| Home > Policy > White Paper, Notice, Announcement > White Paper > EDUCATIONAL STANDARDS IN JAPAN 1965 > CHAPTER |
||
As mentioned in the foregoing sections, advanced countries in the world make substantial investment in education. The method for financing public education varies among countries. In the German Federal Republic, Great Britain and Japan, public education is financed through tax revenues, as well as tuition fees and other income incidental to educational services. In some states of the United States, there are special property taxes which are earmarked to be used for educational purposes. In the U.S.S.R. no tuition fees are imposed, and tax revenues are the only source for educational costs.
The pattern of the whole system of government and finance in a country affects the pattern of the relative shares of the central government in supporting public education. In countries with a centralized system of government, a larger part of expenditures for public education are financed by the central government, while in decentralized countries a high proportion of costs are derived from local sources.
The following table gives the percentage distribution of public education expenditures by source in Japan, the German Federal Republic and the United States.
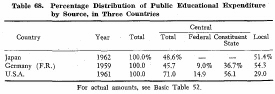
In Japan and the German Federal Republic the greater part of public education expenditures are derived from local sources. In the United States, to the contrary, the central (Federal and State) governments provide more than 70% of all governmental support of education.
As is shown in the following table, the proportion of the share by the central government has been increasing in all of the three countries -Japan, Great Britain and the United States. Such trends have been caused by increasing national demands on education, and more concern to plan and improve educational services on a nation-wide basis, rather than on local bases.
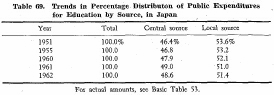
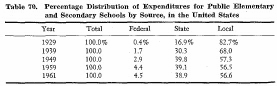
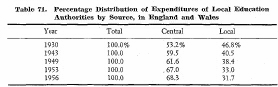
The increasing share of the central (including state) governments is evident in both the United States and Great Britain which have maintained a long tradition of decentralization in government.
This trend reflects growing national concern and responsibility for education.
| Back to Top | MEXT HOME |