER1 3 (2) b | ||
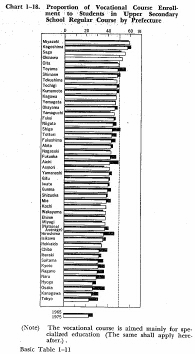
The proportion of upper secondary school students, as classified by courses, and its transition on a prefectural level are shown in Chart 1-18.
It indicates that the proportion of enrollment in regular courses in 1975 averaged 63.0% throughout the nation as against 37.0% for that of students enrolled in specialized courses, but that there are some prefectural gaps in the distribution of these proportions. The proportion of enrollment in the specialized courses is highest in Miyazaki Prefecture at 59.2% and the lowest in Tokyo at 22.9%. As shown in this chart, only in the four prefectures of Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Saga and Okinawa, the proportion of enrollment in the specilized courses exceeds 50%.
During 1965-75, the proportion of enrollment in specialized courses sagged in as many as 32 prefectures including Tokyo, Osaka, Aichi, Fukuoka, etc. On the other hand, this proportion climbed in 14 prefectures, including Hokkaido, Kochi, Wakayama, etc. during the same ten-year period.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |